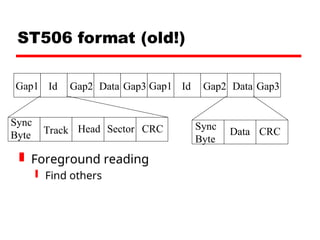
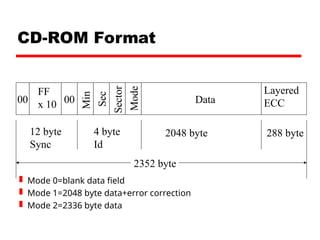
Chapter 5 of William Stallings' book on computer organization and architecture discusses various types of external memory including magnetic disks, optical storage, and magnetic tape. It covers details such as data organization, disk layouts, RAID configurations, and the advantages and disadvantages of each memory type. The chapter emphasizes the importance of understanding the operational characteristics and capabilities of different external storage media.