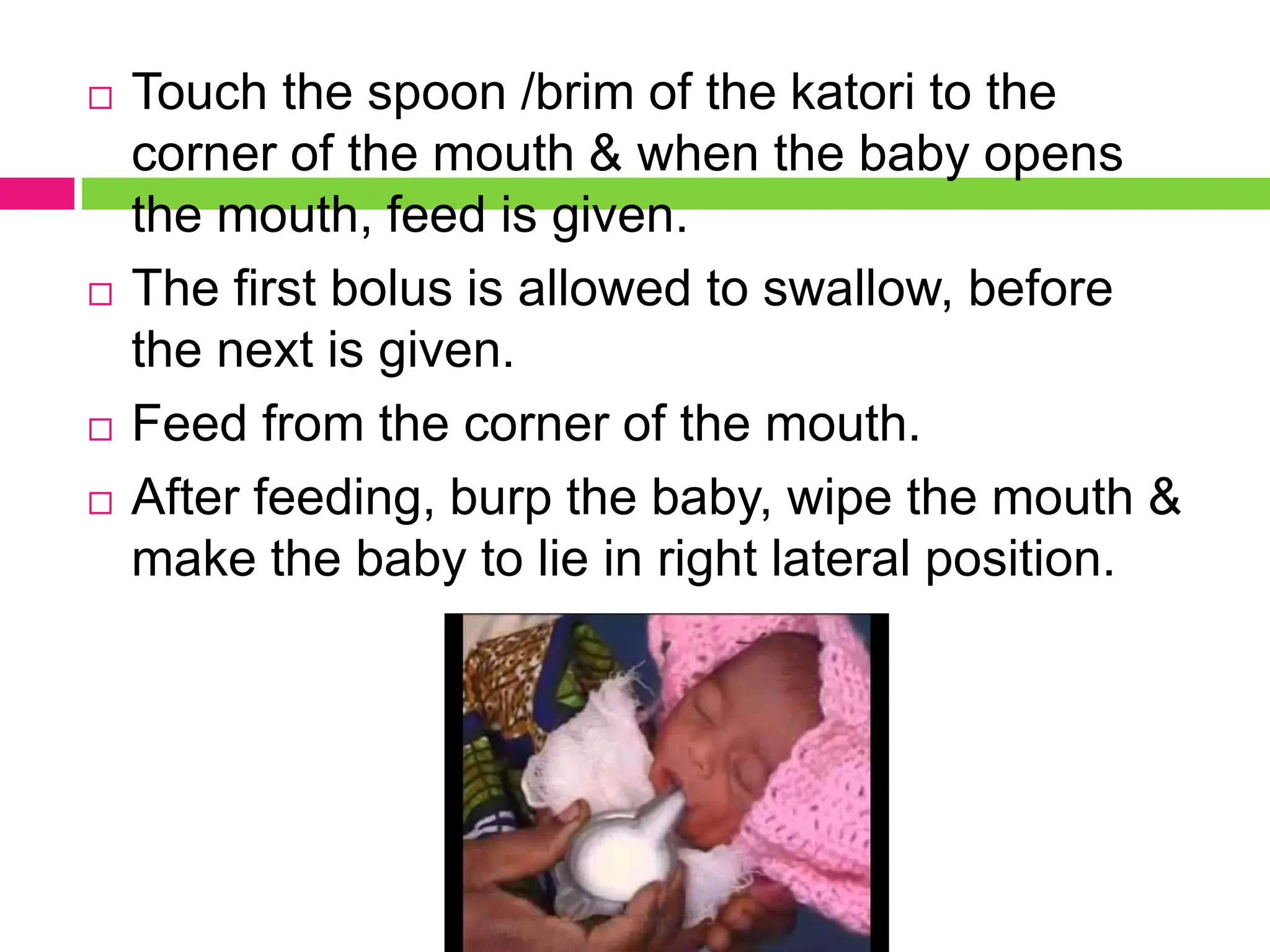
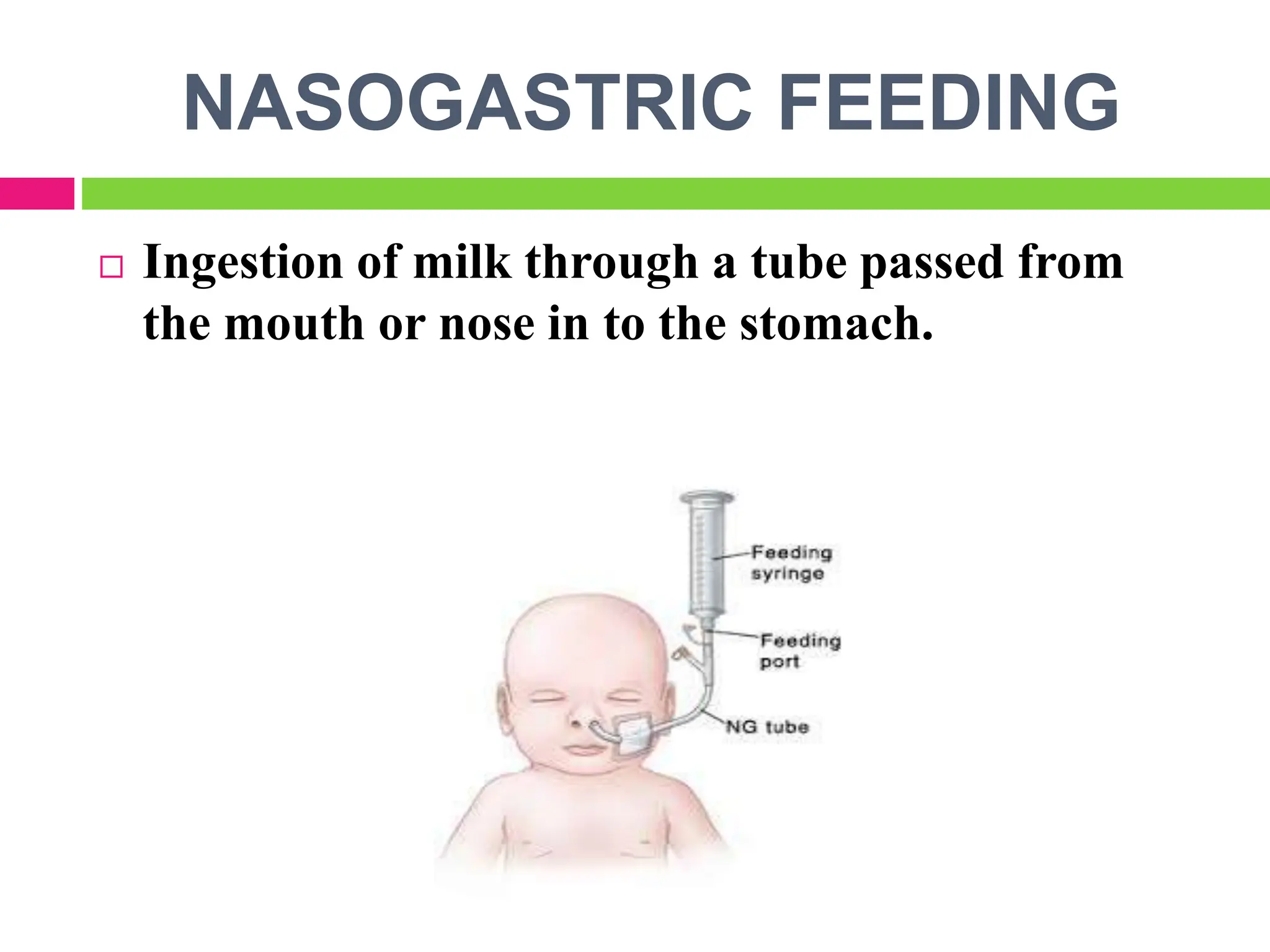
The document outlines artificial or supplementary feeding, which involves using breast-milk substitutes like liquid milk for infants, particularly in cases of maternal absence or inability to breastfeed. It details various methods such as bottle feeding, katori/spoon feeding, cup feeding, and nasogastric feeding, along with preparation techniques for infant formulas and the recommended feeding amounts based on the baby's age and weight. Additionally, it discusses potential problems associated with artificial feeding, including risks of infection and underfeeding or overfeeding.