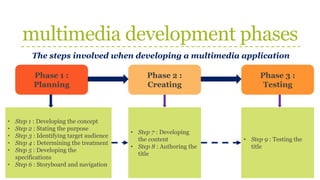
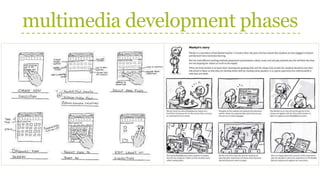
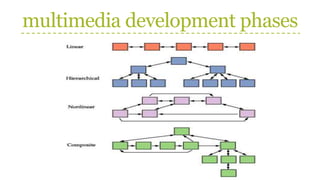
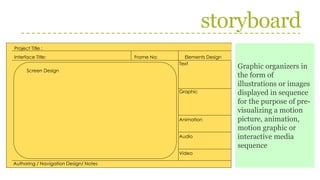
This document discusses the phases of multimedia development and production team roles. It describes 9 phases of multimedia development: 1) Planning, 2) Creating, and 3) Testing. Each phase involves several steps such as developing the concept, stating the purpose, identifying the audience, determining design, developing specifications, storyboarding, creating content, authoring, and testing. It also outlines the roles of team members like project managers, designers, writers, programmers, and producers. Storyboarding is used to represent screen designs and navigation links.