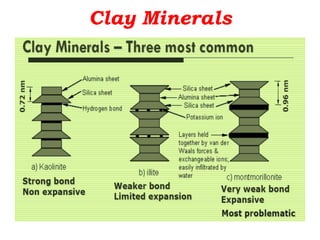
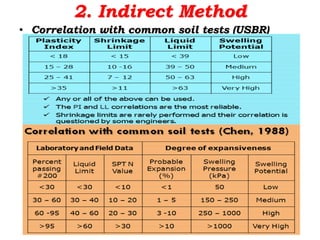
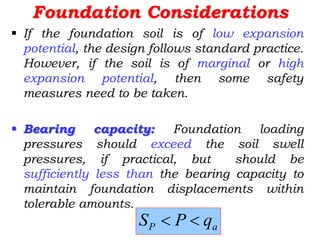
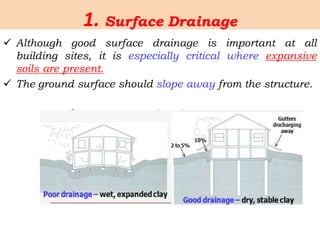
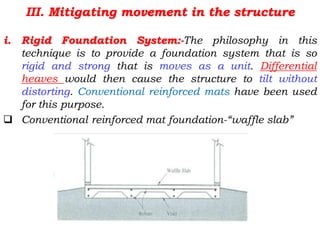
Expansive soils are soils that change volume due to changes in moisture content, swelling when wet and shrinking when dry. Typical expansive soils contain clay minerals like montmorillonite. Damage to structures occurs due to differential swelling and shrinkage of the soil, causing cracking and structural issues. Foundations and light structures are most susceptible. Common preventative measures include proper drainage, using non-expansive backfill, limiting landscaping, and flexible utilities near the home. Additional techniques involve altering the soil through replacement, lime treatment, or pre-wetting; bypassing the active clay zone; or using a rigid foundation system.