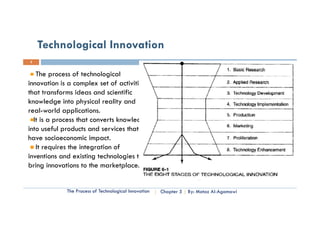
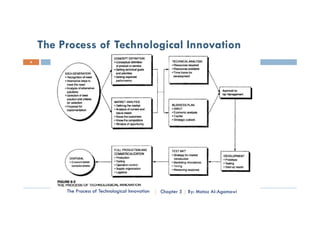
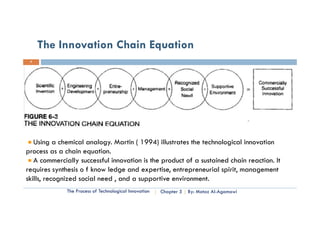
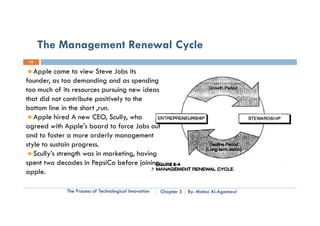
This document is a chapter from a university course on entrepreneurship. It discusses the process of technological innovation over several stages: basic research, applied research, technology development, implementation, production, and marketing. It describes each stage in detail. It also discusses the roles of entrepreneurship and management in innovation and how organizations balance these approaches over a technology's lifecycle. The chapter assignment asks students to present case studies on innovation examples in small groups.