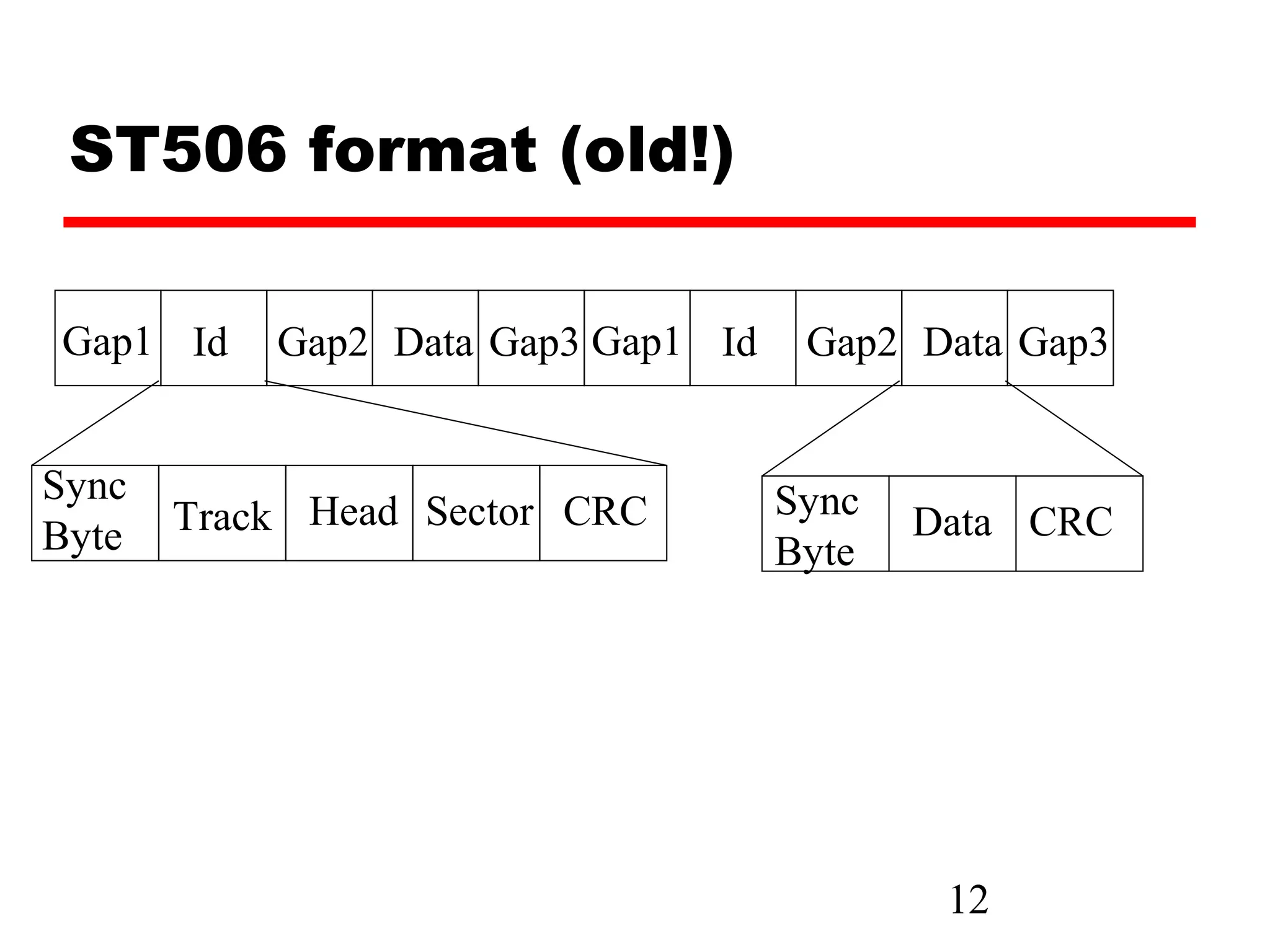
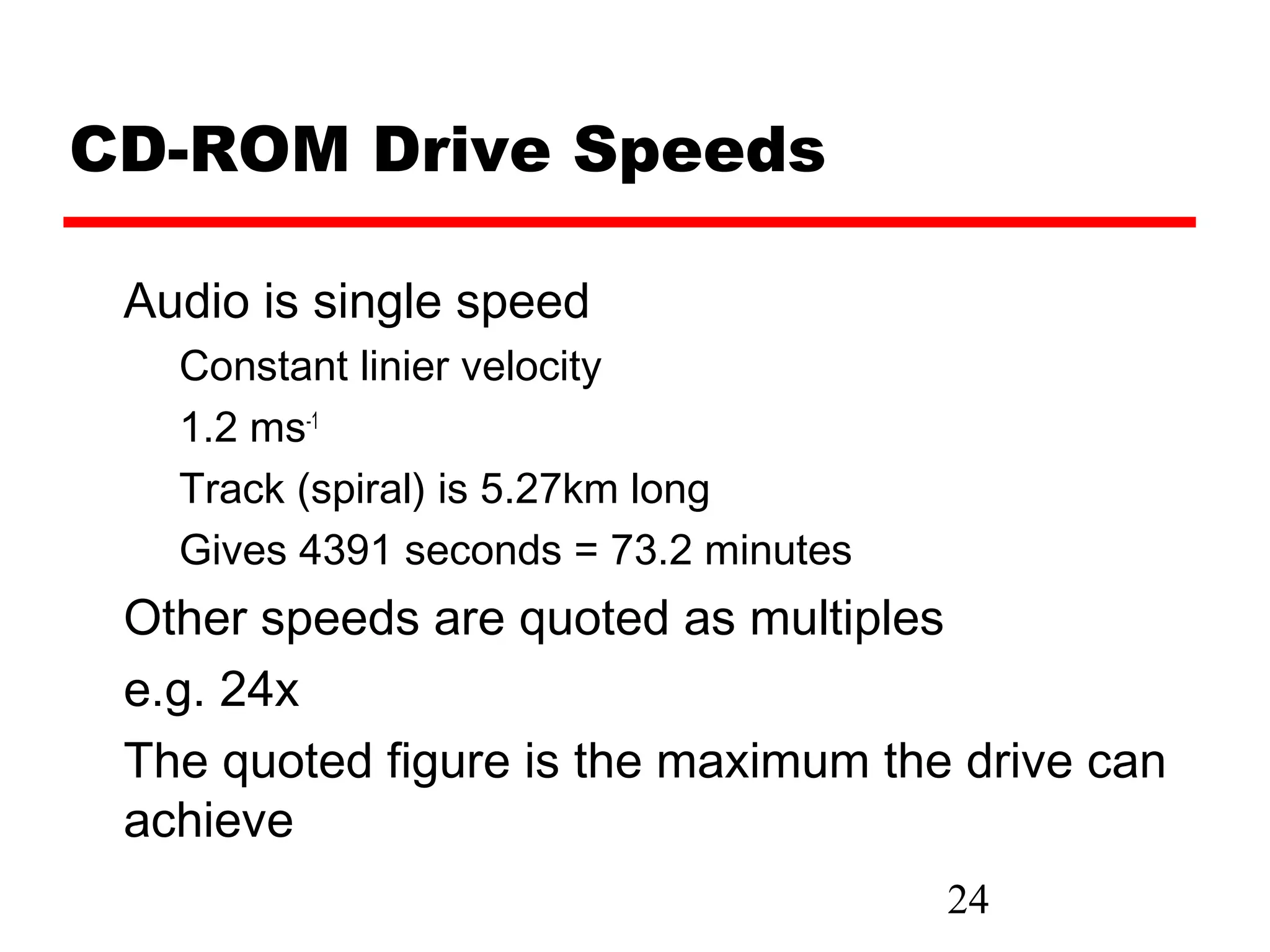
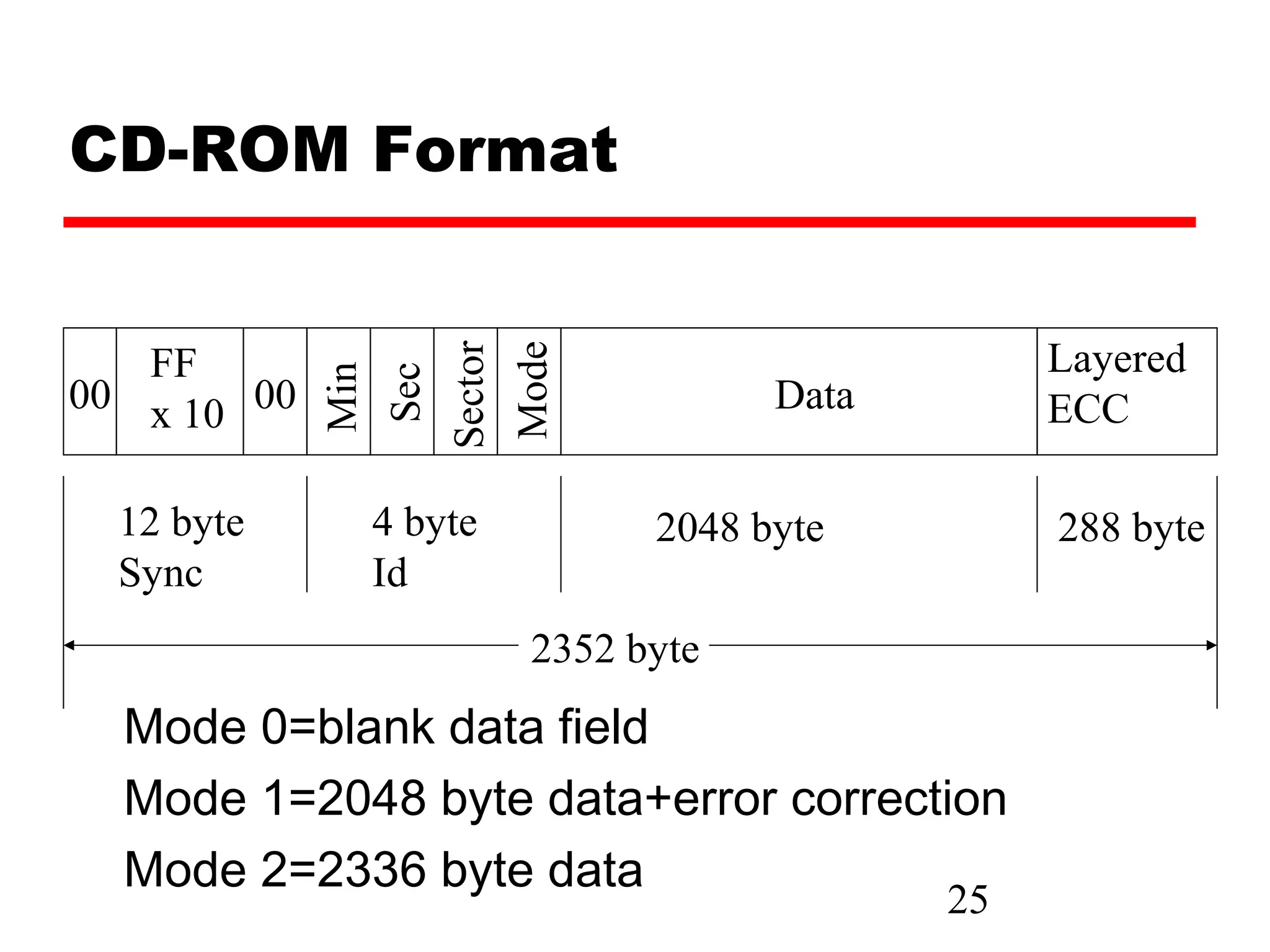
The document discusses various types of external memory including magnetic disk, optical disks, and magnetic tape. It provides details on technologies such as hard disks, floppy disks, CDs, DVDs, and tape drives. RAID configurations are explained which provide data redundancy across multiple disks.