1. Networks allow for sharing of resources like files, printers, and applications between connected computers. This provides benefits like cost savings, centralized management, and increased productivity over standalone computers.
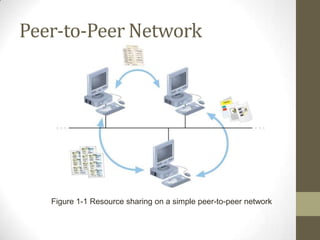
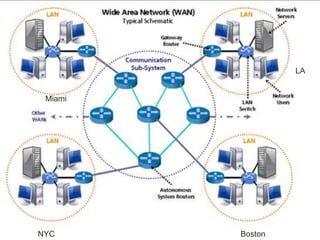
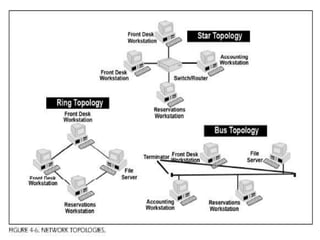
2. Common network topologies include peer-to-peer, client-server, bus, star, and ring. Larger networks often use a hybrid approach to balance reliability, capacity, and costs.
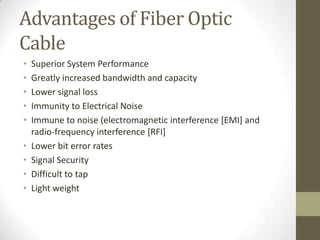
3. Key network components include physical media like cables, wireless cards, and fiber optics. Logical components include servers, clients, switches, and routers that facilitate communication and sharing across the network.