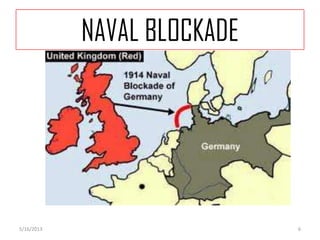
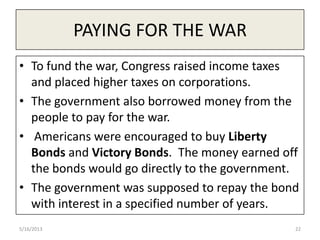
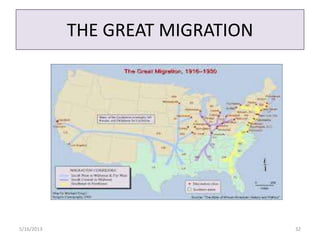
The document provides information on several key events that led the United States to enter World War 1, including the naval blockade by Britain cutting off supplies to Germany, Germany sinking passenger ships like the Lusitania without warning which killed Americans, and the intercepted Zimmerman Telegram proposing a German alliance with Mexico against the U.S. After declaring war in 1917, the U.S. mobilized its economy and workforce through agencies that rationed food, fuel, and materials for the war effort. Hundreds of thousands of African Americans migrated north for new industrial jobs during this period known as the Great Migration.