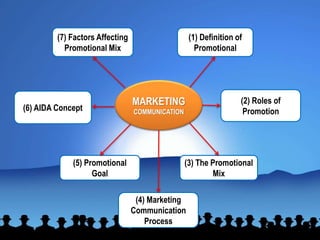
This document provides an overview of marketing communication and promotion. It covers key topics such as:
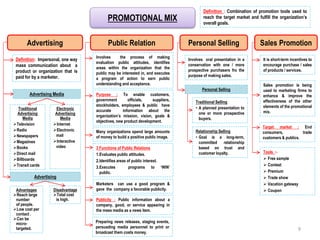
1) Definitions of promotional strategy and the promotional mix.
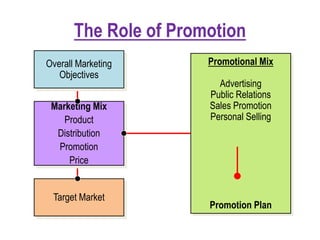
2) The roles of promotion in achieving overall marketing objectives and providing a competitive advantage.
3) Components of the promotional mix including advertising, public relations, sales promotion, and personal selling.
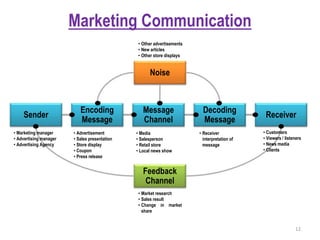
4) The marketing communication process and how messages are encoded, transmitted through channels, and decoded by receivers.
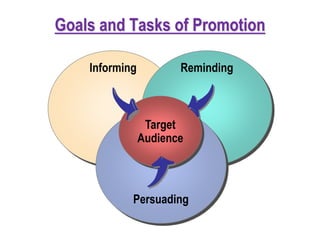
5) Goals of promotion including informing, persuading, and reminding target audiences.
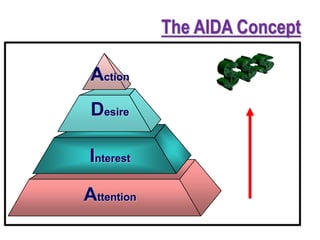
6) The AIDA model of gaining consumer attention, interest, desire, and action.
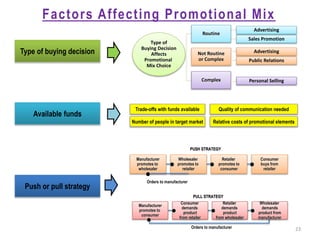
7) Factors that affect promotional mix decisions