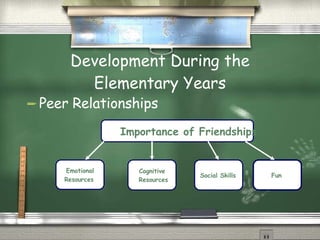
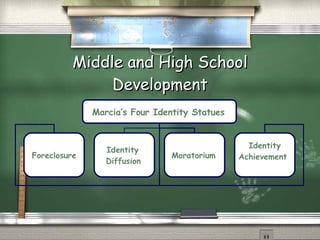
This document summarizes physical, cognitive, and socioemotional development from preschool through adolescence. It describes major developmental milestones in these areas at different ages. It also discusses types of early childhood programs and how development changes as children transition to elementary, middle, and high school. Peer relationships and identity formation become increasingly important during adolescence.