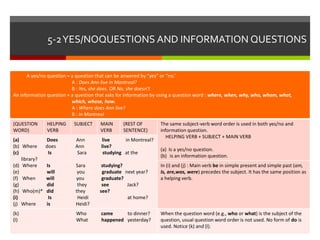
This document discusses different types of questions in English, including yes/no questions, information questions using question words, and question structures using "what", "which", "whose", "how", "how often", "how far", "how long", and "how about". It provides examples of questions and answers for each question type, covering proper word order, contractions, and other grammatical rules for forming questions in English.