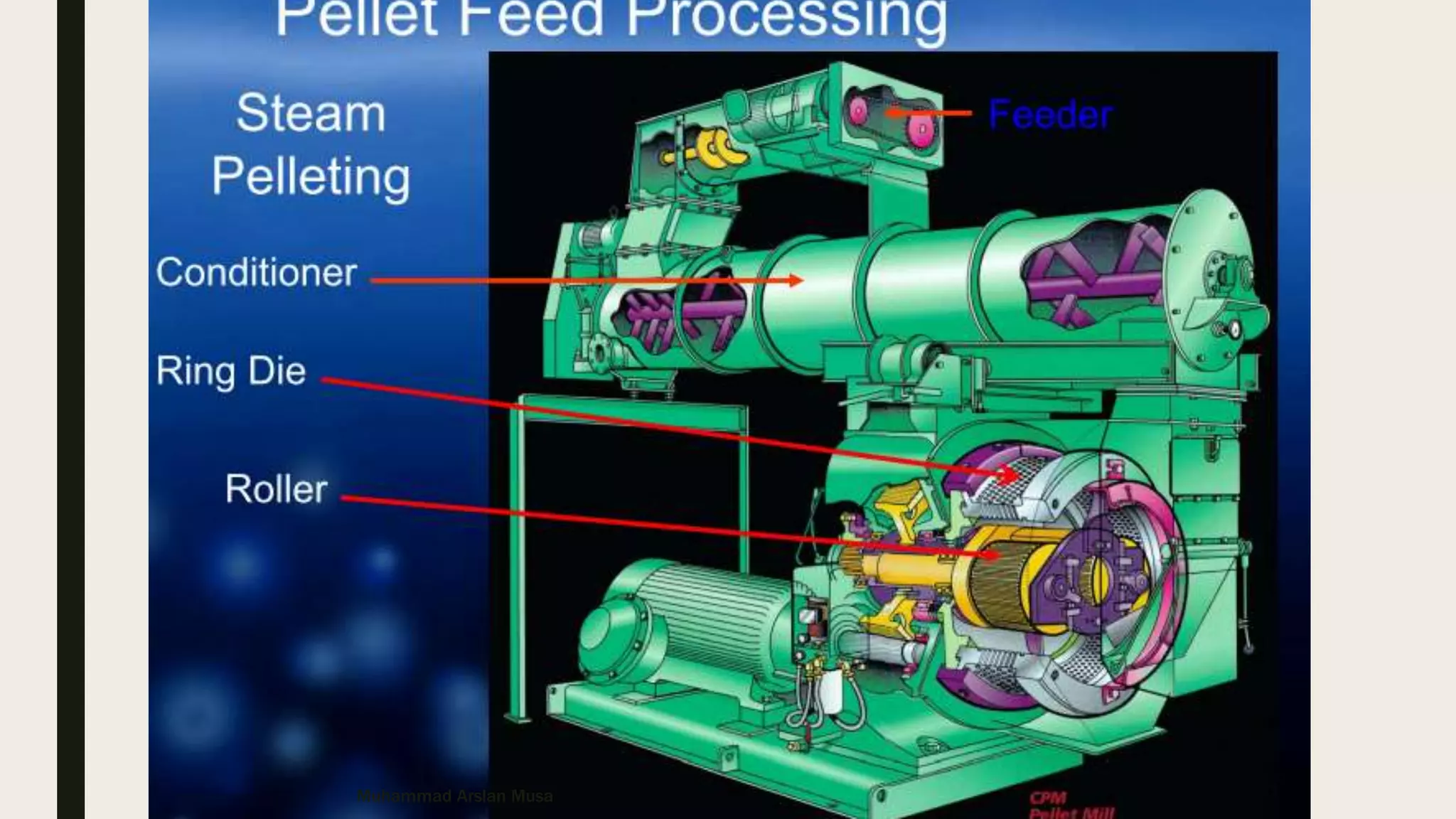
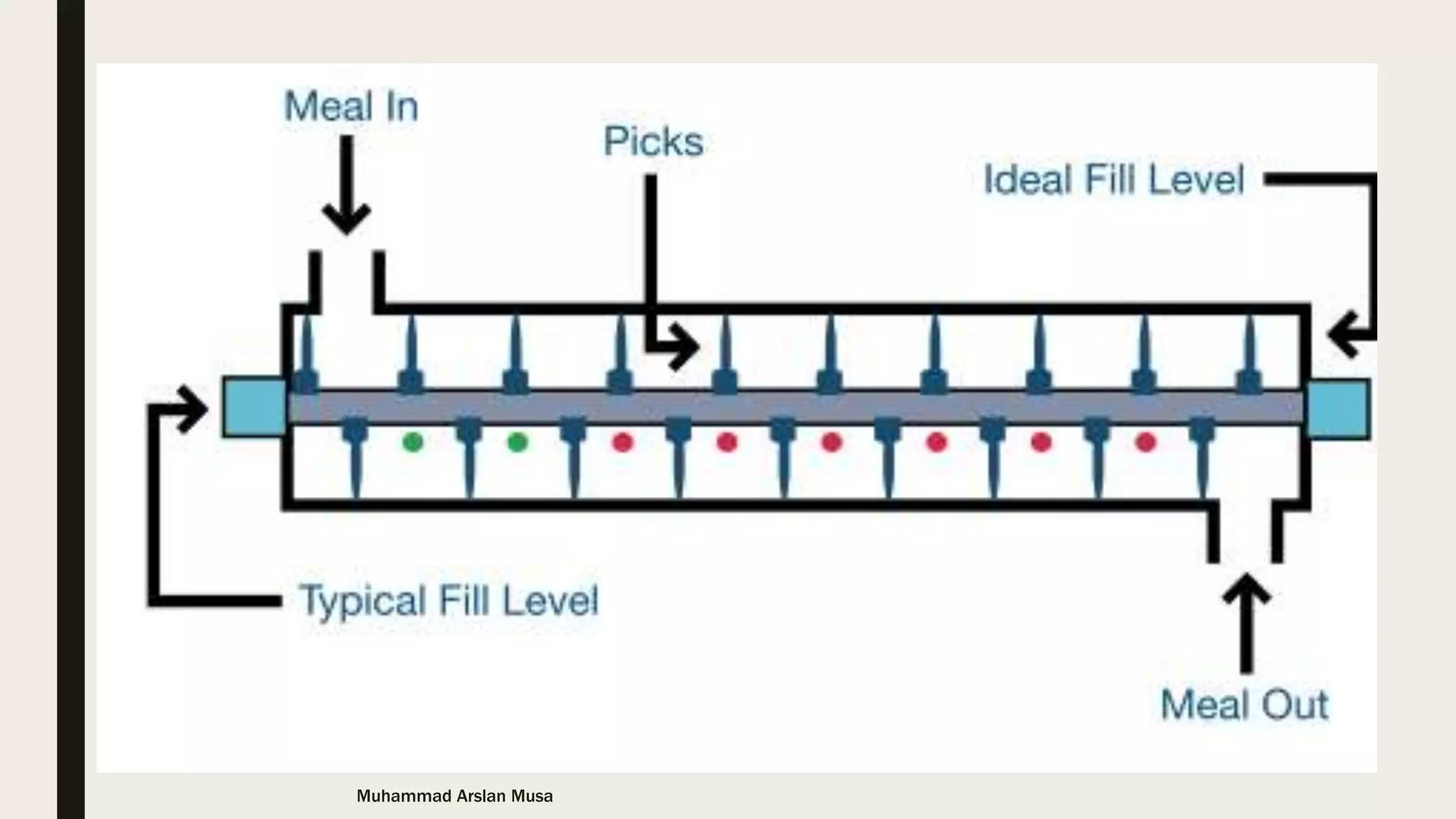
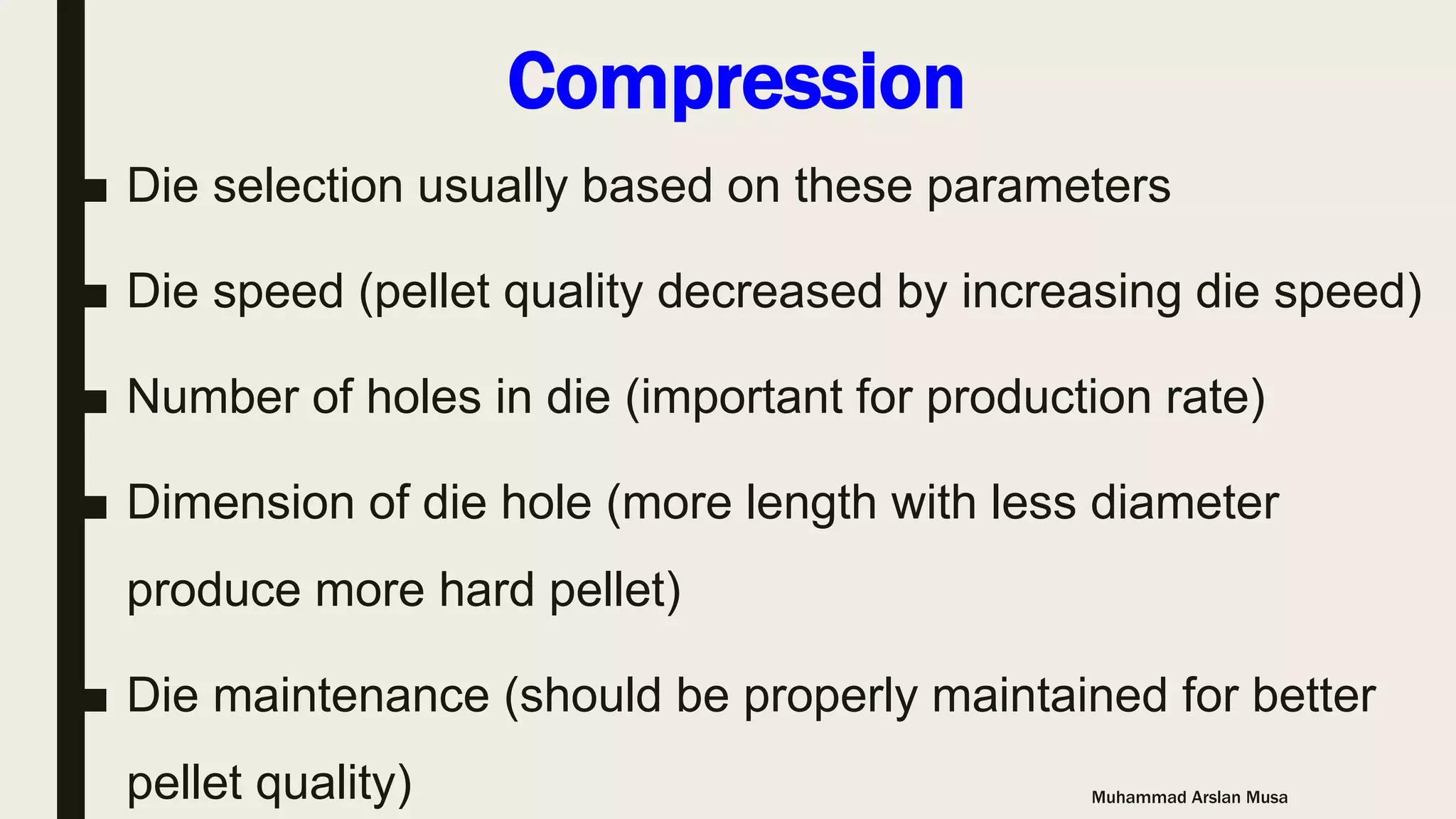
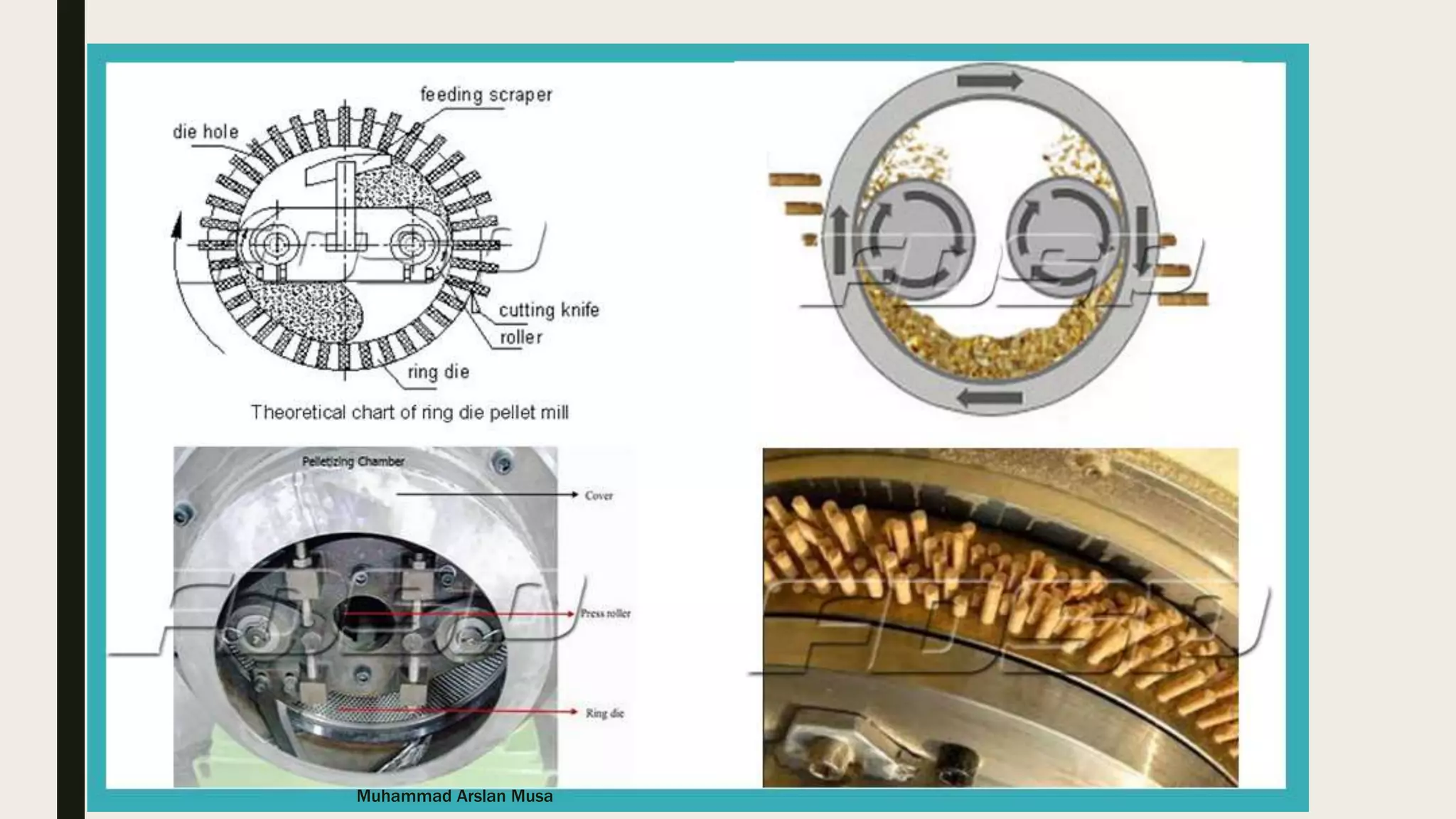
The document discusses the basics of pelleting feed, including the advantages of pelleting such as minimizing feed waste and increasing nutrient availability. The pelleting process involves three main steps: conditioning to add heat and moisture using steam; compression using a die to form pellets; and cooling to remove added moisture and heat from the pellets. Key factors that affect each step like temperature and retention time are outlined.