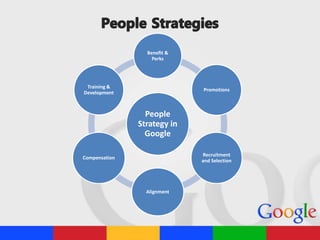
This case study examines the culture at Google and whether it can remain "Googley" as it continues to rapidly expand. It discusses Google's unique culture which encourages innovation, autonomy, informality and risk-taking. The study also analyzes Google's people strategies around recruitment, promotions, compensation and training. It concludes that Google's strong foundations in cultural principles and support from top management have allowed it to remain exceptional while continuing to grow rapidly.
















![Engineering
Product
Management
Product
marketing
SalesOperations
Legal
Finance
Triumvirate
[trahy-uhm-ver-it, -vuh-reyt]
• a board of three officials jointly resp
onsible for some task
• Organized by function
• Flat organization
• Organization structure with few
or no level of middle
management between staff and
executives.
• Loose Organization
• Very nimble without letting
hierarchy, organization
structure, titles and levels get in
the way of creativity and
execution.
• People are self managed and
self-motivated at every level](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/keepinggooglefinalreadyforsubmissionver1-160321053159/85/Keeping-google-googley-18-320.jpg)





