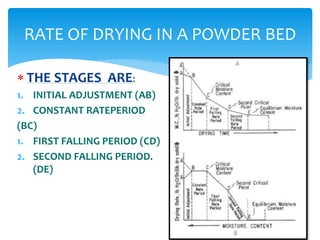
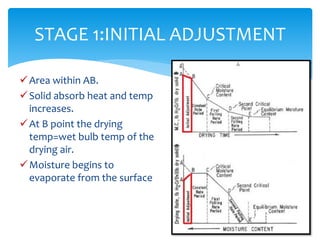
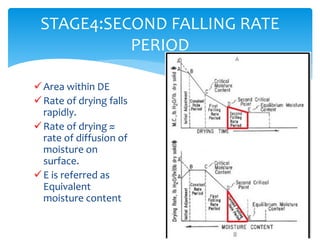
Drying is the removal of water or solvent from a solid or semi-solid through the application of heat and involves both heat and mass transfer processes. It is used in the pharmaceutical industry for preservation of drugs, improved product characteristics like flowability and compressibility, and to decrease corrosion and facilitate handling of bulk products. Drying occurs in stages - an initial adjustment period, a constant rate period where moisture diffuses to the surface and evaporates at the same rate, and falling rate periods where the rate decreases as dry areas form. Different dryer types are used including tray, drum, fluidized bed, and spray dryers depending on the material properties and desired end product.
![PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING [PT-507]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ananyachoudhuryroll66-181006183816/85/PHARMACEUTICAL-DRYING-1-320.jpg)






![ THESE RELATIONSHIP CAN BE DESCRIBED BY TWO GRAPH
1.MOISTURE CONTENT V/S DRYING TIME(Graph A)
2.DRYING RATE V/S MOISTURE CONTENT(Graph B)
BASIC FORMULAS:
%MOISTURE CONTENT=[Mass of water in sample/mass of
the dry sample]×100
DRYING RATE=Weight of water in sample/(time ×weight
of dry solid)
RATE RELATIONSHIP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ananyachoudhuryroll66-181006183816/85/PHARMACEUTICAL-DRYING-8-320.jpg)