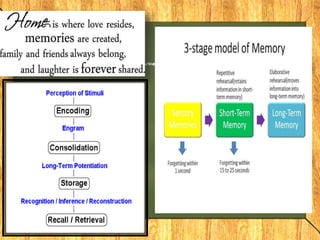
The document discusses memory, intelligence, and states of mind. It describes memory as the mental faculty of retaining past experiences, and identifies three processes involved - encoding, retrieval, and storage. It notes we have three storage capabilities: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Long-term memory is divided into declarative, semantic, and episodic memory. The document also discusses theories of forgetting, including interference, retrieval failure, failure to store, and motivated forgetting. It defines intelligence as general cognitive problem-solving skills and describes relaxation and hypnosis in psychology.