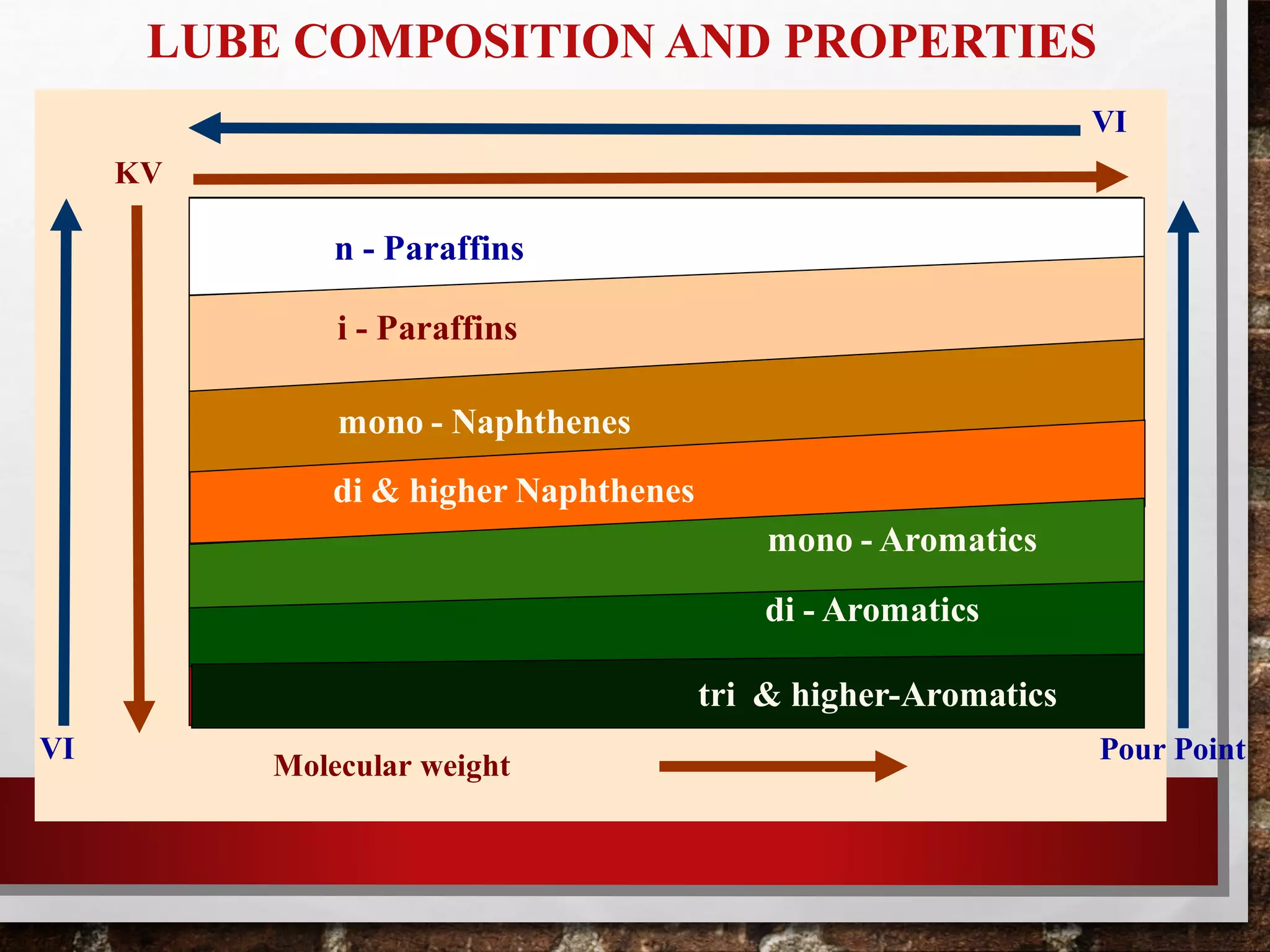
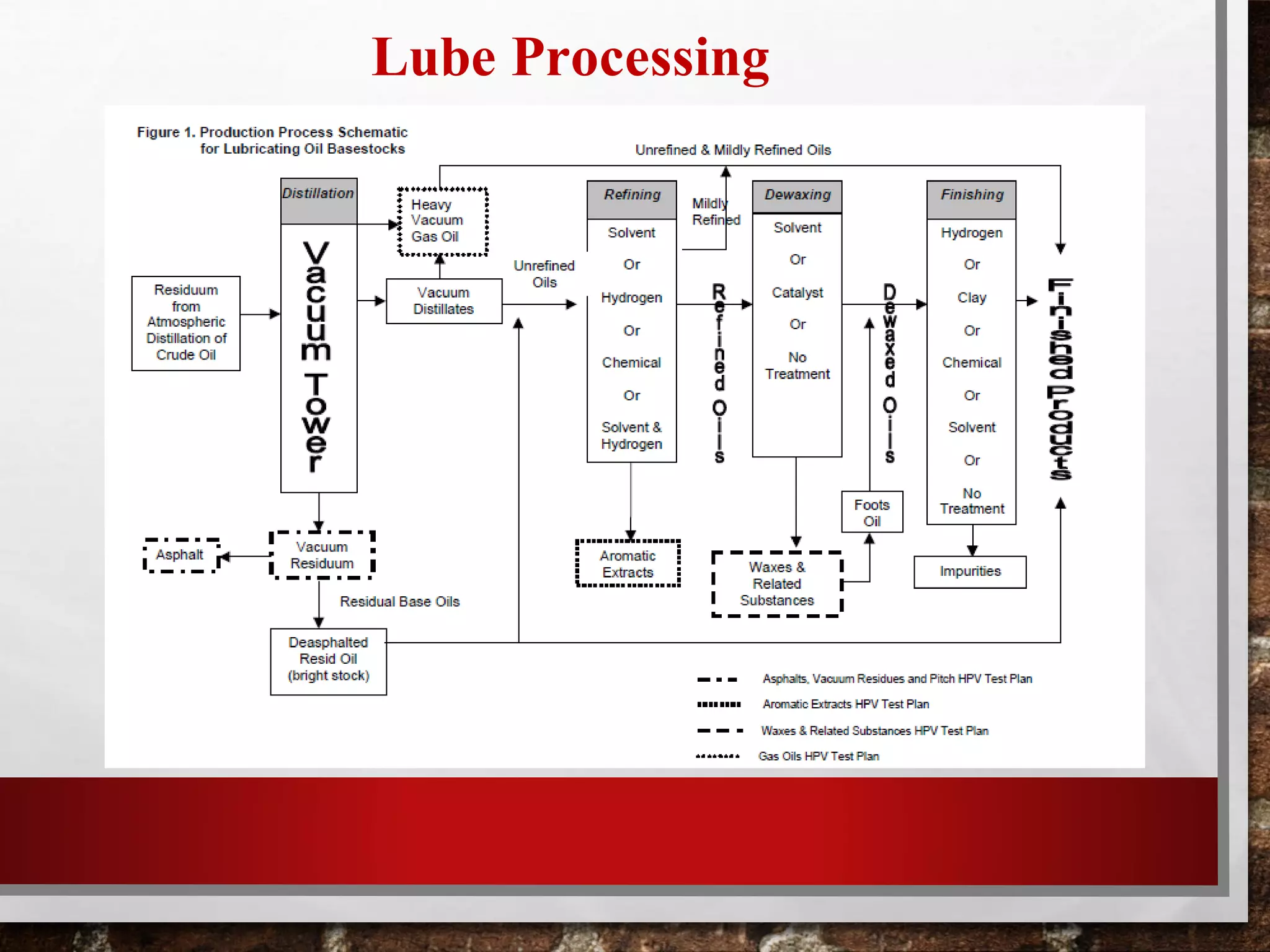
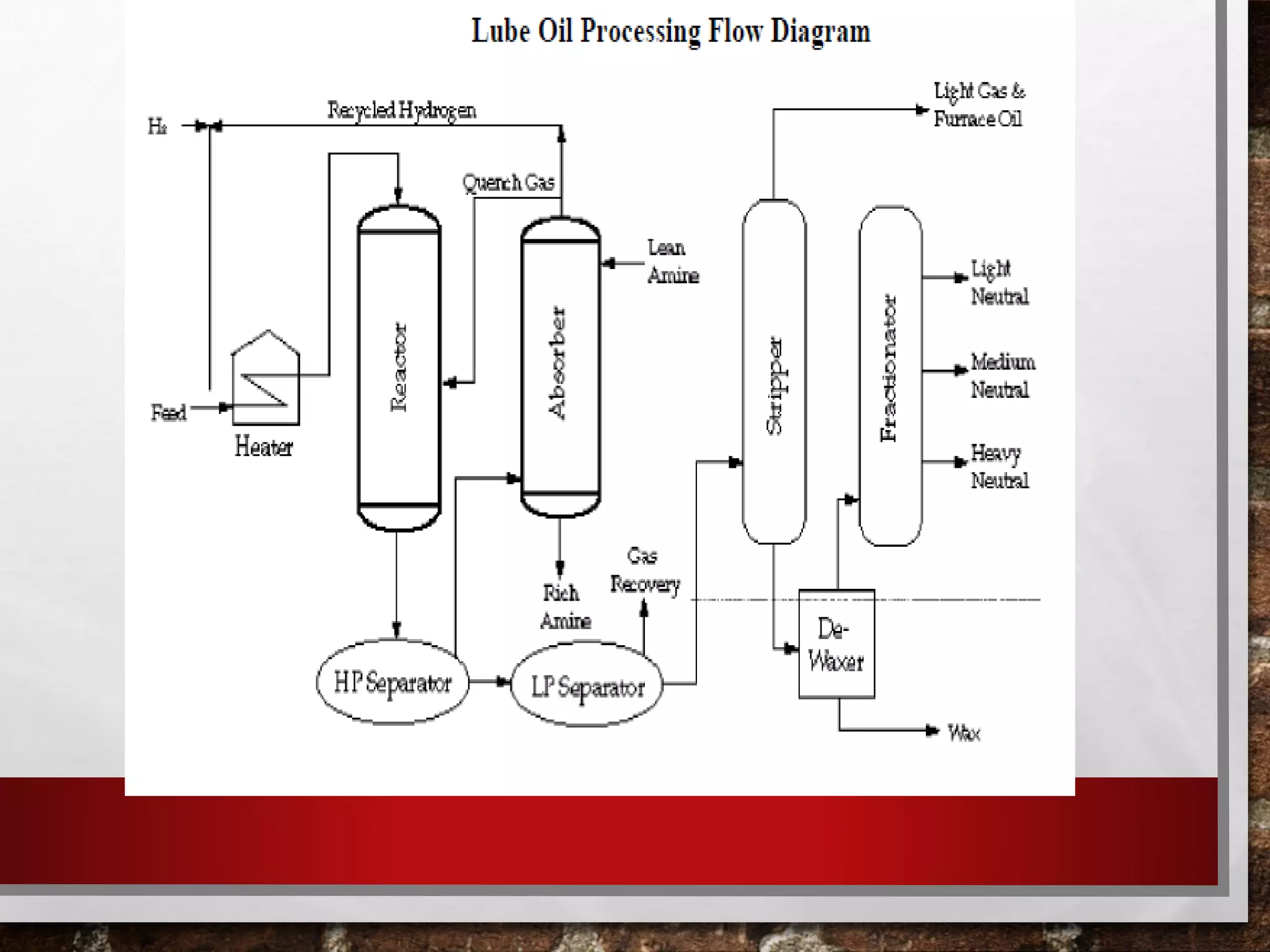
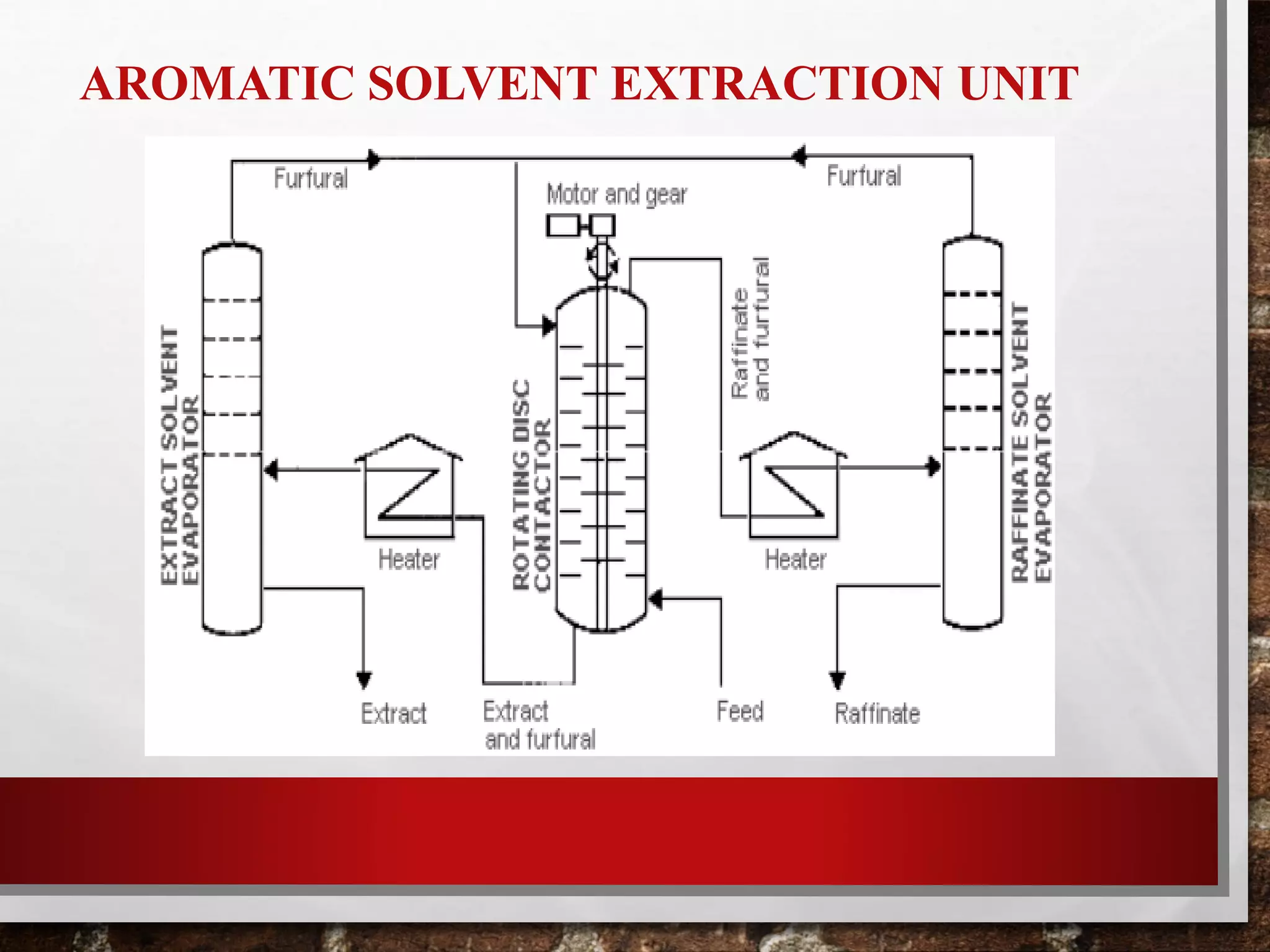
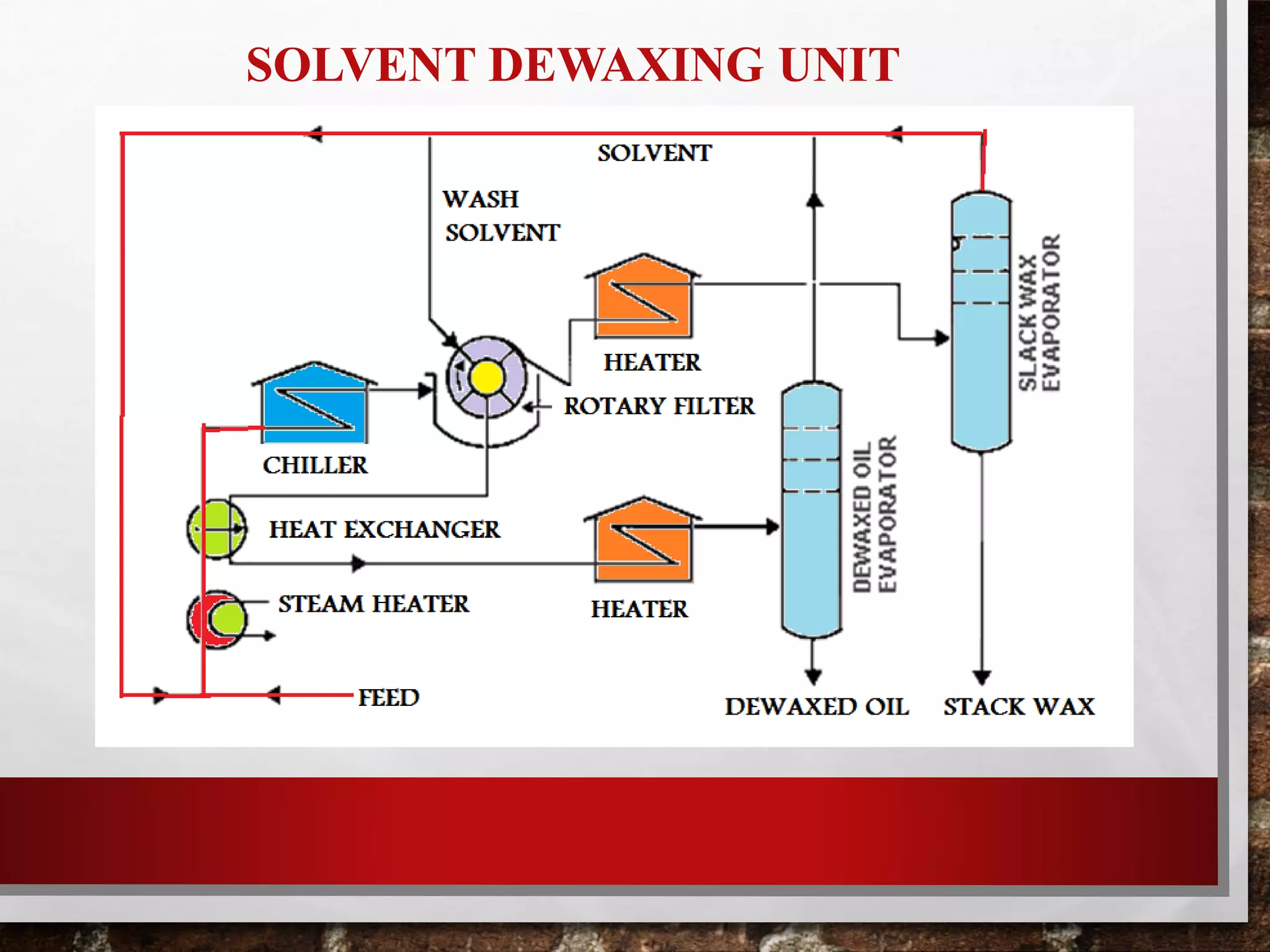
Heavy oil processing involves upgrading heavy crude oils and residues through various refining processes. Heavy oils are found globally and will be an increasingly important source of crude supply. They are more viscous, contain higher concentrations of contaminants, and are more difficult and costly to produce and refine than conventional oils. Key upgrading processes include solvent deasphalting to separate heavy fractions, various hydrotreating methods to remove contaminants, and lube oil processing steps like solvent extraction, dewaxing, and hydrofinishing to produce base oils and fuels from heavy feedstocks.