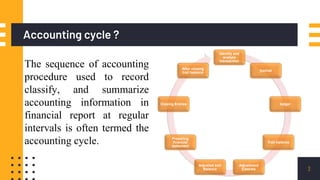
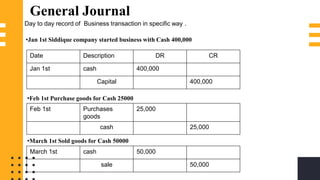
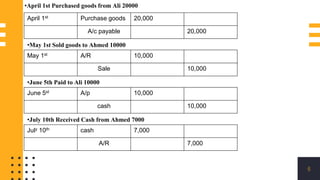
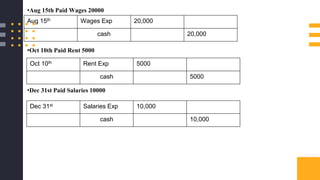
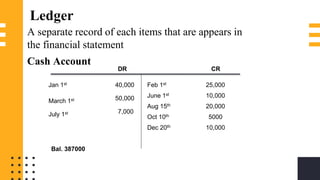
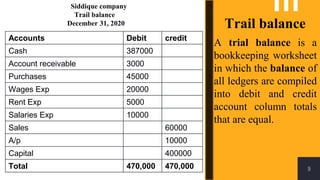
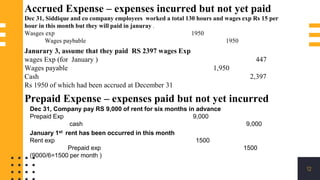
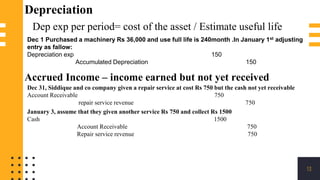
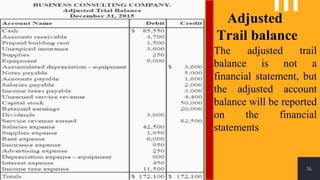
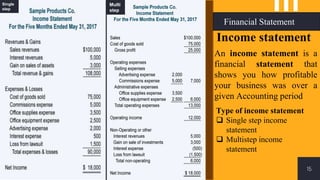
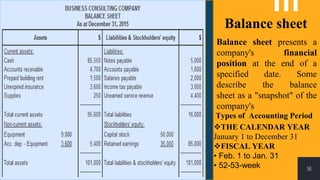
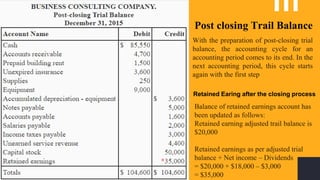
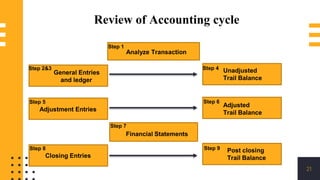
The accounting cycle involves a series of steps to record business transactions and prepare financial statements. The steps include: 1) identifying and recording transactions in a general journal, 2) posting transactions to ledger accounts, 3) preparing an unadjusted trial balance, 4) making adjusting entries for accruals, prepayments, and depreciation, 5) preparing an adjusted trial balance, 6) making closing entries to clear revenue and expense accounts, 7) preparing a post-closing trial balance, and 8) using the adjusted accounts to prepare financial statements such as an income statement and balance sheet. The accounting cycle ensures transactions are properly recorded and financial statements accurately reflect the company's performance and financial position.