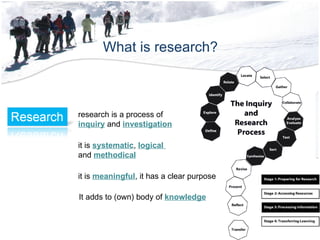
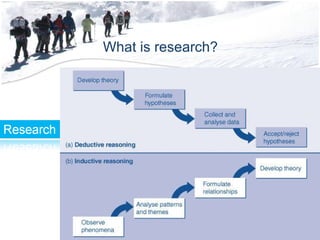
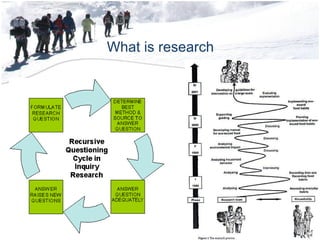
The document discusses the structure and content of a business research methods course. It includes an overview of the course schedule, structure, assignments, and requirements. Key topics to be covered include research fundamentals, statistics, data collection and analysis, writing reports, and exam requirements. The last part defines what research is, including that it is a systematic, logical, and methodical process to increase knowledge through discovery of non-trivial facts and insights.