1. The document discusses the simple present and present progressive tenses in English. It provides examples of how each is used and explains the differences between them.
2. The simple present is used to describe habitual or repeated actions, general truths, and schedules. It uses the base form of the verb. The present progressive expresses an action that is ongoing or in progress at the time of speaking. It uses the verb "be" plus the "-ing" form of the main verb.
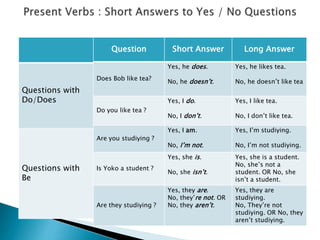
3. The document also covers frequency adverbs, subject-verb agreement, regular and irregular verbs, short answers, and non-action verbs in the simple present and present progressive tenses.