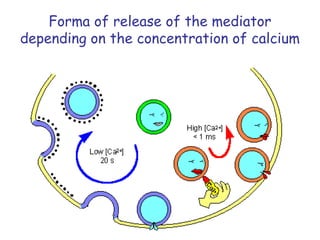
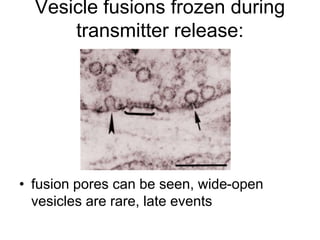
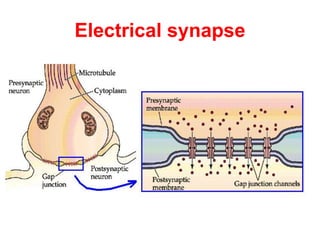
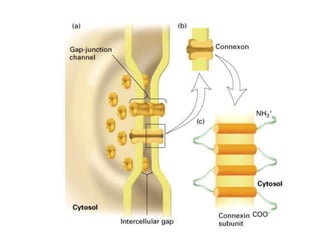
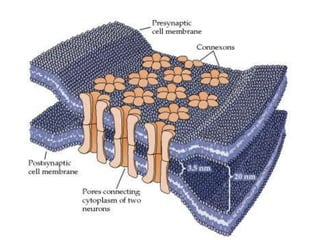
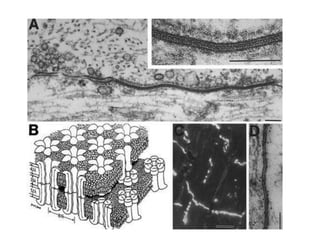
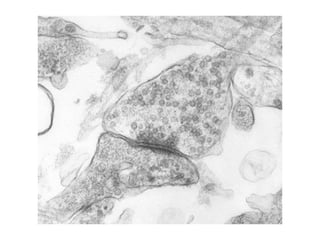
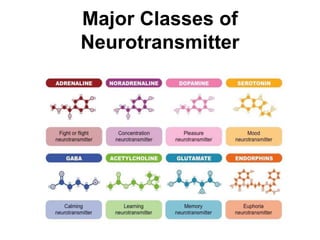
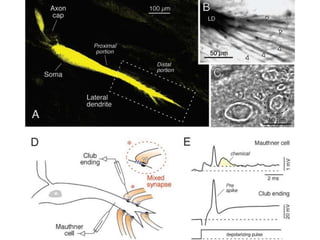
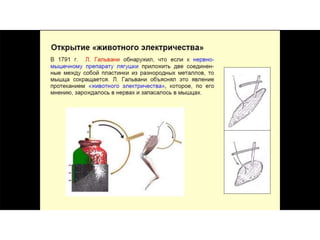
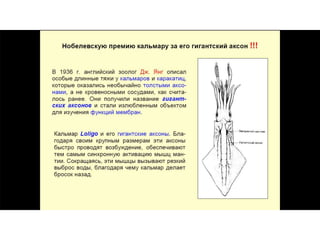
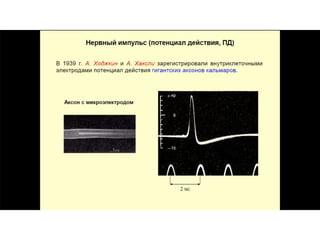
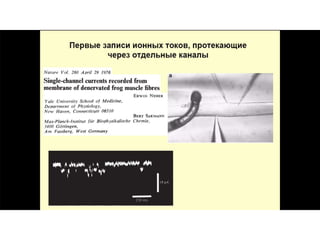
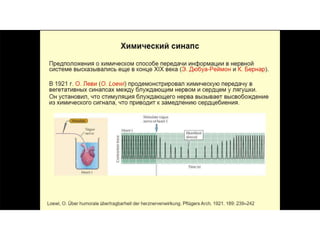
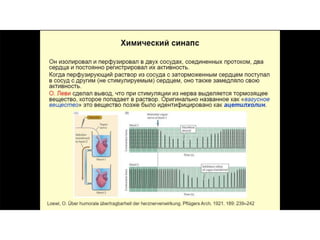
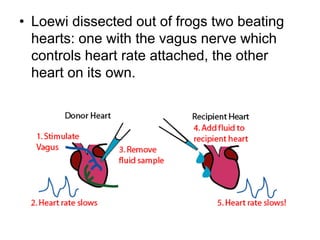
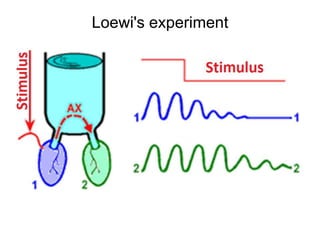
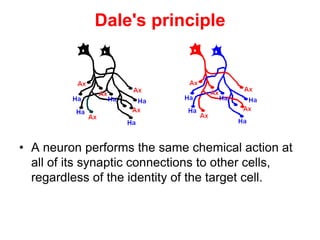
This document provides information about Otto Loewi's famous experiment that helped identify acetylcholine as the first neurotransmitter. It discusses how Loewi discovered that stimulating the vagus nerve of one frog heart caused it to slow down, and how the liquid bathing that heart then caused a second isolated heart to also slow down, proving the involvement of a soluble chemical transmitter. It notes Loewi called the chemical "Vagusstoff" and that it was later identified as acetylcholine. The document also briefly discusses Loewi's career and his shared Nobel Prize with Henry Hallett Dale for this seminal work establishing chemical transmission in the nervous system.










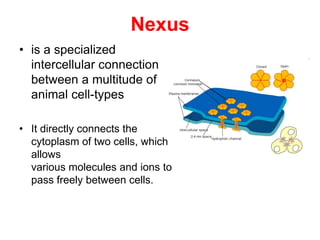
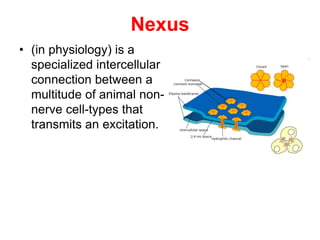








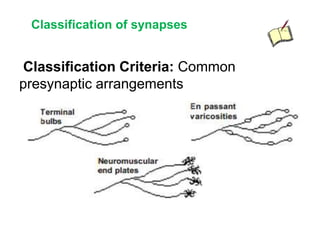
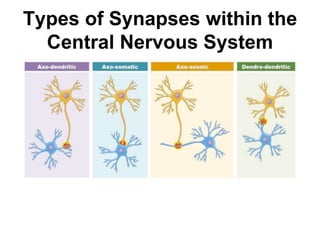
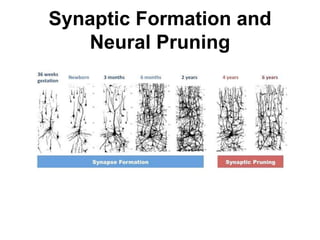
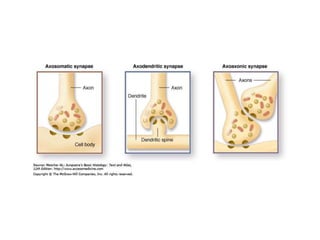
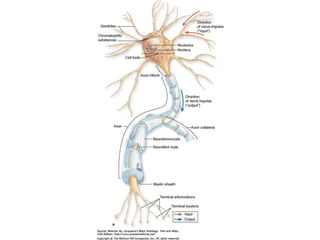
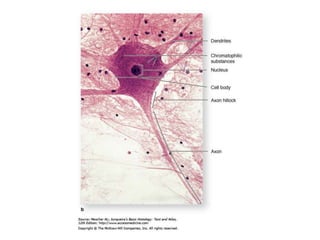



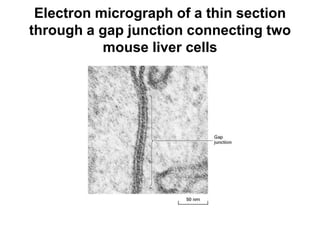
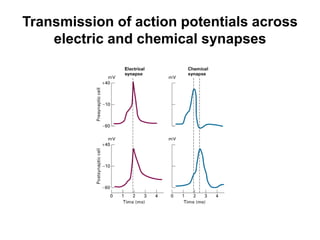
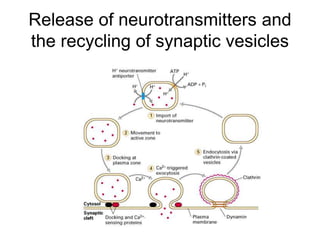


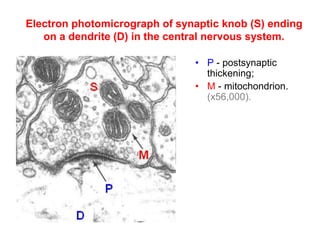
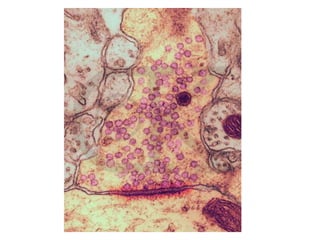
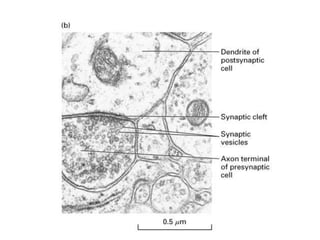
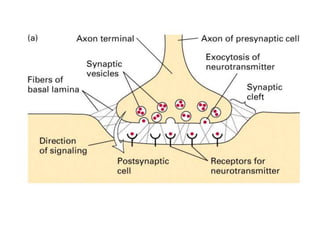
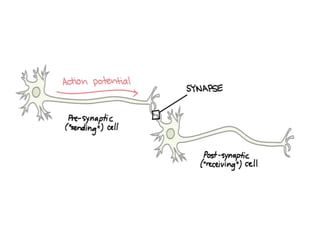
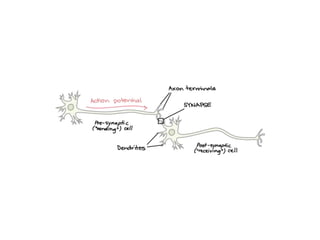
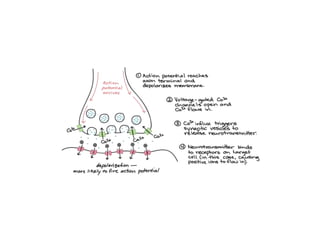
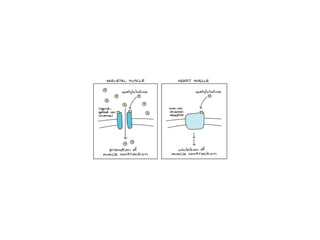


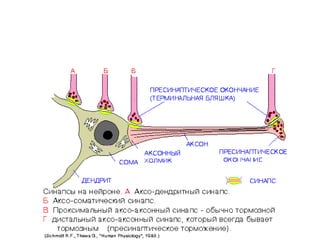
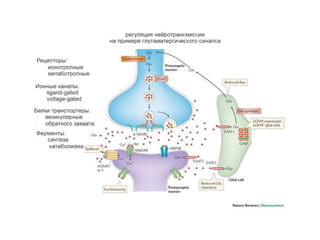
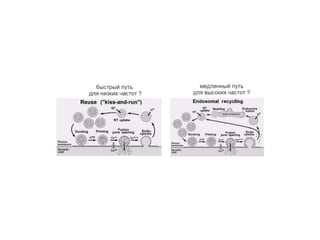
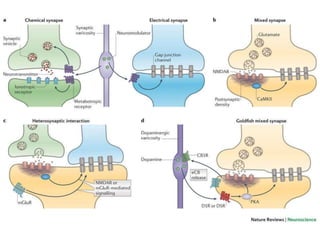
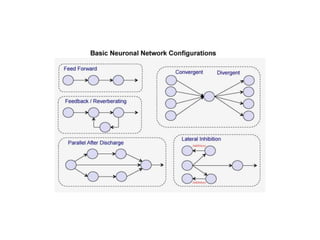
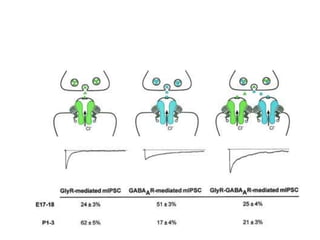
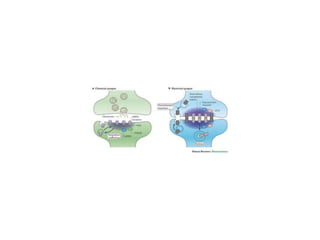
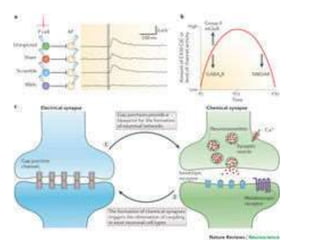
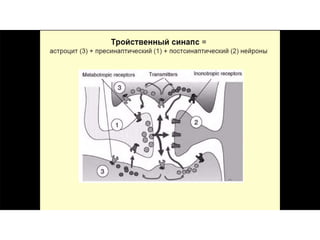
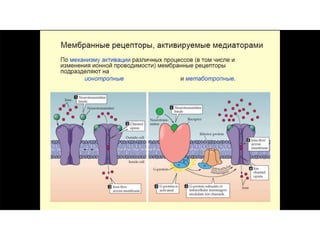
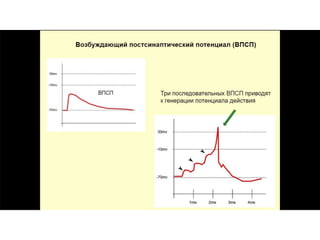






















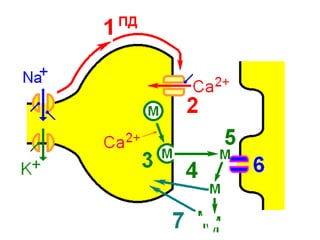
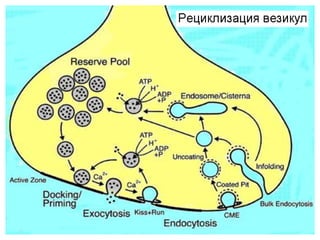
![Steps of the synaptic transmission
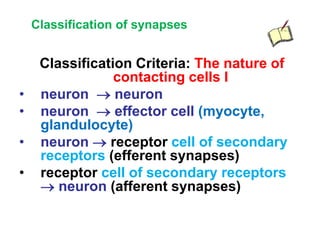
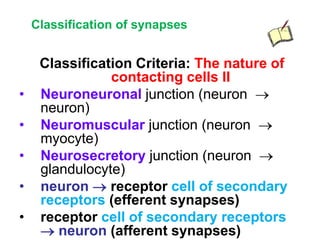
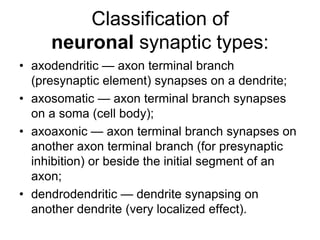
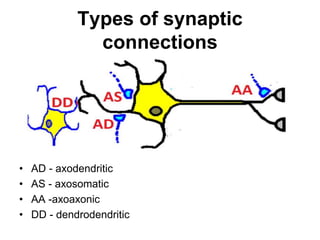
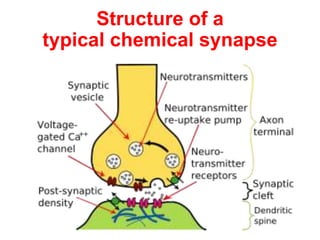
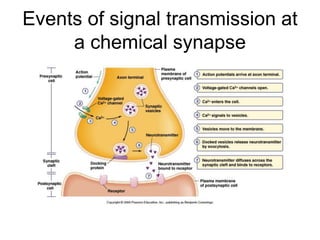
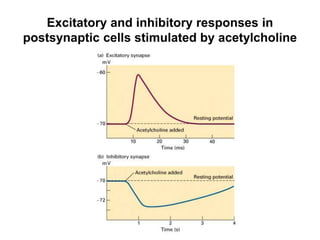
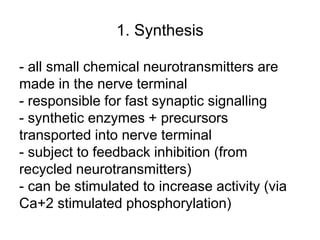
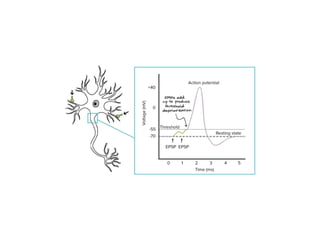
• AP on the pre-synaptic neuron
• opening of voltage-gated calcium channels
• increase in [Ca2+]
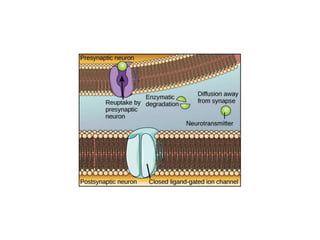
• migration and fusion of vesicles containing the
neurotransmitter
• neurotransmitter release
• diffusion of the neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft
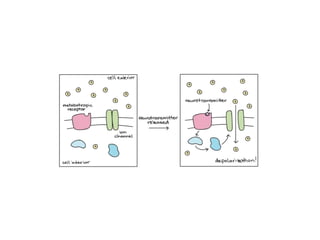
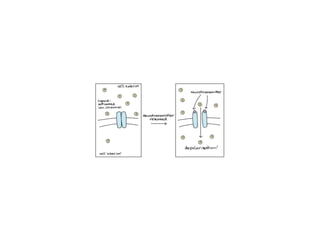
• binding of neurotransmitter to receptors on the post-
synaptic cell
• change in the permeability (membrane potential) of the
postsynaptic cell](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-191018115514/85/2-4-lecture-4-synapses-130-320.jpg)