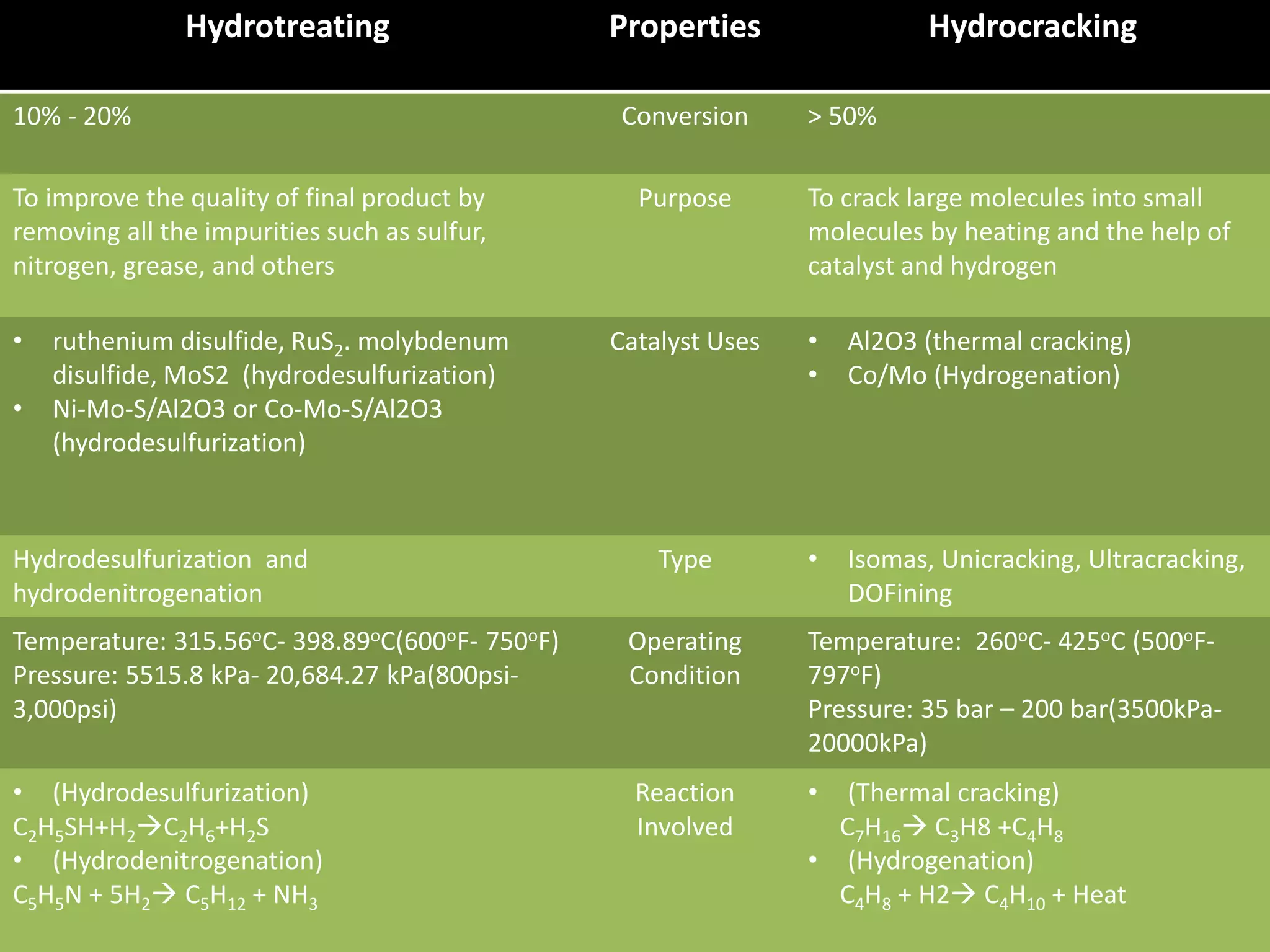
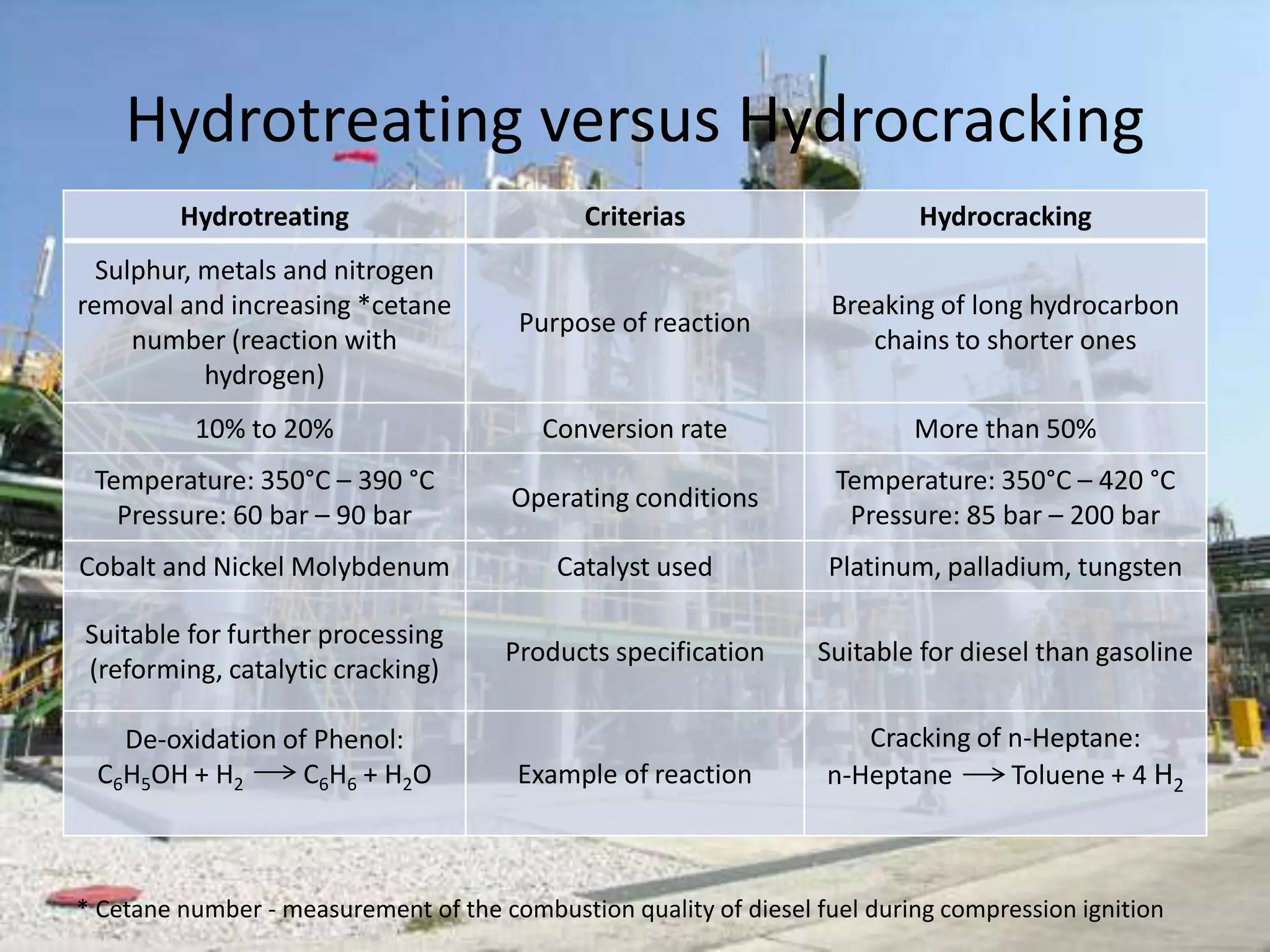
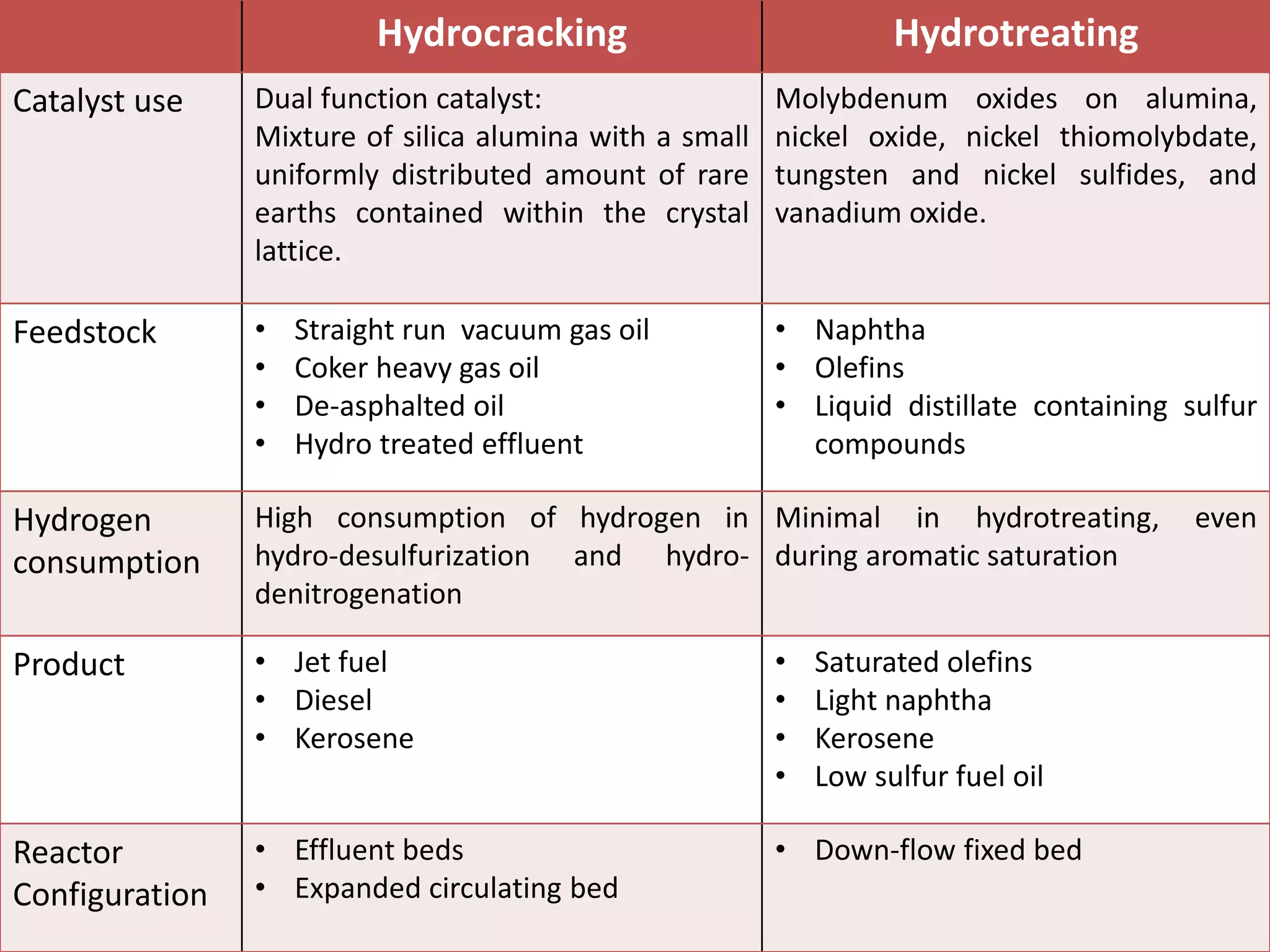
Hydrotreating and hydrocracking are refinery processes that use hydrogen and catalysts. Hydrotreating primarily removes sulfur, nitrogen, and other impurities from petroleum feeds using catalysts like nickel and molybdenum. Its purpose is to improve final product quality. Hydrocracking breaks longer hydrocarbon chains into shorter molecules using platinum or palladium catalysts. It has a higher conversion rate of over 50% compared to 10-20% for hydrotreating. Both processes operate at high temperatures and pressures but hydrocracking conditions are more severe.