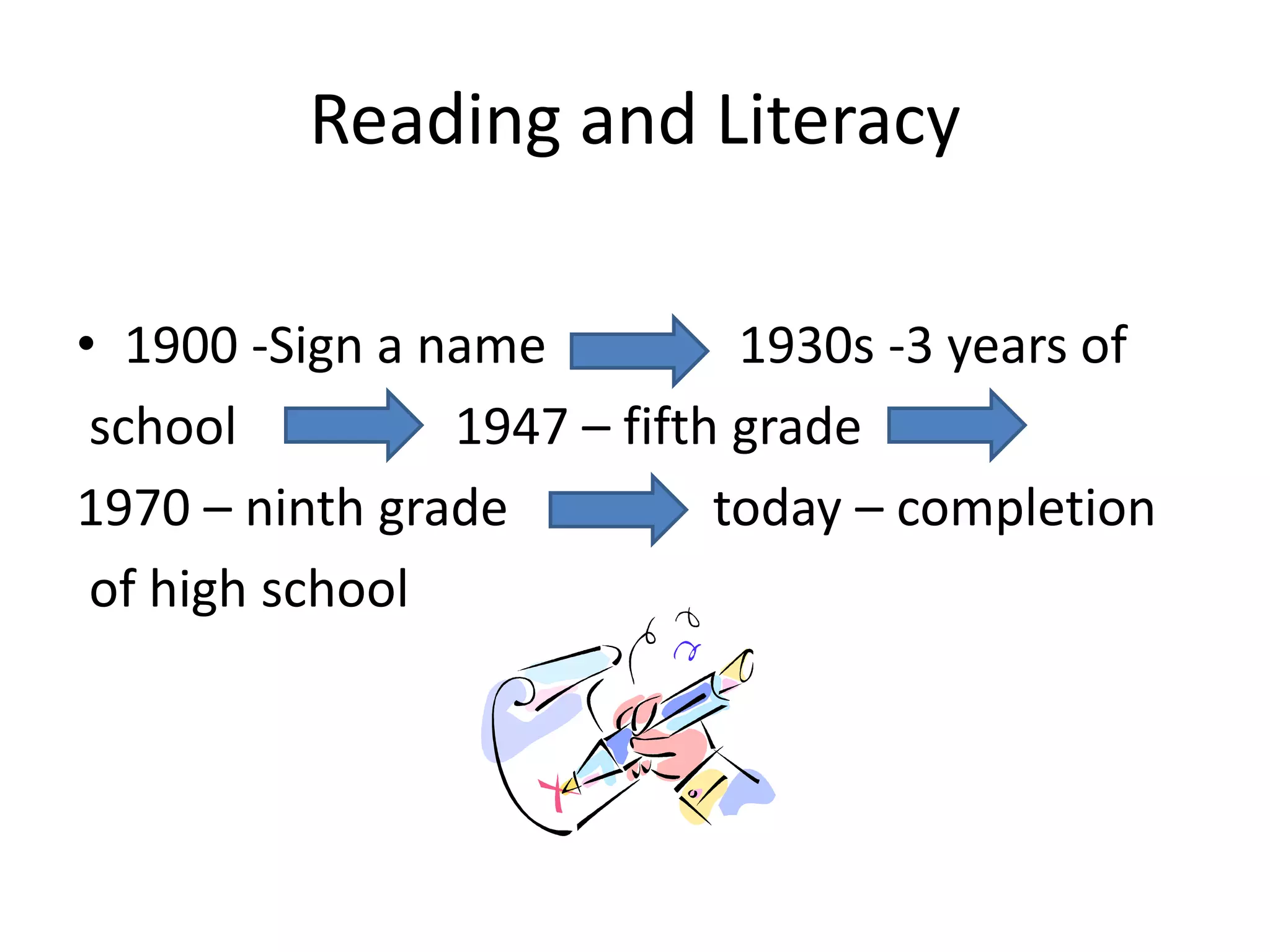
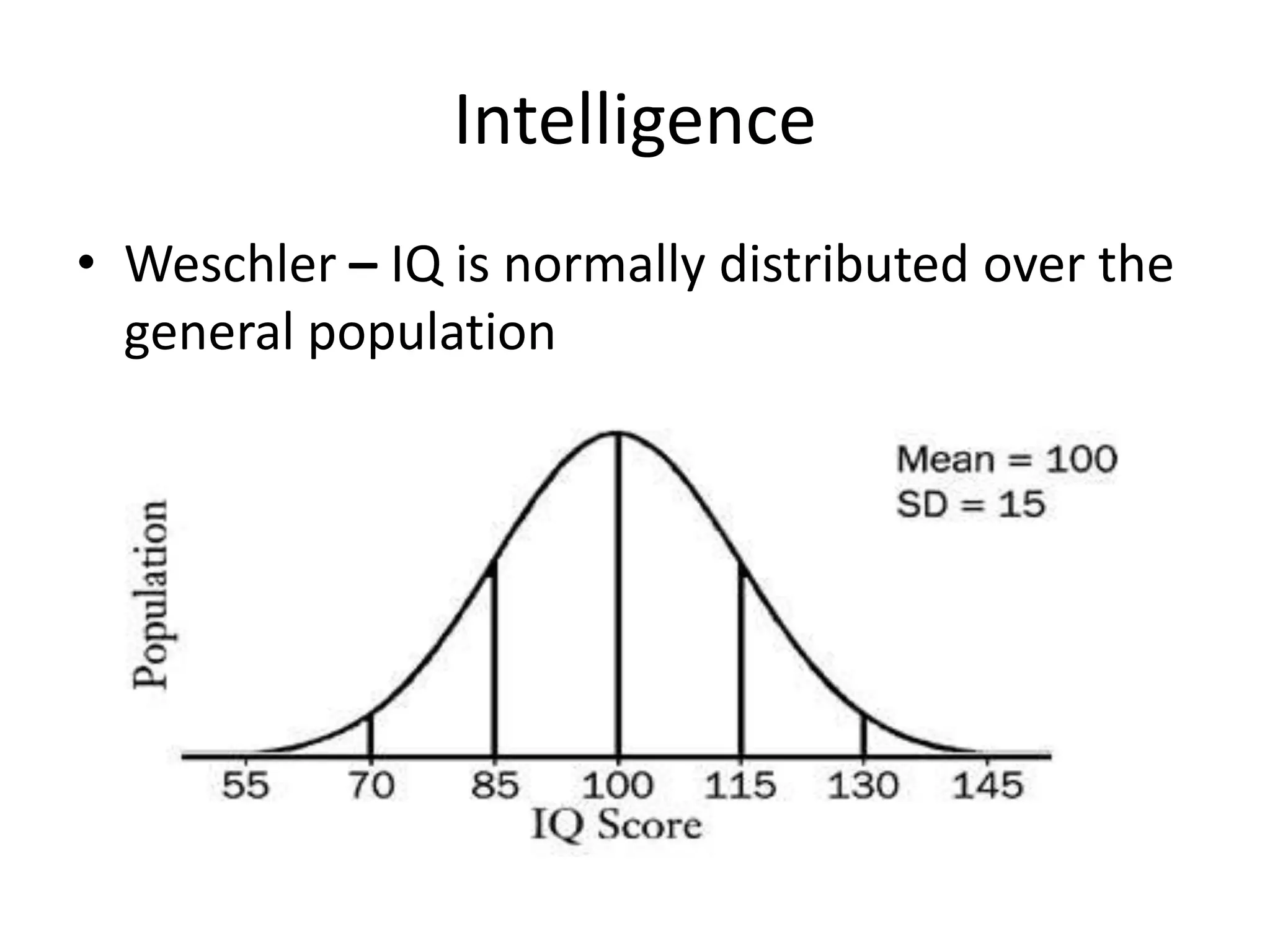
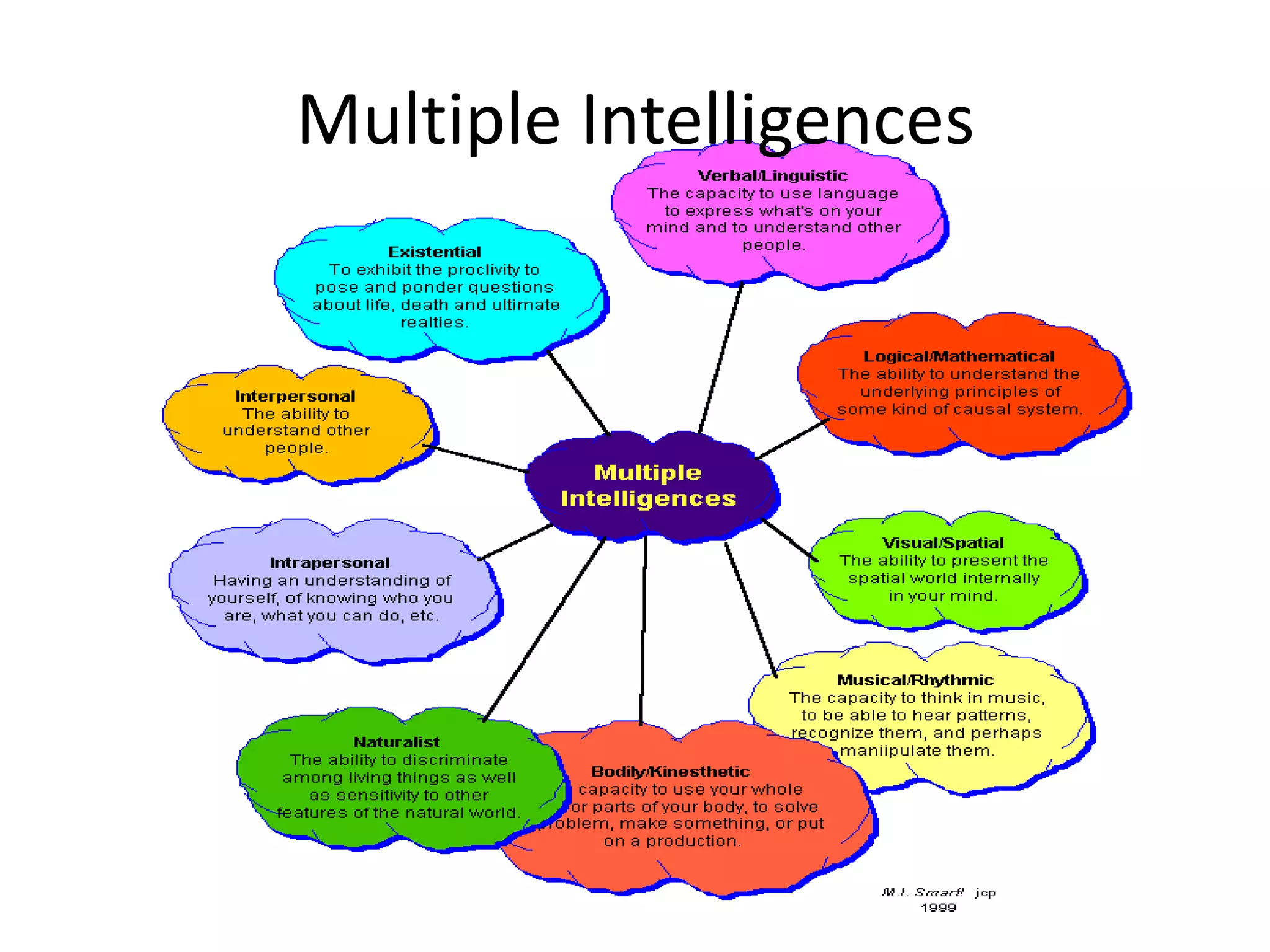
This document discusses various aspects of student diversity that teachers may encounter, including cultural background, ethnicity, race, religion, gender, socioeconomic status, language proficiency, and exceptionalities. It addresses the differences between culture, ethnicity, and race, and warns against stereotyping while acknowledging cultural characteristics. The document also notes controversies around teaching English language learners and issues relating to bilingual education versus pull-out programs. It discusses intelligence and learning disabilities as well as Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences.