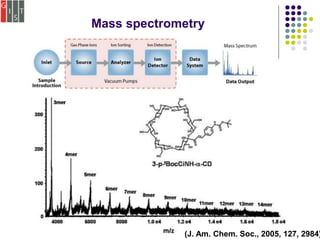
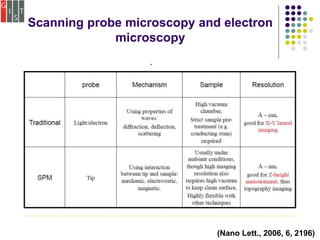
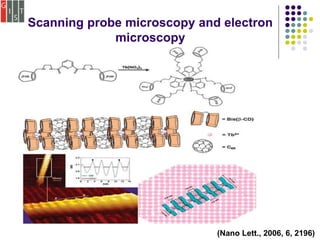
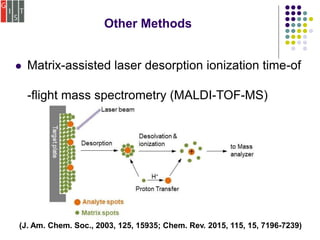
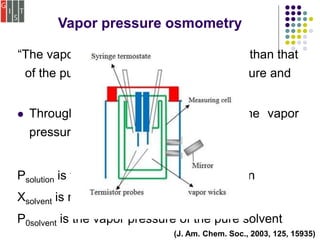
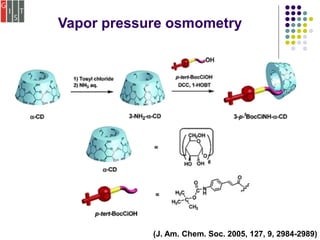
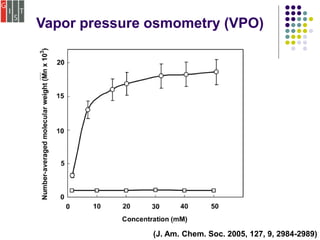
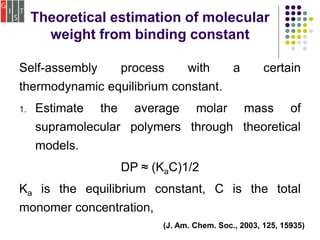
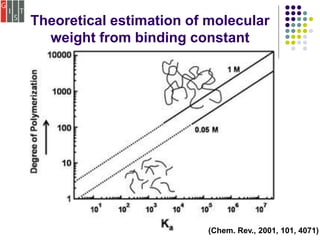
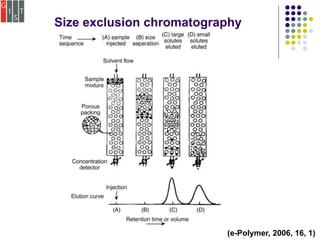
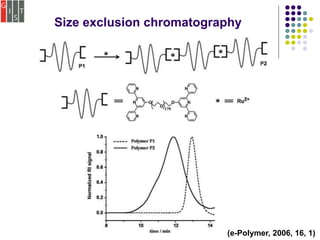
This document discusses several methods for characterizing supramolecular polymers, which are challenging to characterize due to their dynamic nature. Vapor pressure osmometry uses Raoult's law to relate vapor pressure to molecular weight. Theoretical estimation of molecular weight can be obtained from binding constants using equilibrium models. Size exclusion chromatography separates polymers by hydrodynamic radius. Viscometry uses the Mark-Houwink equation to relate intrinsic viscosity to molecular weight. Mass spectrometry, scanning probe microscopy, electron microscopy, and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry also provide characterization of supramolecular polymers.

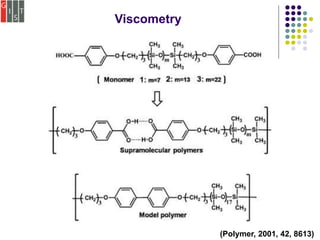
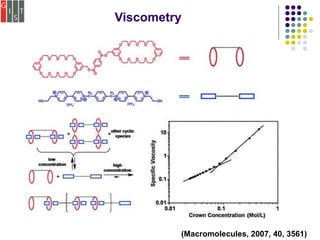
![Viscometry
To determine a polymer molecular weight distribution.
The relationship between the intrinsic viscosity and the
molecular weight can be expressed by the empirical
Mark–Houwink equation, [η] = KMa, (K and a are both emp
irical constants)
For a given polymer, values of K and a may be obtained
from suitable calibration experiments with a series of
sharp fractions..
(Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 5922-5932)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/characterizationmethods-200102144011/85/Characterization-of-Supramolecular-Polymers-11-320.jpg)