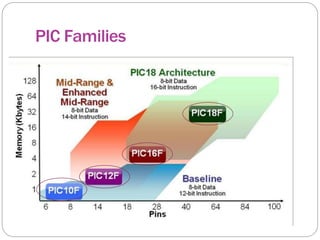
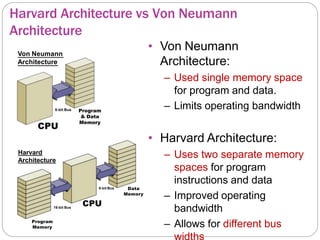
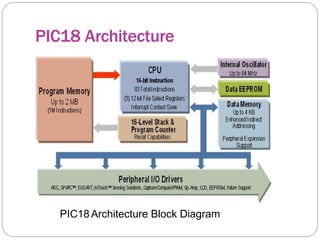
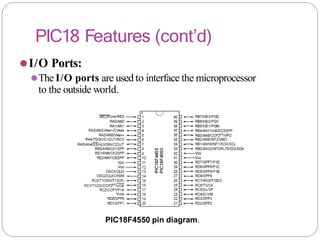
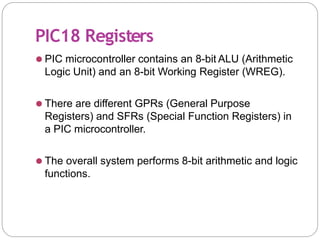
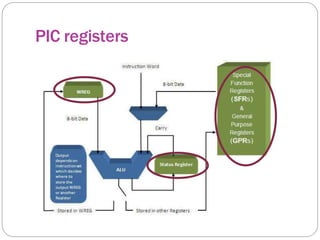
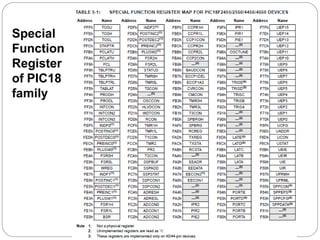
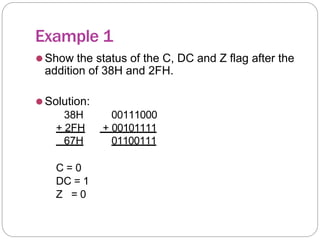
This document provides an overview of the PIC18 microcontroller architecture. It discusses the PIC18 family, which uses an 8-bit architecture with up to 16 MIPS of processing power. It describes the PIC18 architecture, which is based on Harvard architecture with separate memory spaces for instructions and data. The document outlines the PIC18 features such as the CPU core, program ROM, data memory, I/O ports, and internal devices. It also discusses the registers in PIC18 microcontrollers including the WREG, general purpose registers, special function registers, status register, and provides an example of setting flags in the status register.