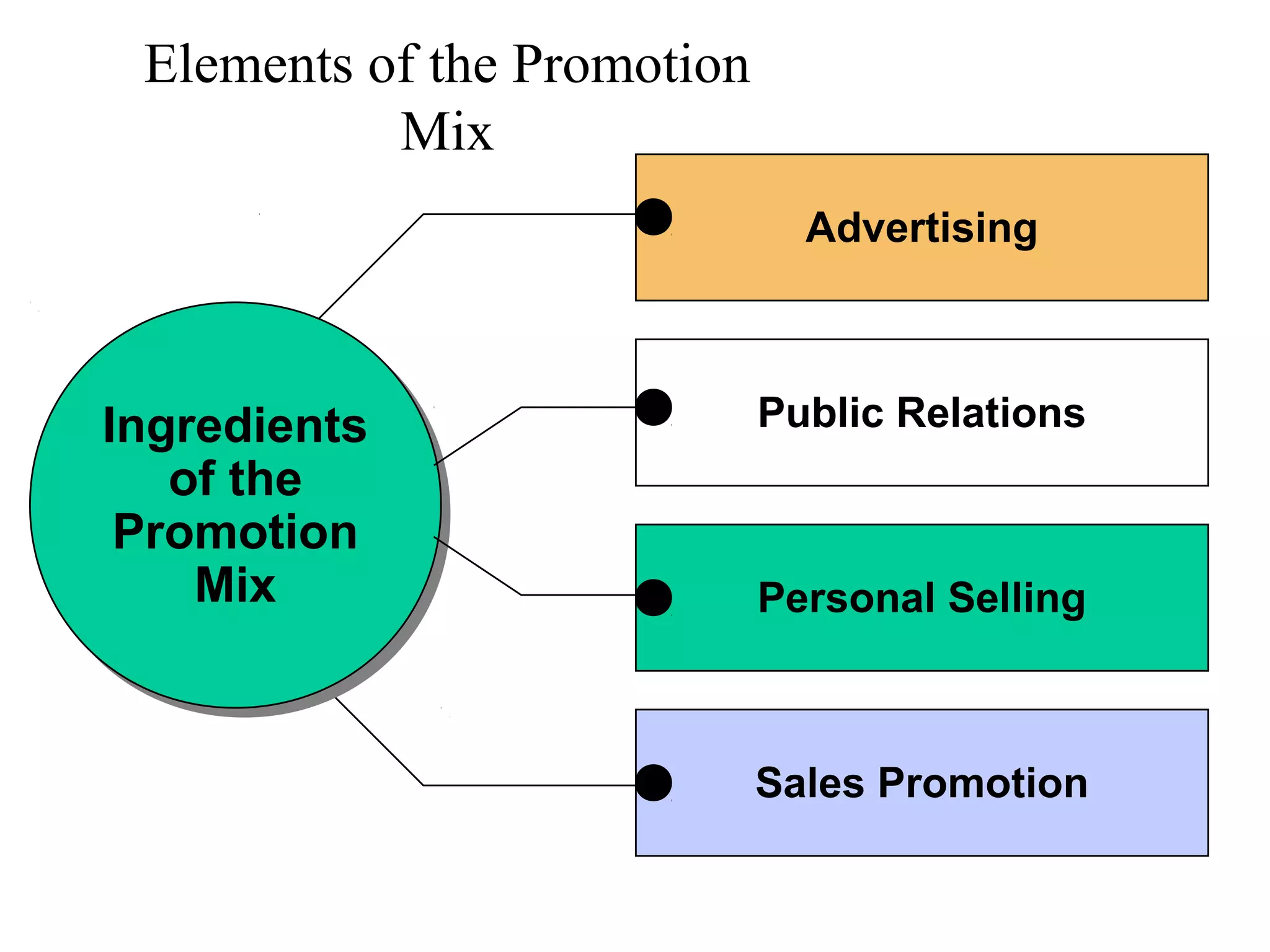
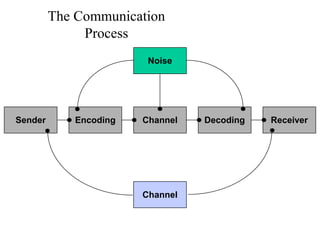
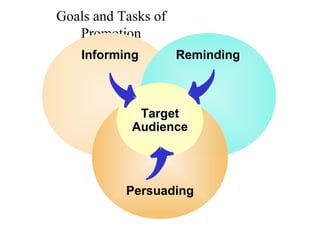
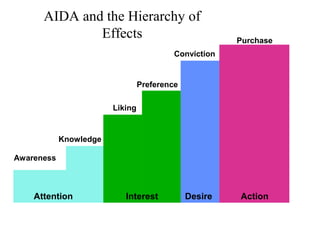
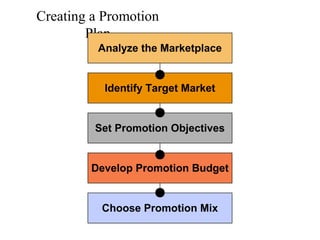
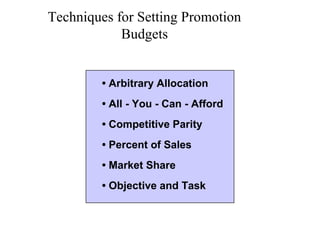
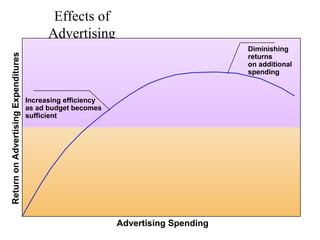
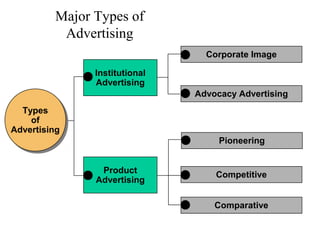
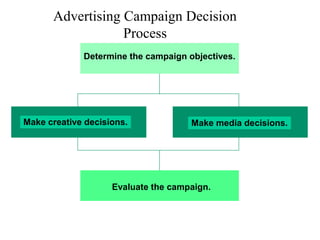
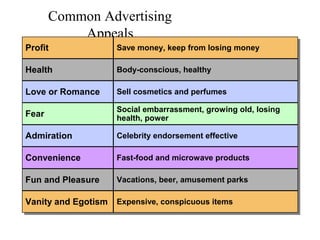
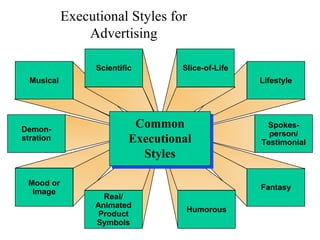
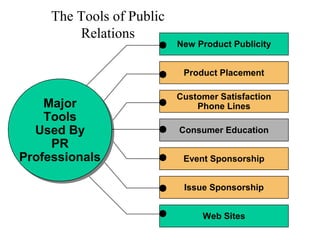
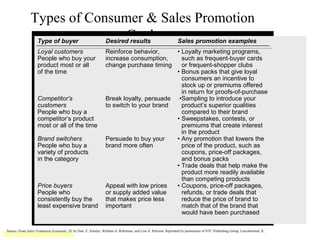
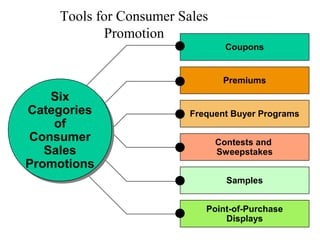
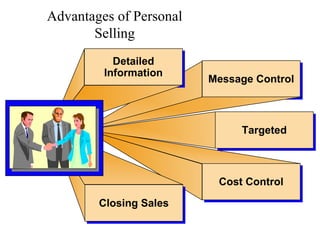
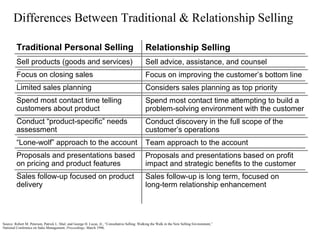
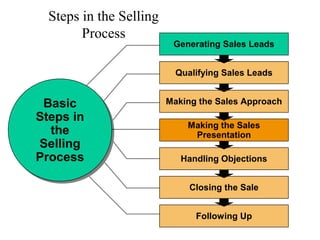
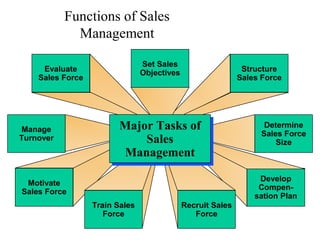
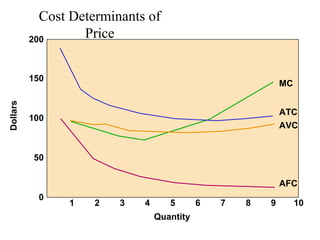
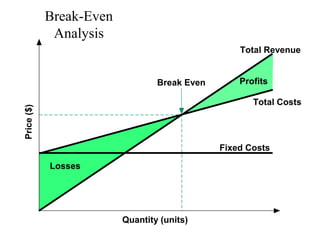
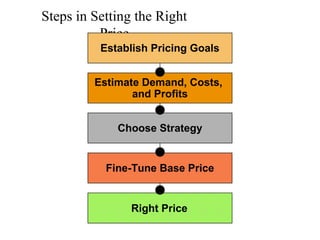
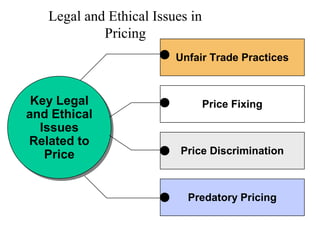
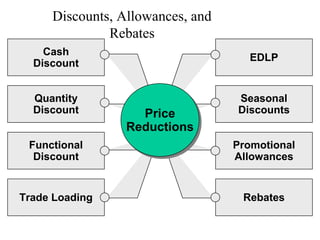
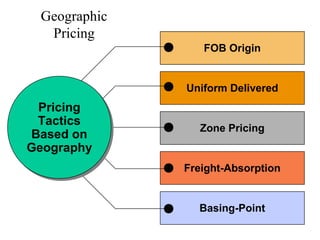
This document provides an overview of key concepts in marketing communications and promotion. It discusses the major elements of the promotion mix including advertising, public relations, personal selling, and sales promotion. It also covers topics such as the communication process, goals of promotion, models for how promotion works like AIDA, factors that influence the promotion mix, techniques for developing a promotion plan, objectives of promotion, and regulations.