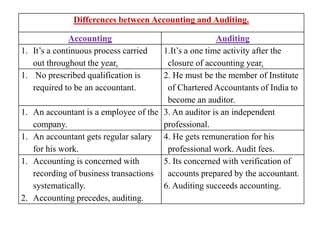
The document outlines the steps and components of an audit program, emphasizing its importance in organizing audit work, providing guidance, and ensuring systematic processes while noting potential disadvantages such as mechanization and reduced creativity. It discusses the significance of maintaining an audit notebook and working papers as evidence of auditing procedures, further detailing their content and ownership issues. Additionally, it contrasts accounting with auditing, highlighting their distinct roles within financial management.