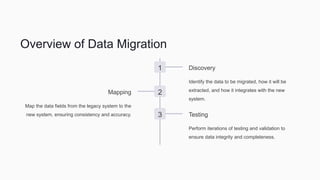
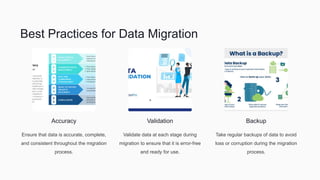
As businesses adopt ERP systems, integration and data migration are critical processes, facing challenges like data inconsistencies, process changes, and user acceptance. The document outlines the steps for effective data migration, including discovery, mapping, and testing, as well as best practices for ensuring accuracy and validation. It emphasizes the importance of efficiency, collaboration, and future-proofing in ERP integration to enhance system performance and adaptability.