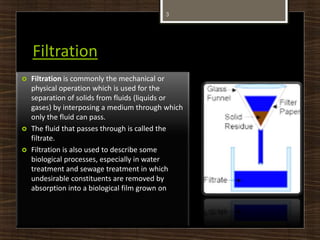
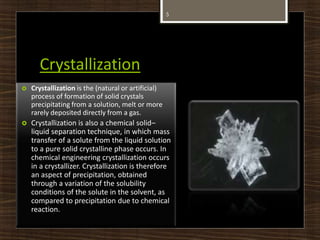
This document defines and describes several chemical separation processes: filtration, sublimation, crystallization, and distillation. It provides brief definitions of each process. Filtration separates solids from liquids by passing the liquid through a filter medium. Sublimation is the direct transition from solid to gas phases without passing through the liquid phase. Crystallization involves the formation of solid crystals from a solution or melt. Distillation separates mixtures based on differences in boiling points, with the more volatile components distilling off first. Examples of each process are also given.