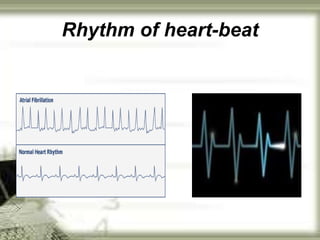
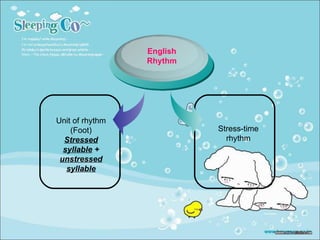
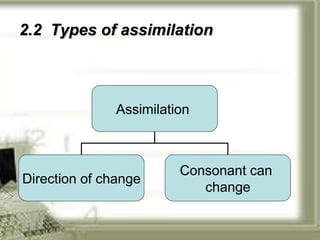
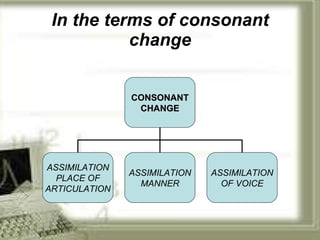
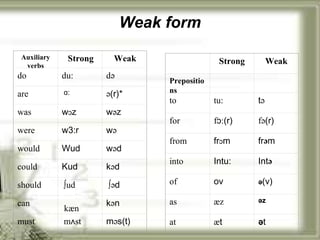
The document summarizes key aspects of connected speech in English, including rhythm, assimilation, elision, and linking. It defines each concept and provides examples. Rhythm refers to the regular stress pattern in speech. Assimilation is the change in pronunciation of sounds due to surrounding sounds, such as in "newspaper." Elision is the omission of sounds, like the 't' in "night." Linking describes how words and sounds are connected together in fluent speech according to five basic rules.