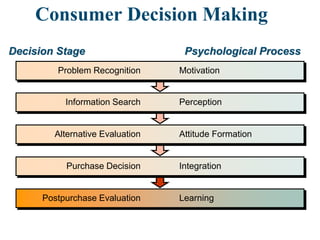
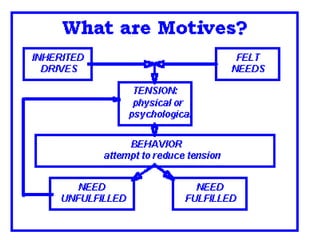
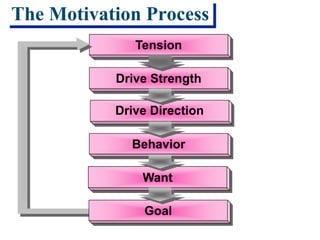
This document discusses consumer motivation and the consumer decision making process. It defines motivation as the internal process that drives consumers to achieve goals. The motivation process involves a need or tension that the consumer wants to resolve. Marketers aim to understand consumers' manifest and latent motivations in order to develop products that satisfy those needs. The summary examines different theories of motivation and how understanding motivation can help guide marketing strategy.