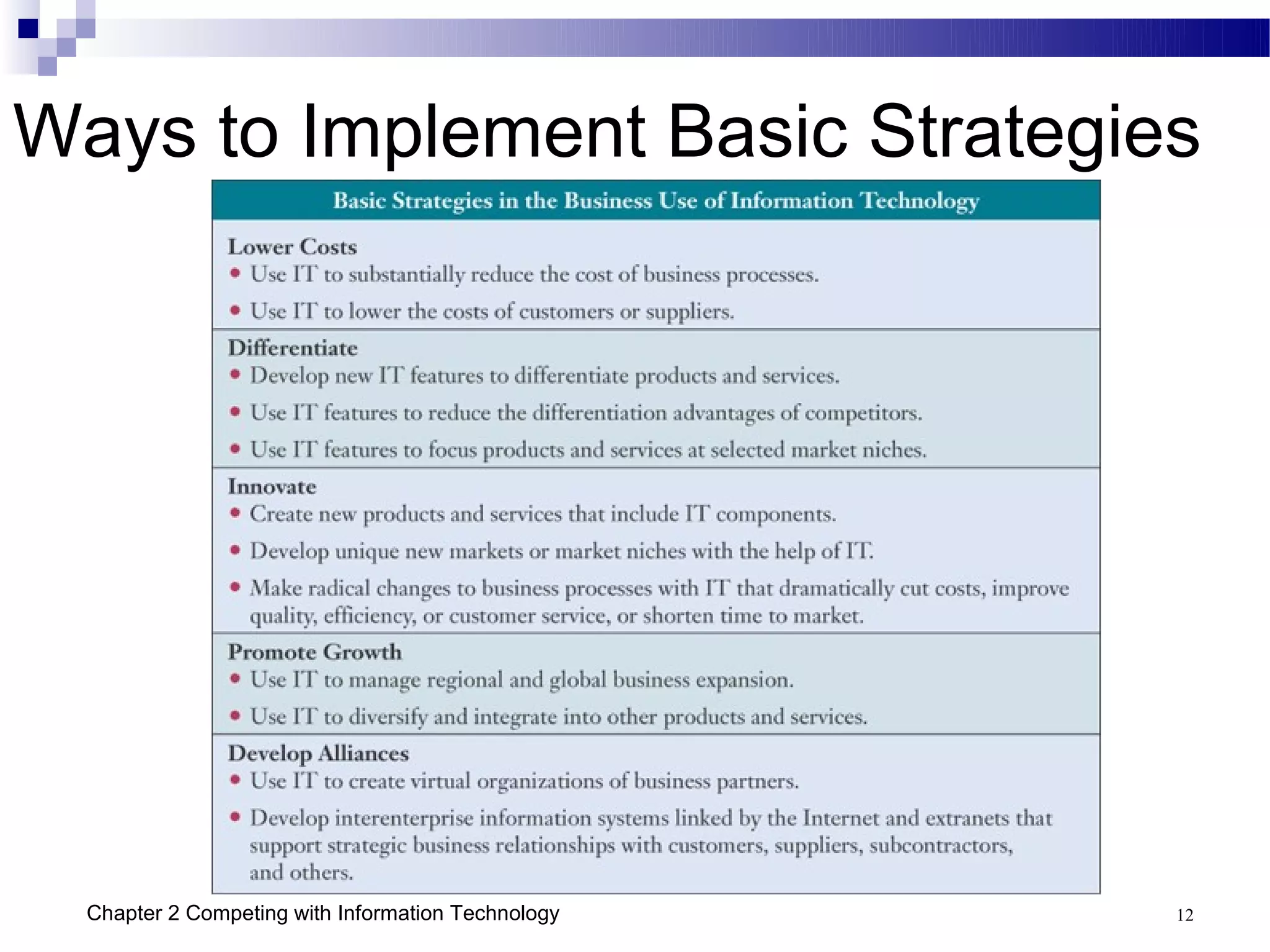
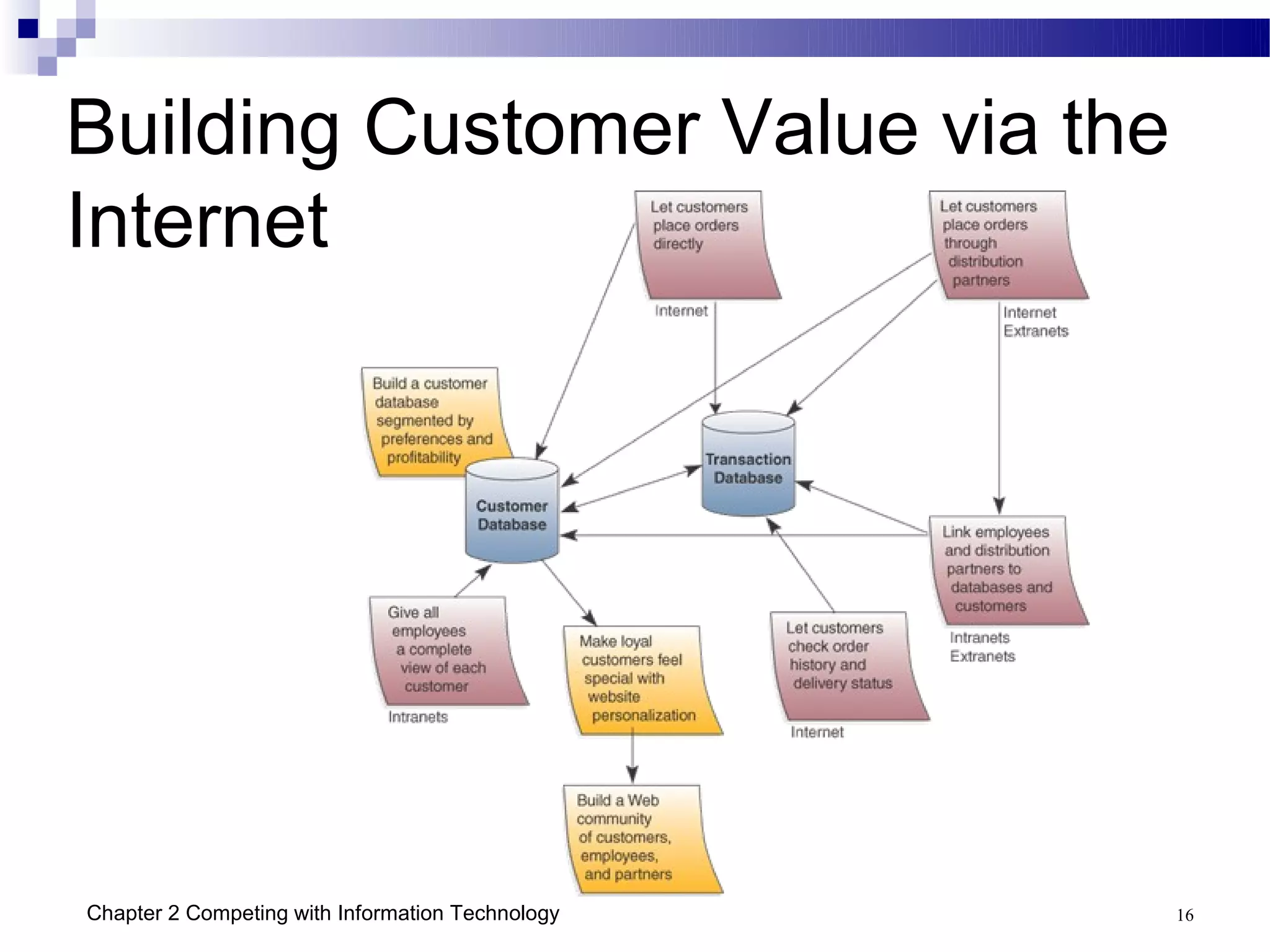
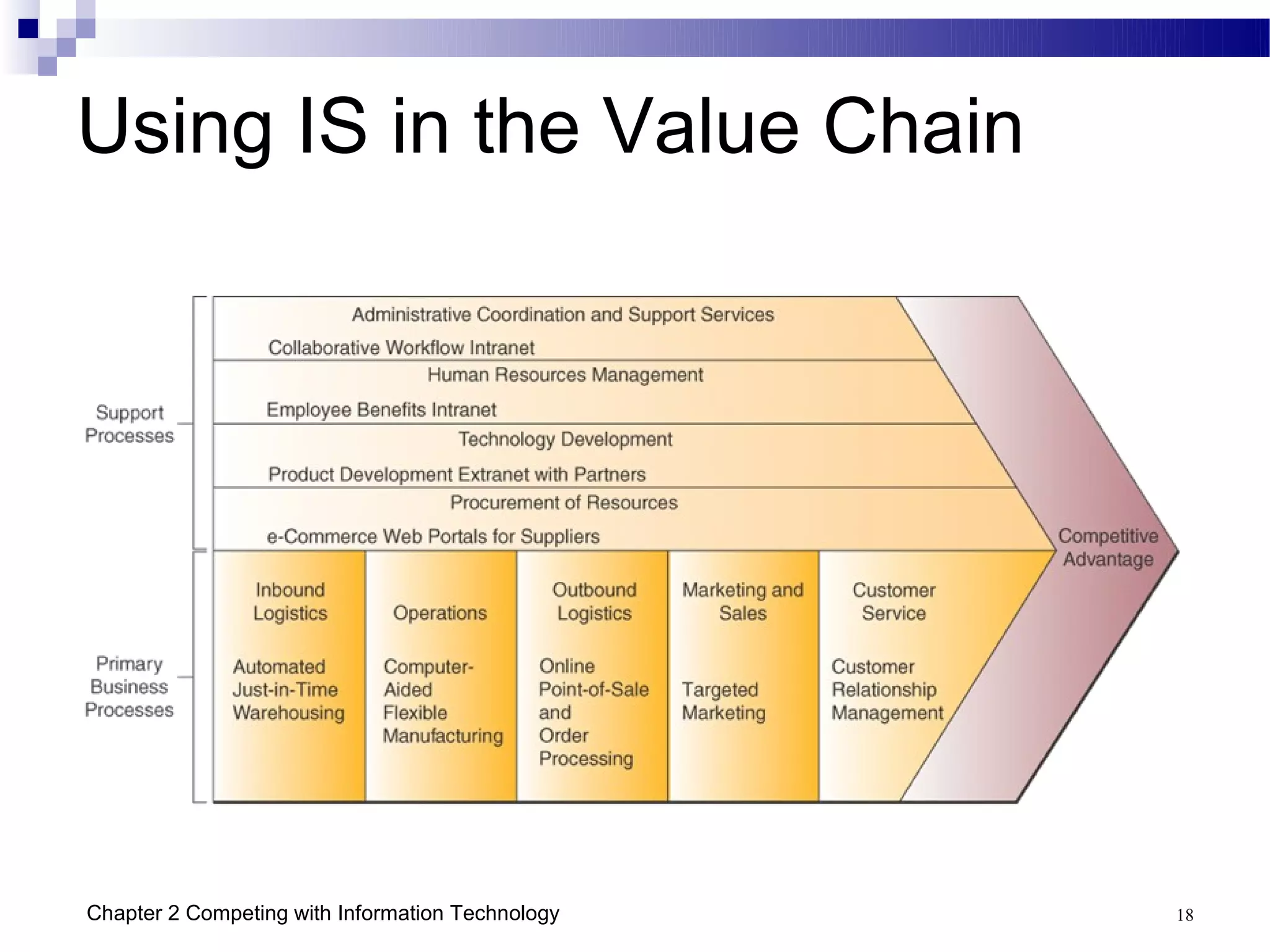
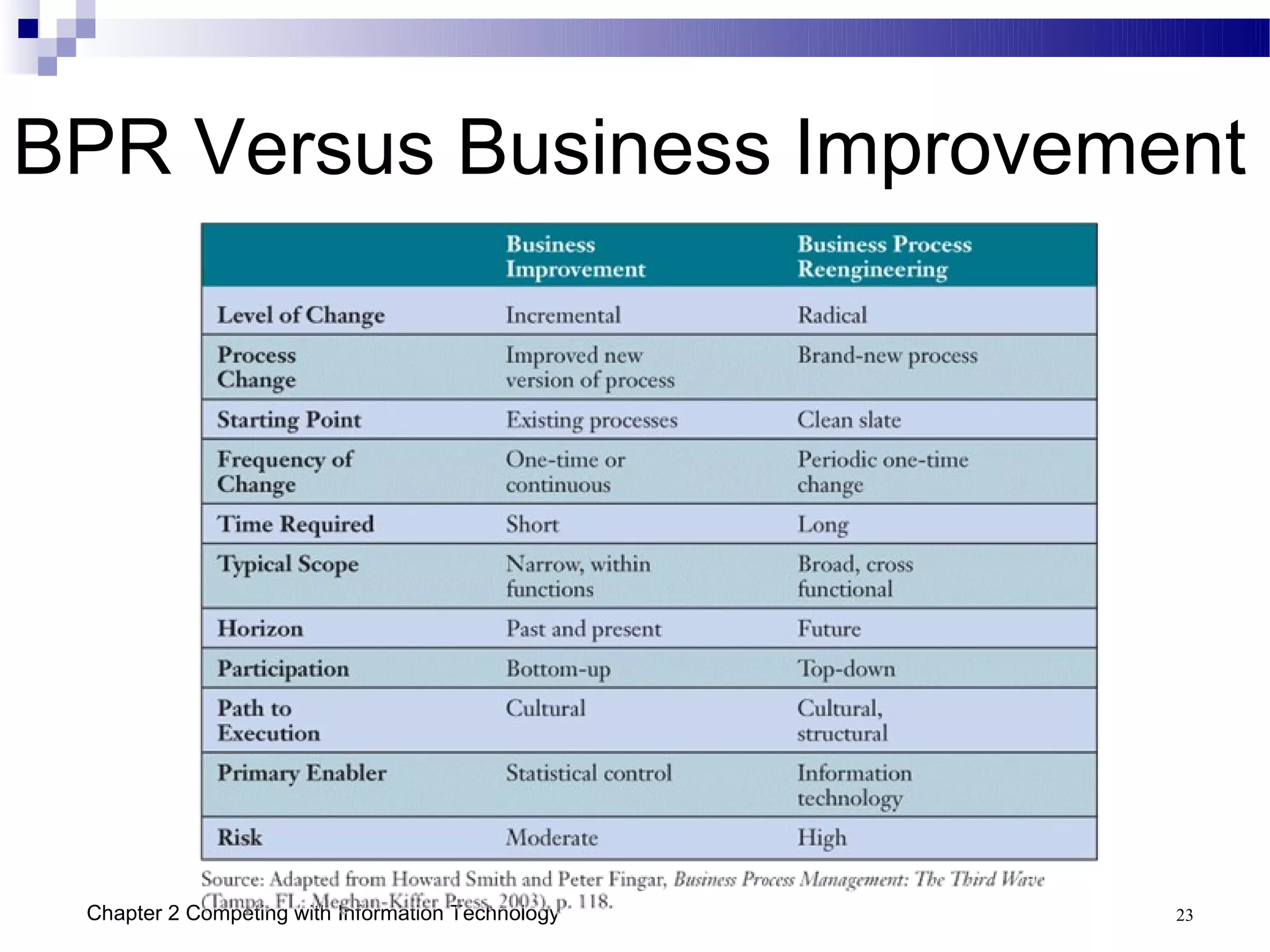
This chapter discusses how businesses can use information technology to gain competitive advantages. It identifies five main competitive strategies - cost leadership, differentiation, innovation, growth, and alliance. IT can be leveraged in various ways to implement these strategies such as improving business processes, building customer relationships, creating agile and virtual organizations, and managing organizational knowledge. Several case studies are presented that demonstrate how companies have successfully used IT for strategic purposes such as GE, Dell, and the US Department of Commerce.