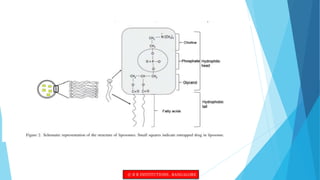
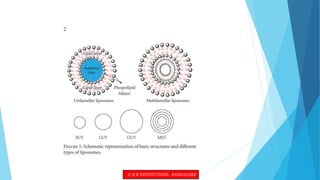
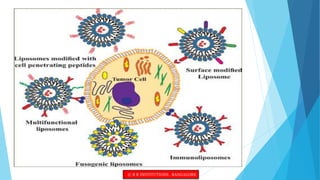
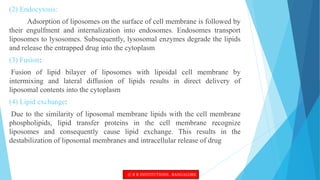
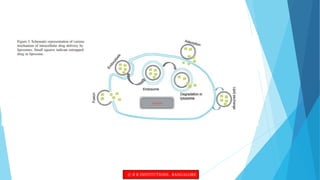
This document provides an overview of ocular liposomes. It discusses the structural components of liposomes including phospholipids, sterols, and sphingolipids. The advantages of liposomes for ophthalmic drug delivery include enhancing permeation and residence time on the corneal surface. Various types of liposomes are described based on structural parameters, composition, and preparation method. Common preparation techniques include conventional method, sonication, extrusion, solubilization, and reverse phase evaporation. Mechanisms of permeation through the ocular surface include adsorption, endocytosis, fusion, and lipid exchange. Liposomes show potential for improving ophthalmic drug pharmacokinetics and reducing toxicity.