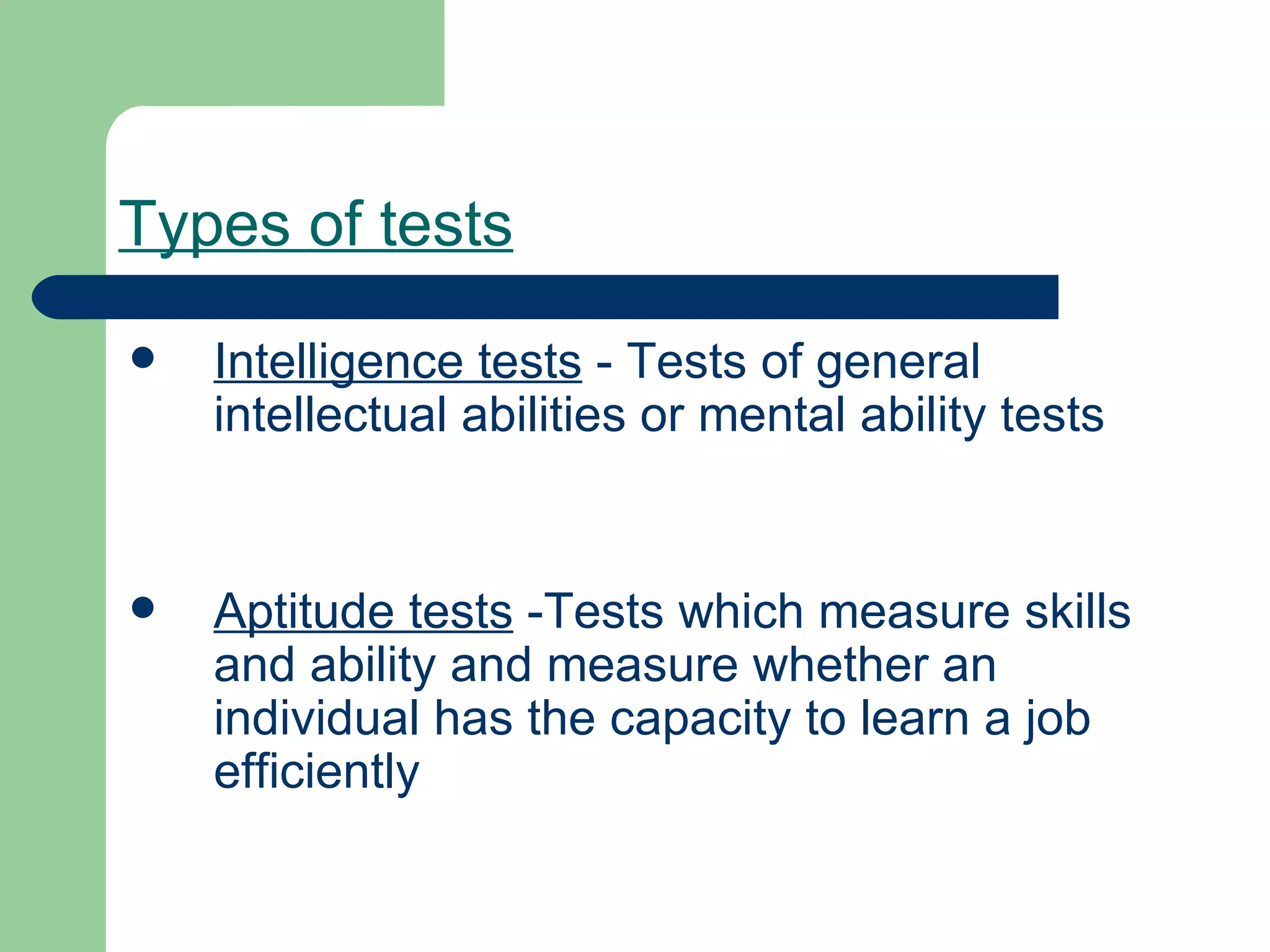
The document discusses various types of tests used in human resources management for employee selection. It describes intelligence, aptitude, personality, interest, performance, general knowledge, perception, situational, and achievement tests. It outlines the characteristics of a good test and discusses developing a testing program by deciding objectives, choosing tests, administering, relating to criteria, and analyzing results. It also provides a case study example of using a consolidated HR system to track employee data and headcount across multiple locations and systems.