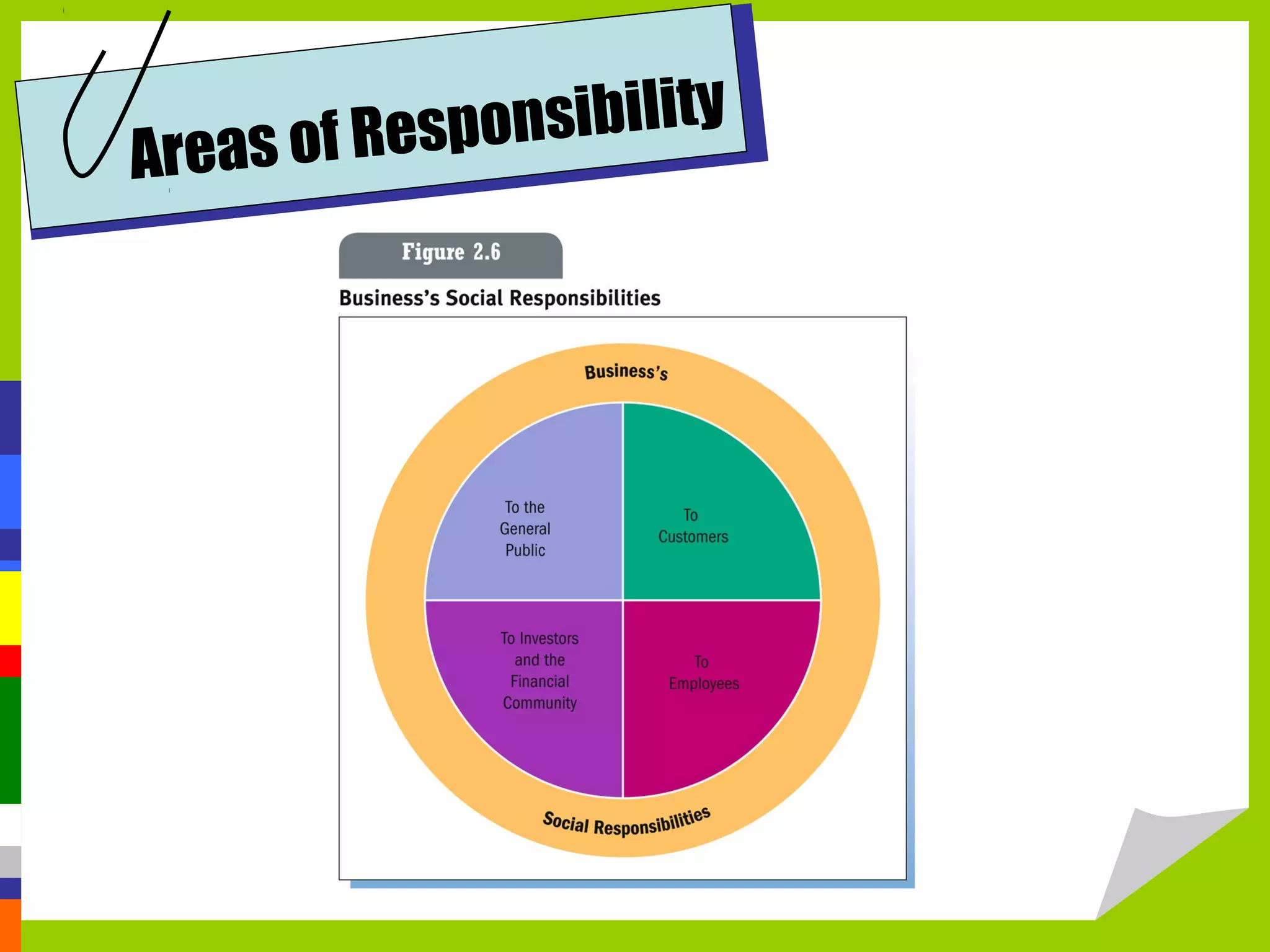
Business ethics refers to the standards of conduct and moral values that govern decisions made in a business environment. There is often a balance required between what is profitable and what is ethical. Organizations shape ethical conduct through codes of conduct, ethical education and training, and ensuring ethical leadership from executives. Social responsibility involves considering profit, customer satisfaction, and societal well-being equally. Organizations are responsible to the public, customers, employees, and investors through various initiatives and regulations regarding issues like the environment, health and safety, equal opportunity, and transparency.