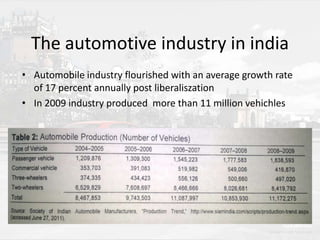
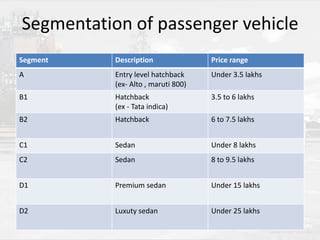
Tata launched the Nano car in 2009 with the goal of providing an "ultra low-cost" vehicle priced at Rs. 1 lakh. There were two options considered for positioning the Nano - as a family transport vehicle or for specific usage situations. The automotive industry in India has high growth rates but low per capita vehicle ownership compared to developed countries. The Nano faced competition from other small and low-cost vehicles. Initial bookings were strong but sales declined in late 2010 due to safety issues and rising material costs, which Tata addressed through improvements and an extended warranty.