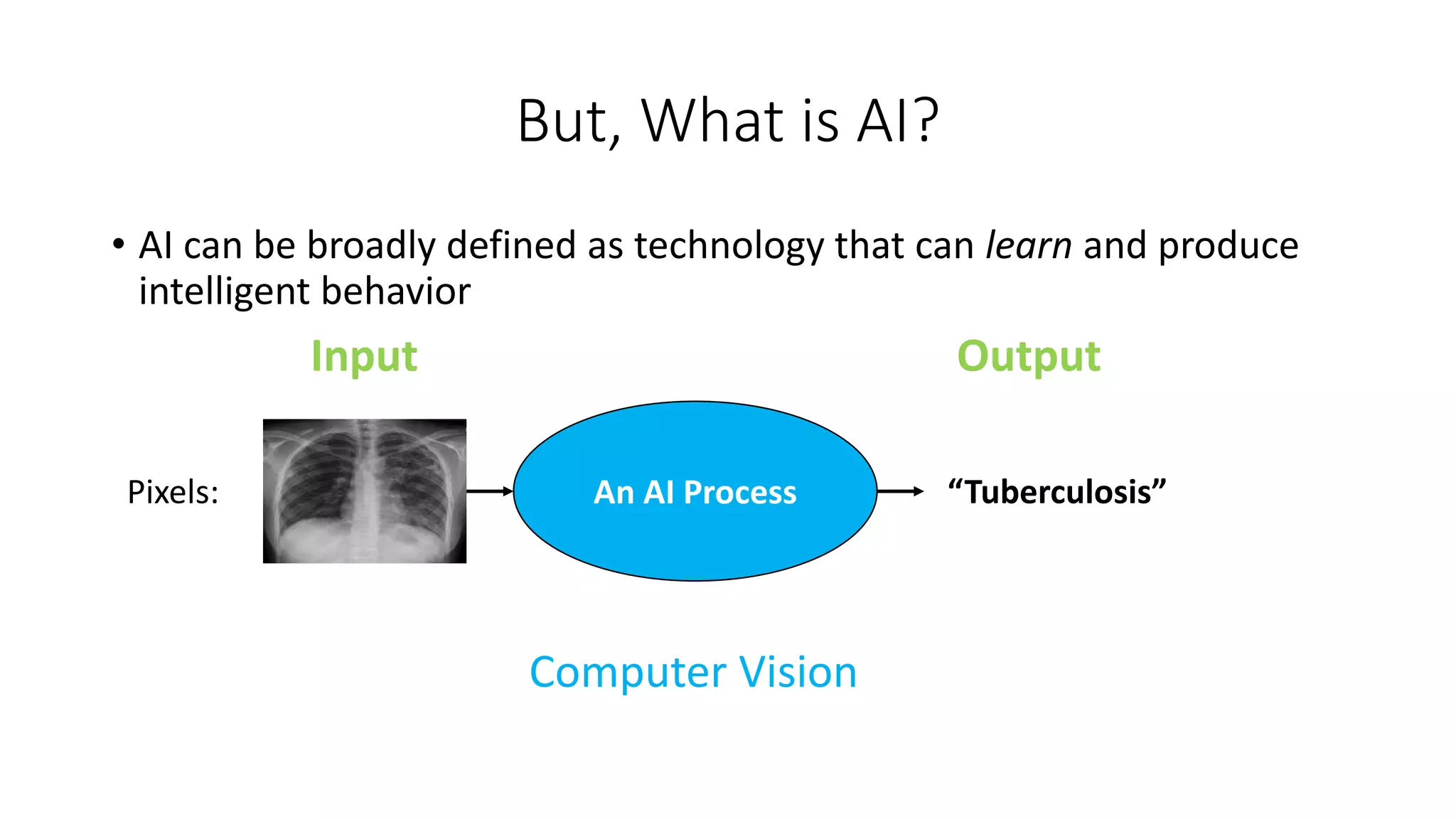
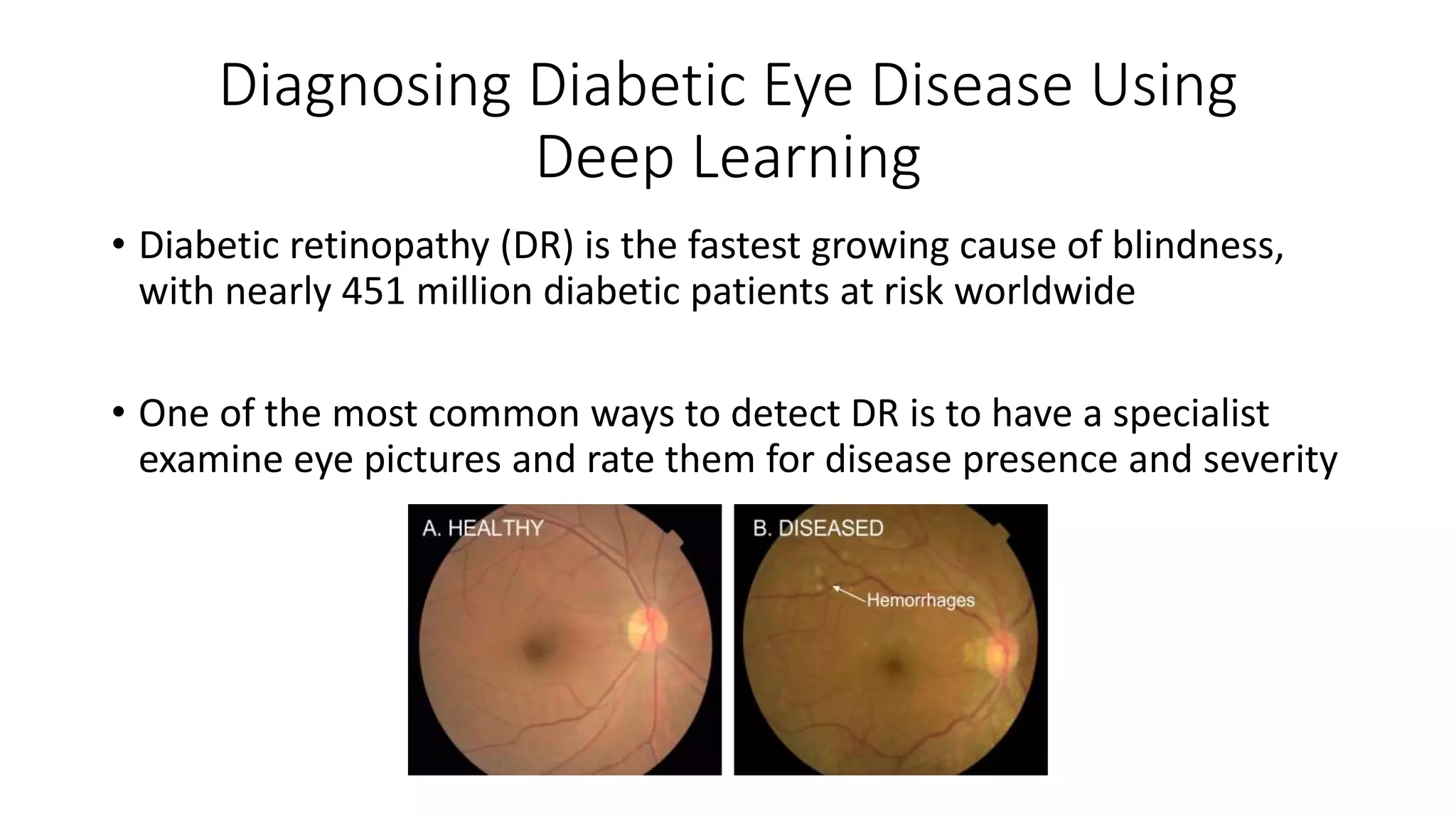
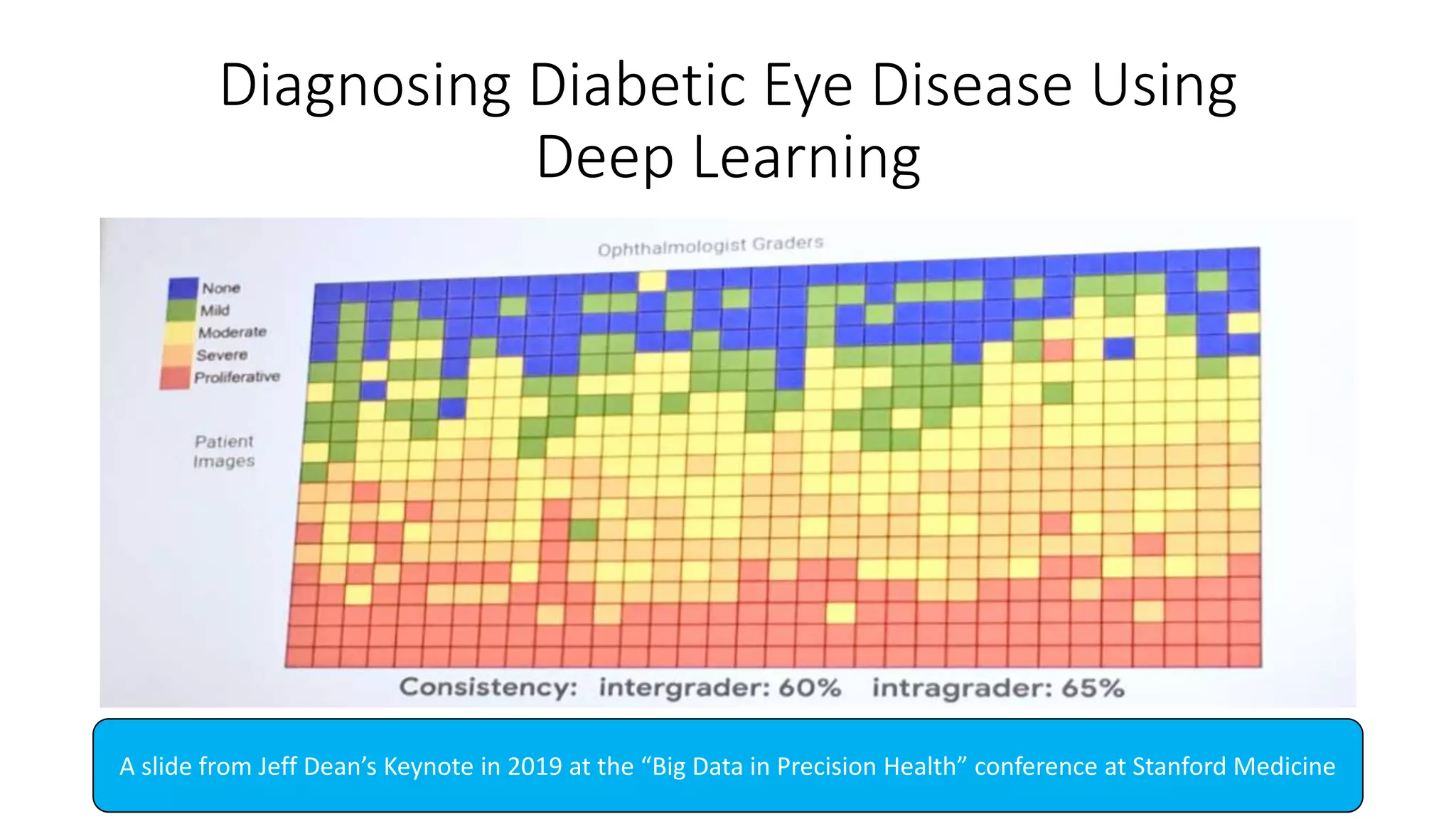
1. The lecture introduces AI applications in medicine, including diagnosing diabetic eye disease and detecting anemia from retinal images using deep learning with high accuracy near that of experts.
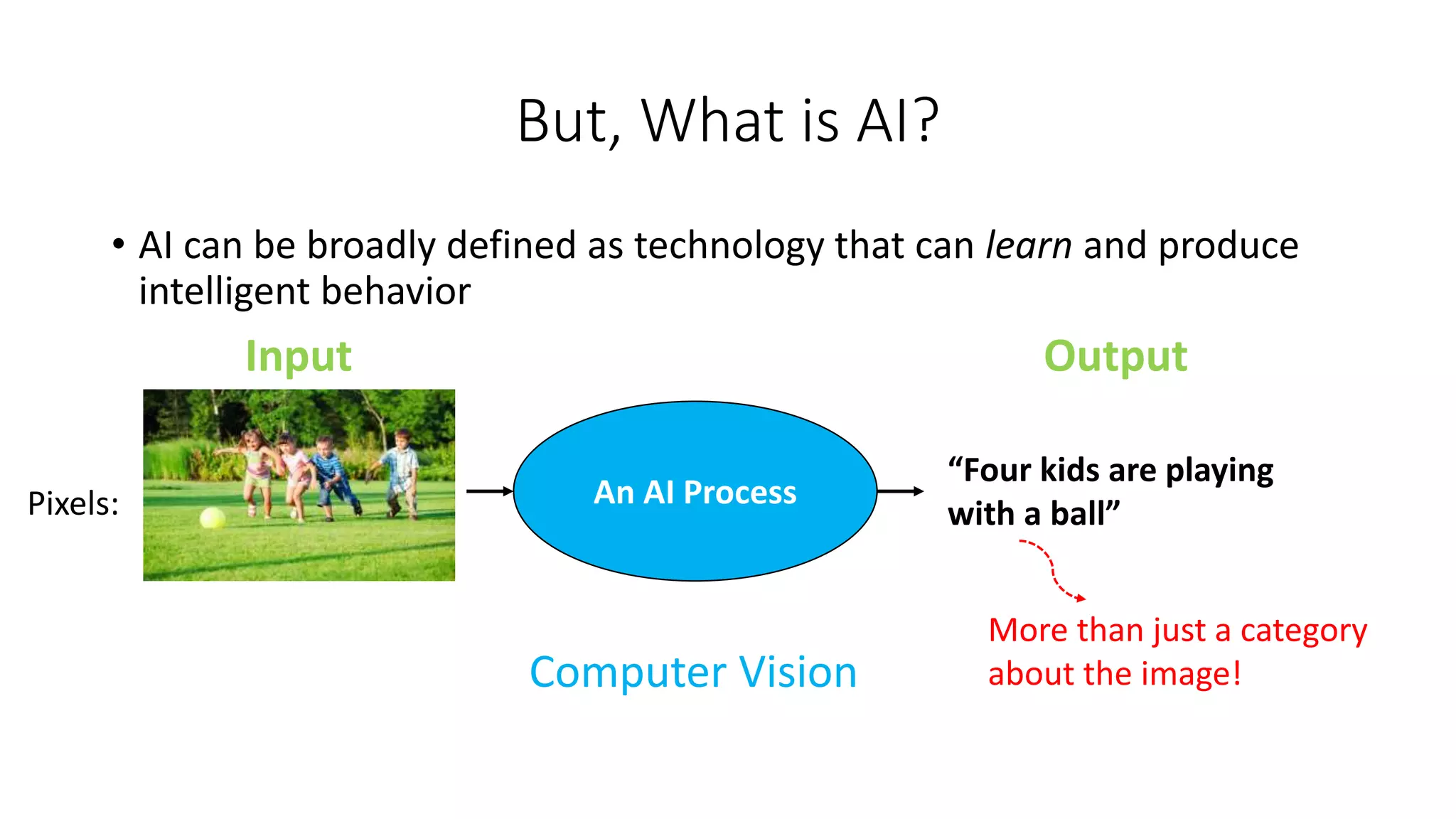
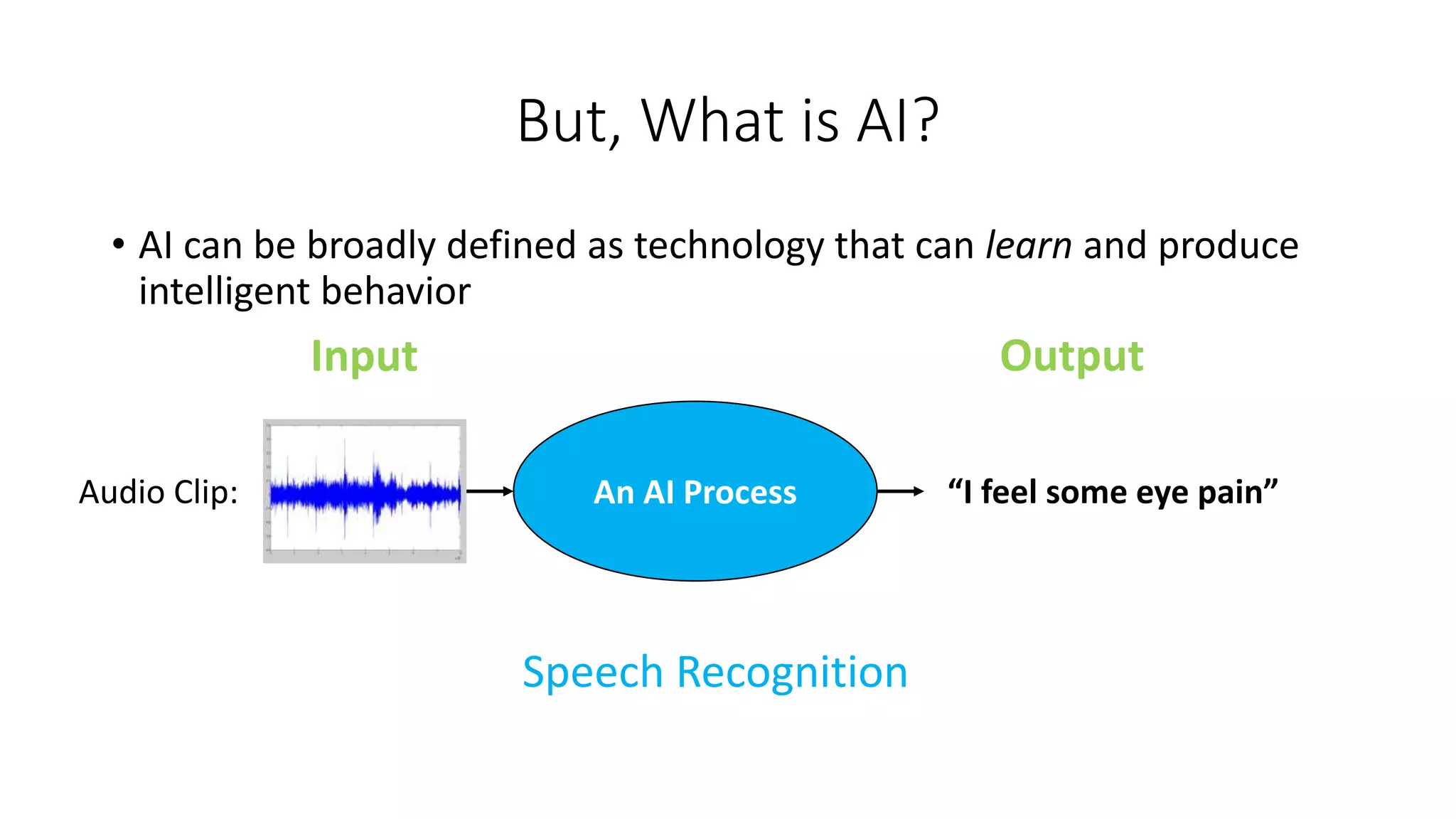
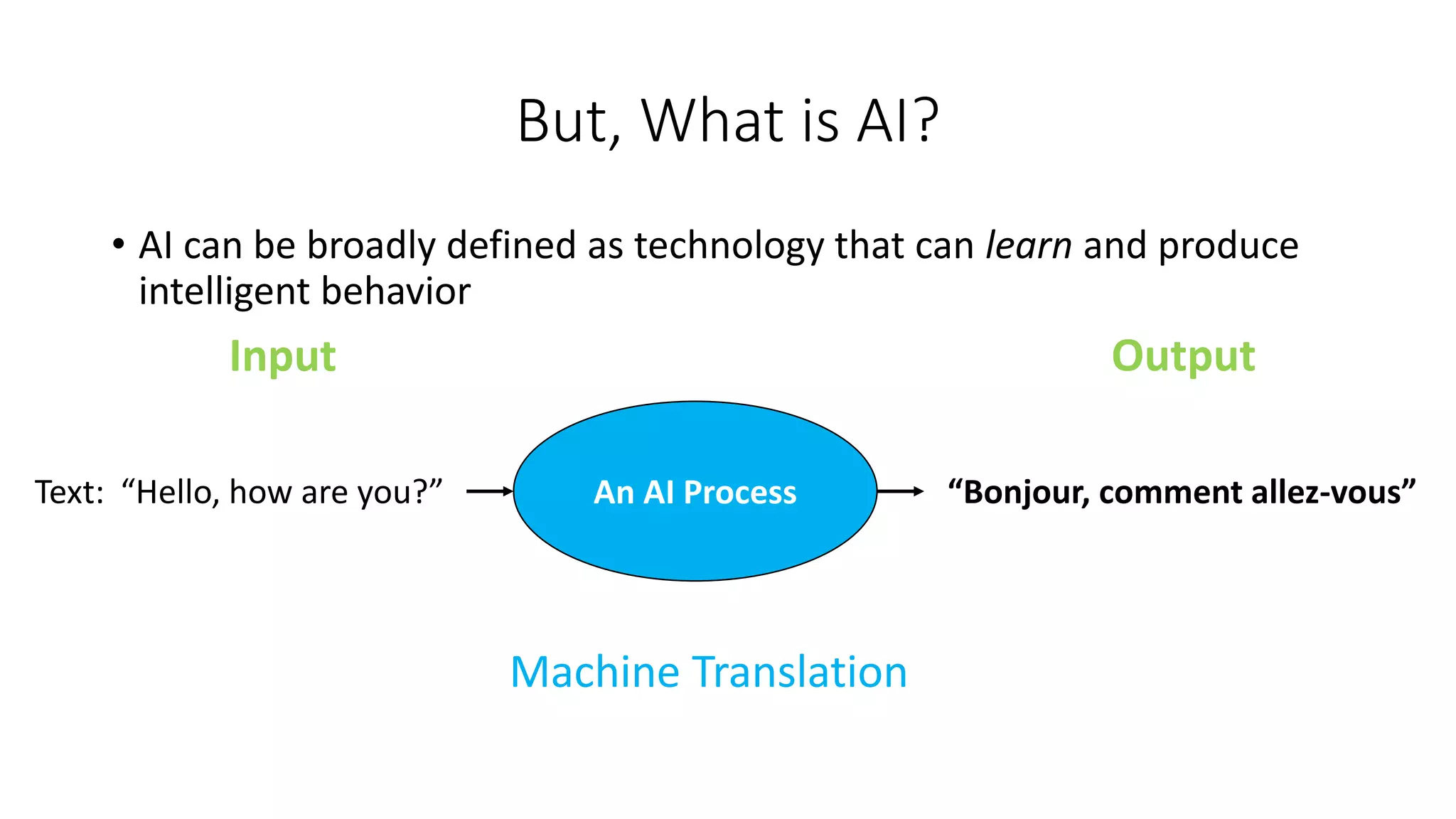
2. Other applications discussed are predicting cardiovascular risk factors from retinal photos using deep learning and extracting symptoms from clinical conversations using neural networks.
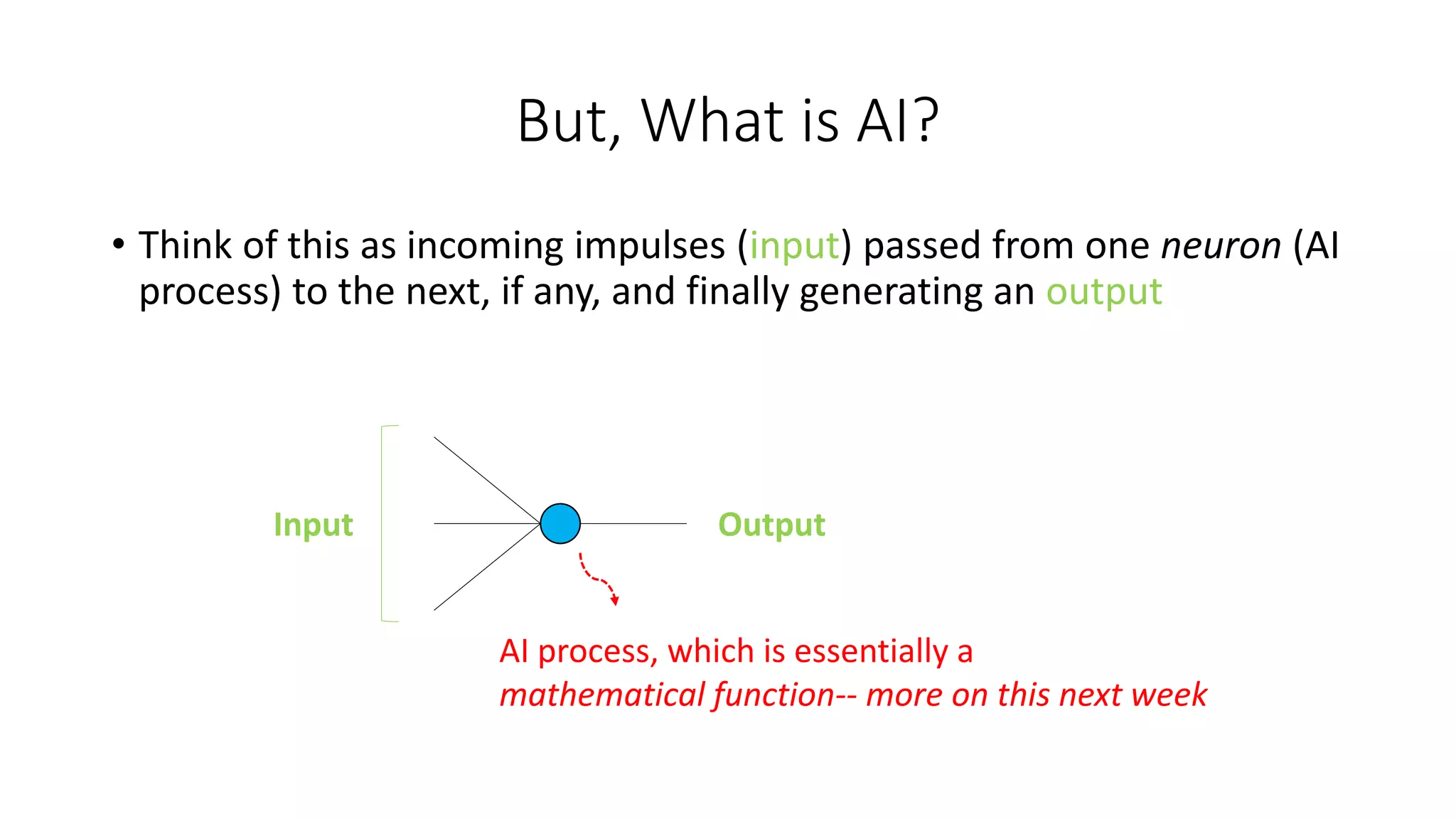
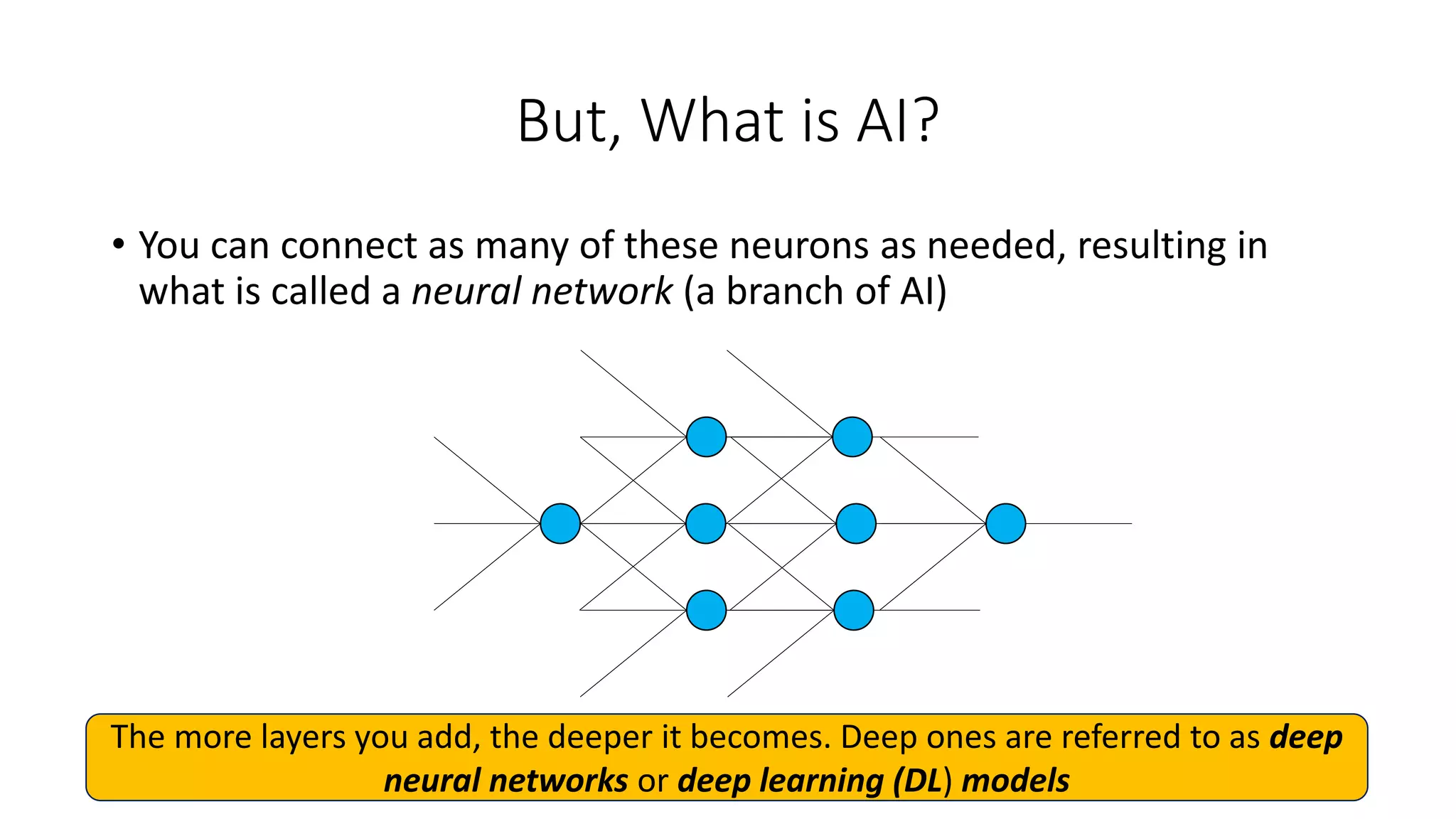
3. The course objectives are to demystify AI concepts, showcase medical AI applications, and discuss societal and ethical issues regarding AI.

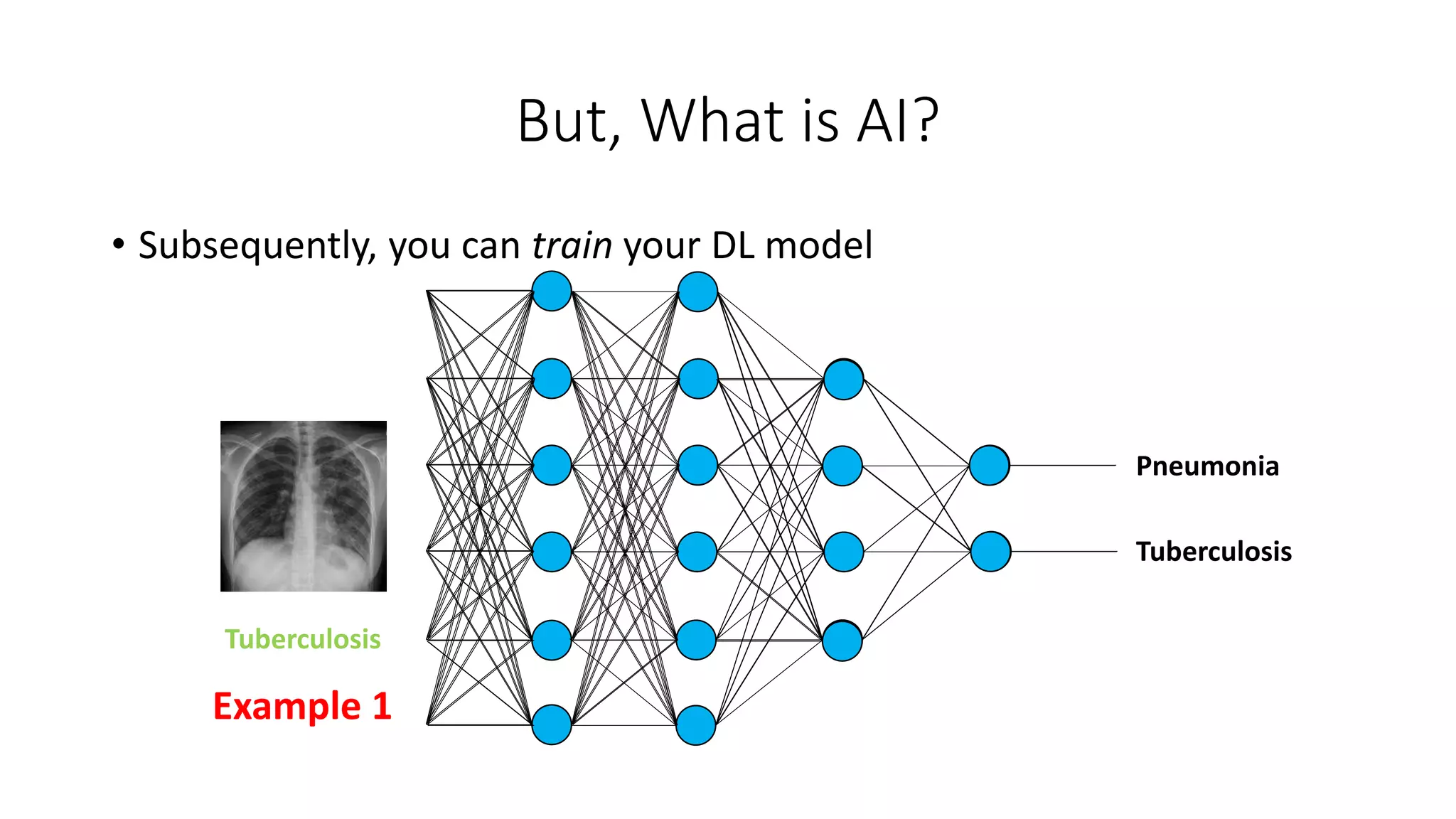
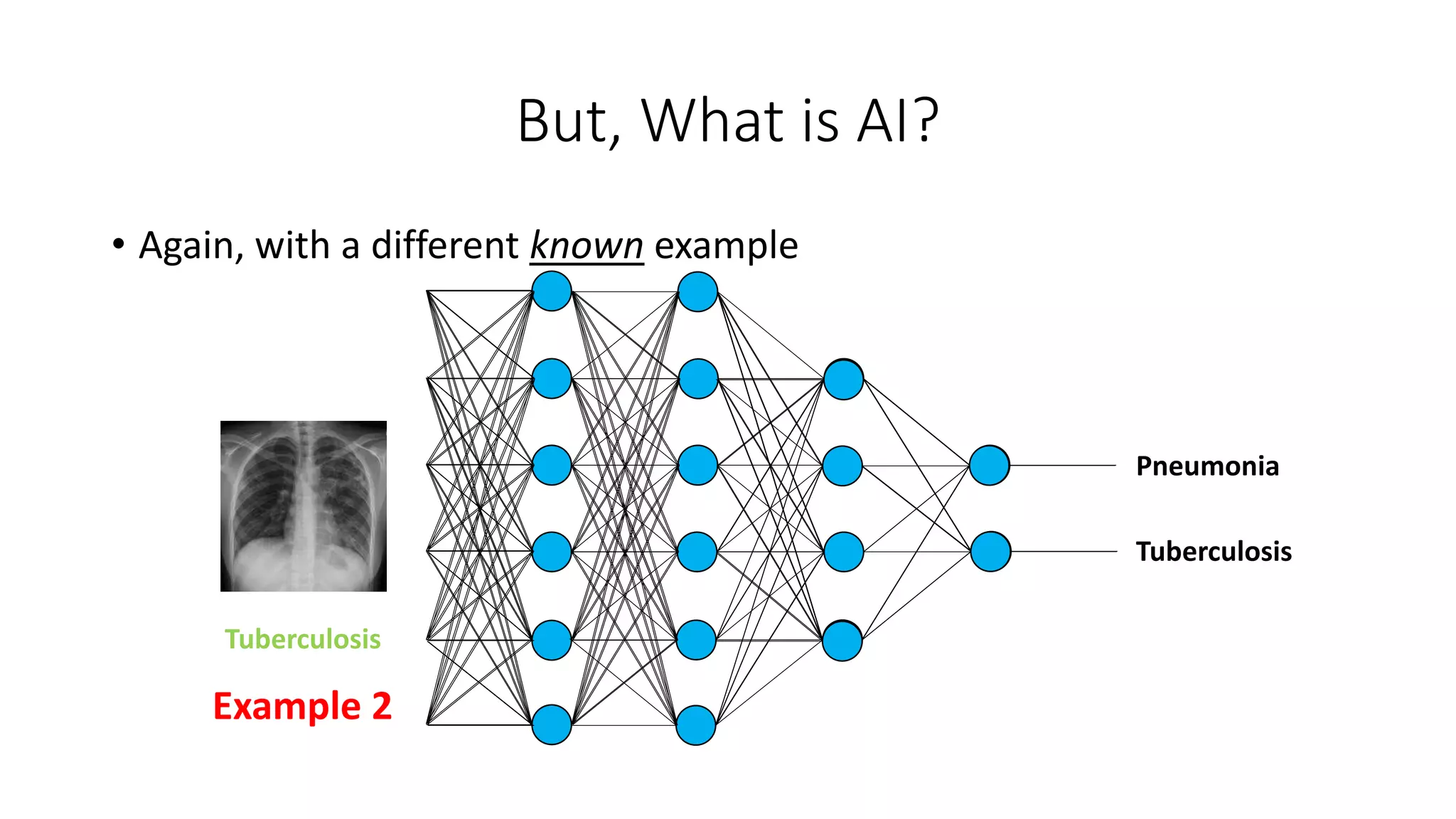
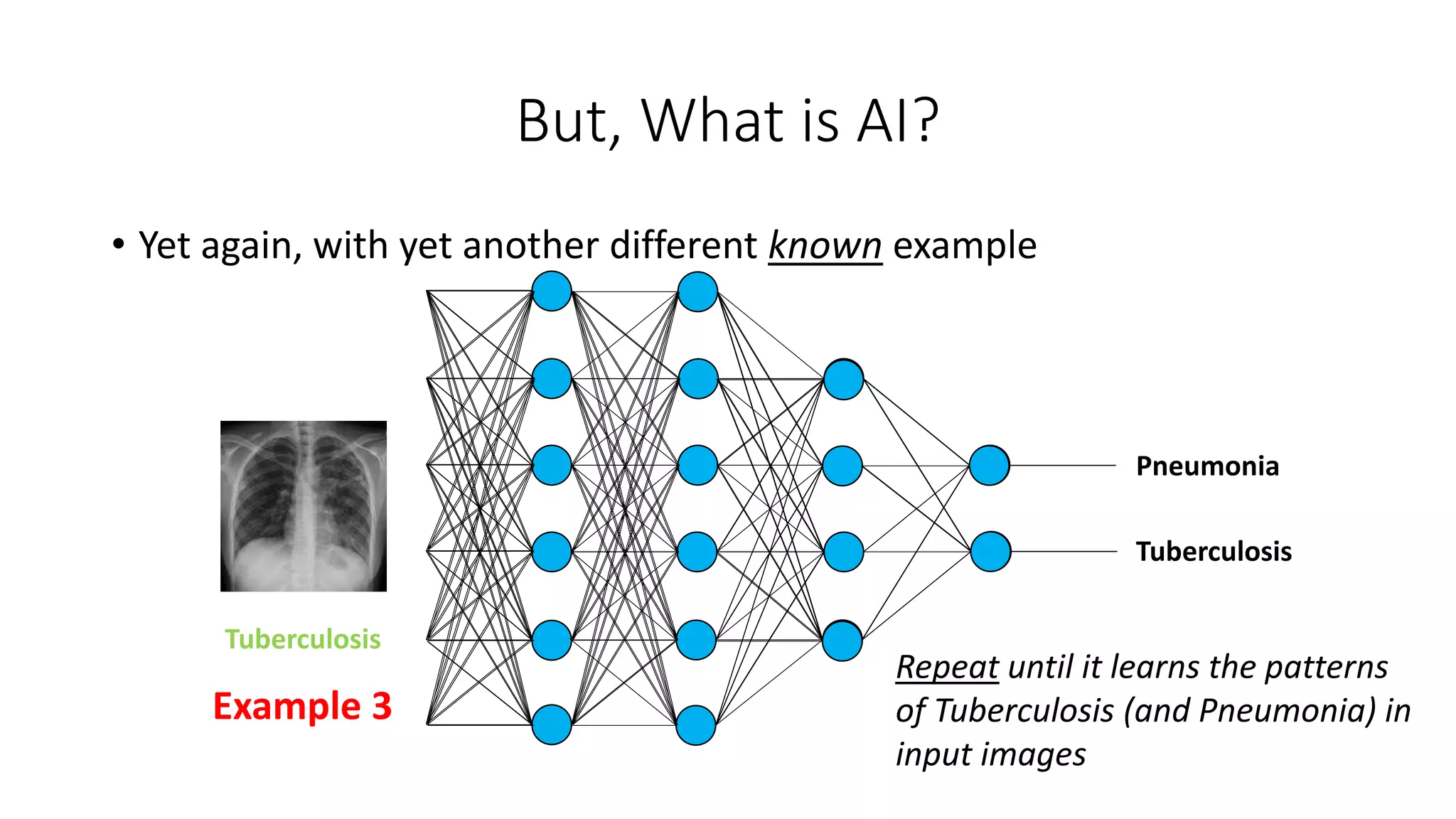
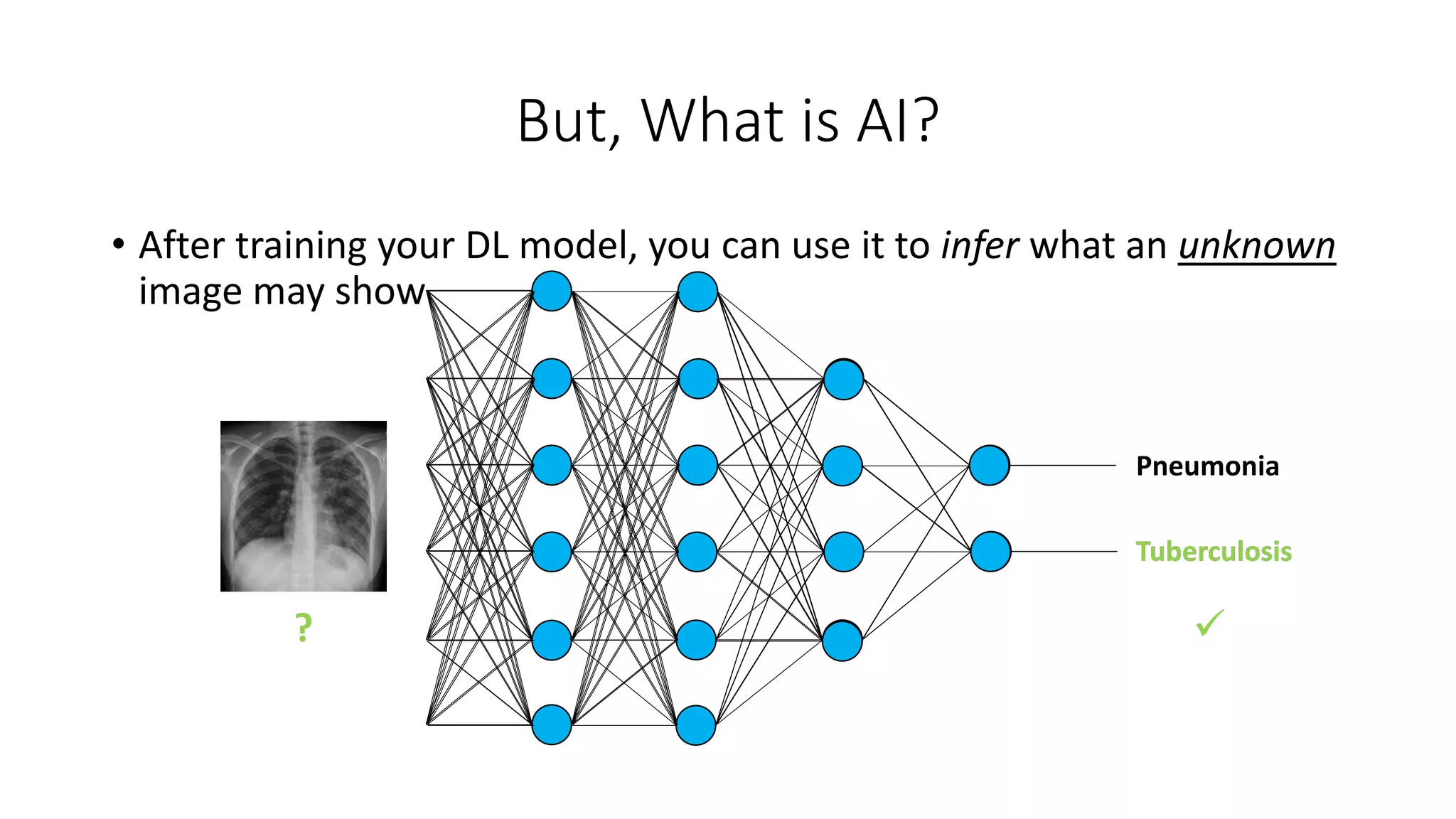
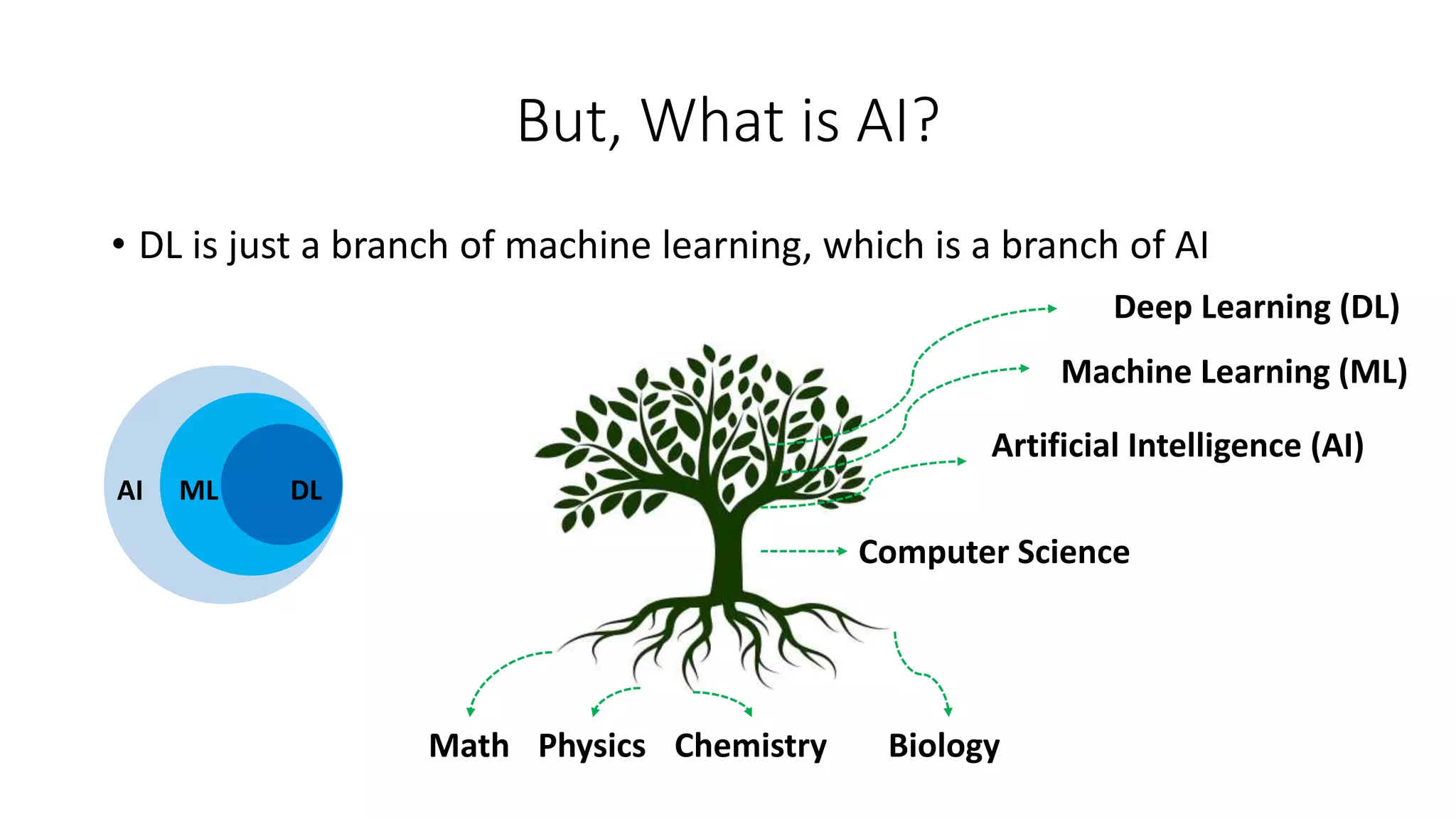



![Some Applications of AI in Medicine
1. Diagnosing diabetic eye disease using deep learning [1]
2. Detecting anemia from retinal fundus images using deep learning [2]
3. Predicting cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs
using deep learning [3]
4. Performing differential diagnosis using probabilistic graphical models
[4]
5. Extracting symptoms and their status from clinical conversations using
recurrent neural networks [5]
6. Predicting osteoarthritis using machine learning [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1-introduction-jan18-2021-230117024000-38958938/75/Lecture1-Introduction-Jan18-2021-pptx-21-2048.jpg)
![Some Applications of AI in Medicine
1. Diagnosing diabetic eye disease using deep learning [1]
2. Detecting anemia from retinal fundus images using deep learning [2]
3. Predicting cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs
using deep learning [3]
4. Performing differential diagnosis using probabilistic graphical models
[4]
5. Extracting symptoms and their status from clinical conversations using
recurrent neural networks [5]
6. Predicting osteoarthritis using machine learning [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1-introduction-jan18-2021-230117024000-38958938/75/Lecture1-Introduction-Jan18-2021-pptx-22-2048.jpg)



![Some Applications of AI in Medicine
1. Diagnosing diabetic eye disease using deep learning [1]
2. Detecting anemia from retinal fundus images using deep learning [2]
3. Predicting cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs
using deep learning [3]
4. Performing differential diagnosis using probabilistic graphical models
[4]
5. Extracting symptoms and their status from clinical conversations using
recurrent neural networks [5]
6. Predicting osteoarthritis using machine learning [6]
Next week on Monday …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1-introduction-jan18-2021-230117024000-38958938/75/Lecture1-Introduction-Jan18-2021-pptx-28-2048.jpg)

