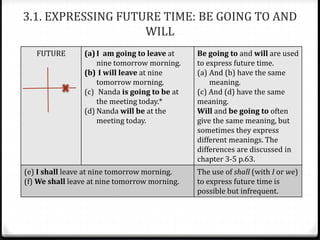
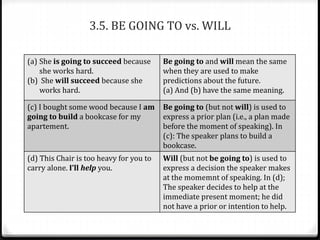
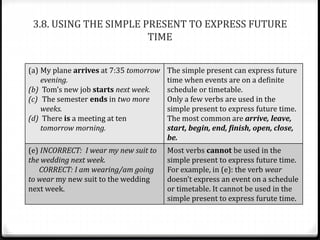
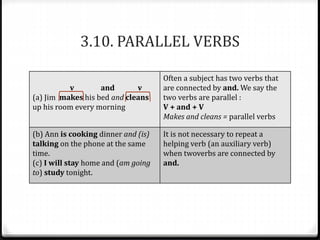
This document discusses various ways to express future time in English, including using "be going to", "will", simple present tense, present progressive tense, and other constructions. It provides examples of each structure and notes the differences between them in terms of certainty, prior plans, or events on a schedule. Key points include: "be going to" expresses prior plans while "will" expresses decisions made at the moment; simple present can indicate future events on a schedule; present progressive can describe future plans already made; and structures like "be about to" or conditionals refer to the immediate future.