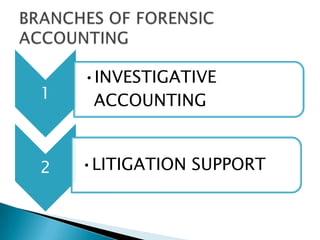
Forensic accounting involves investigating financial crimes and disputes. It includes two main areas: investigative accounting which deals with crimes like theft and fraud, and litigation support which helps quantify economic damages in legal cases. Forensic accountants gather and analyze financial evidence, develop tools to analyze evidence, and communicate their findings through reports and testimony in court. While starting in the US in 1995, forensic accounting is growing in India due to increased fraud and a shortage of qualified professionals. Common areas forensic accountants work include fraud investigation, business disputes, and insurance and personal injury claims.