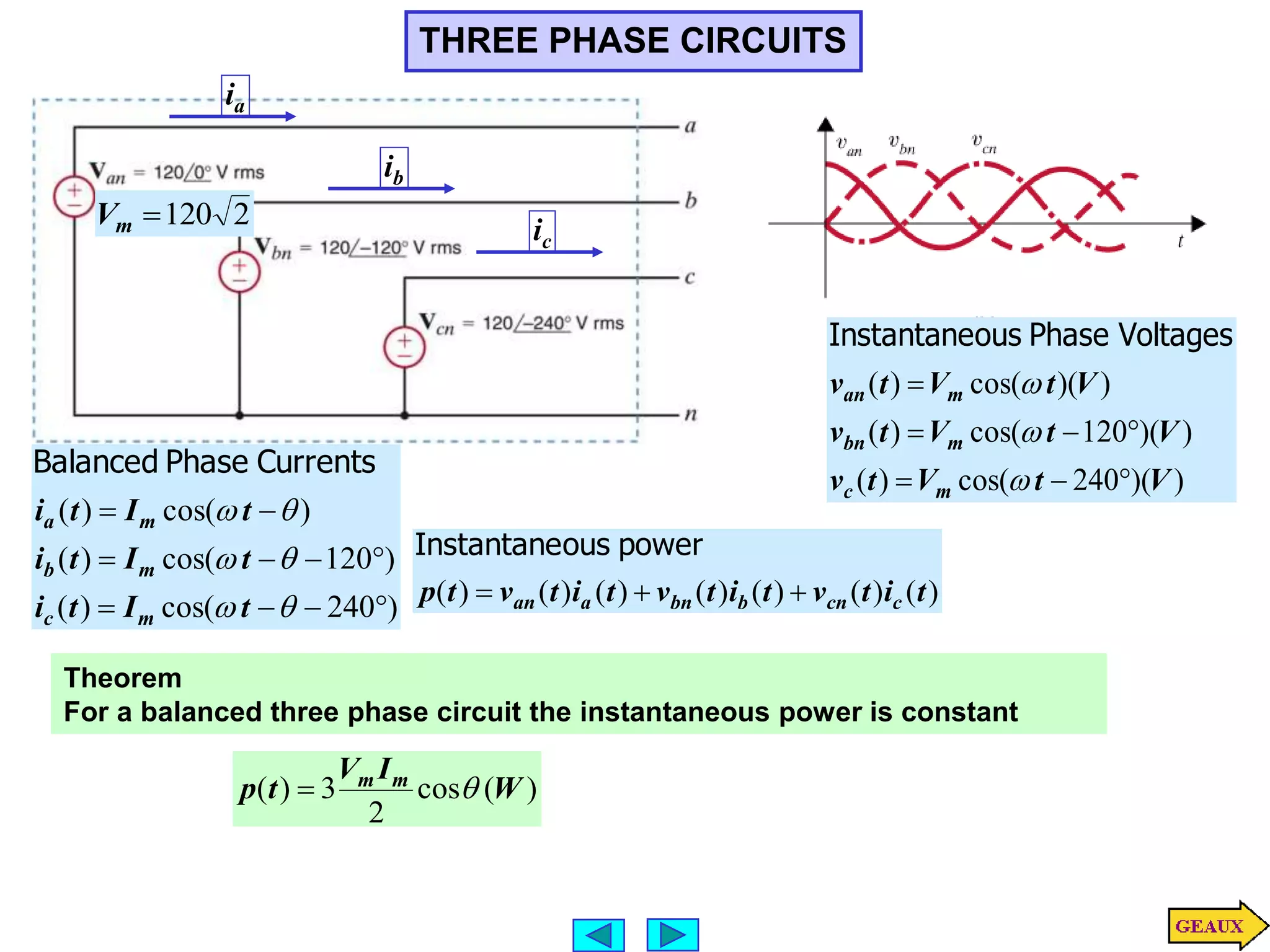
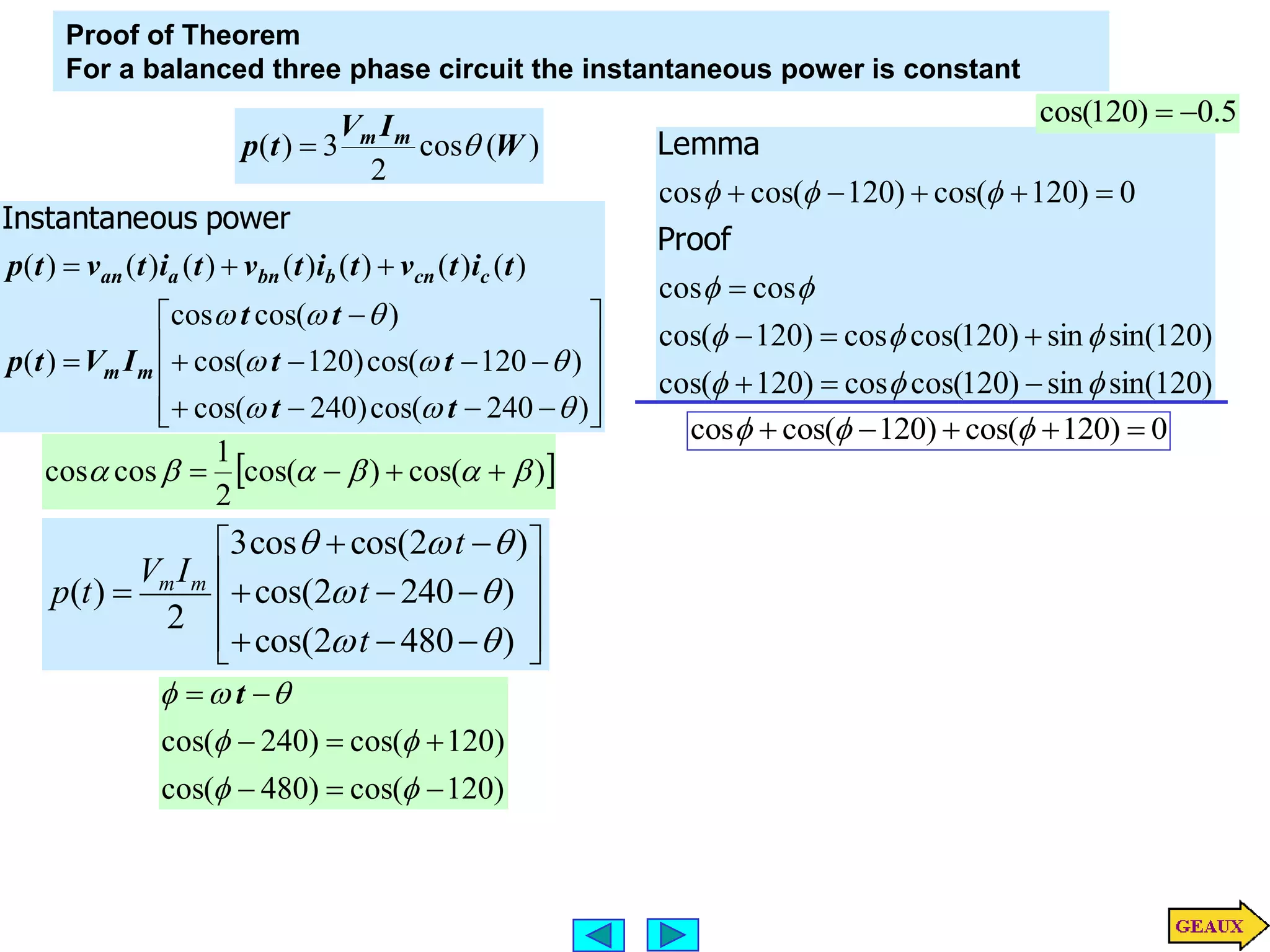
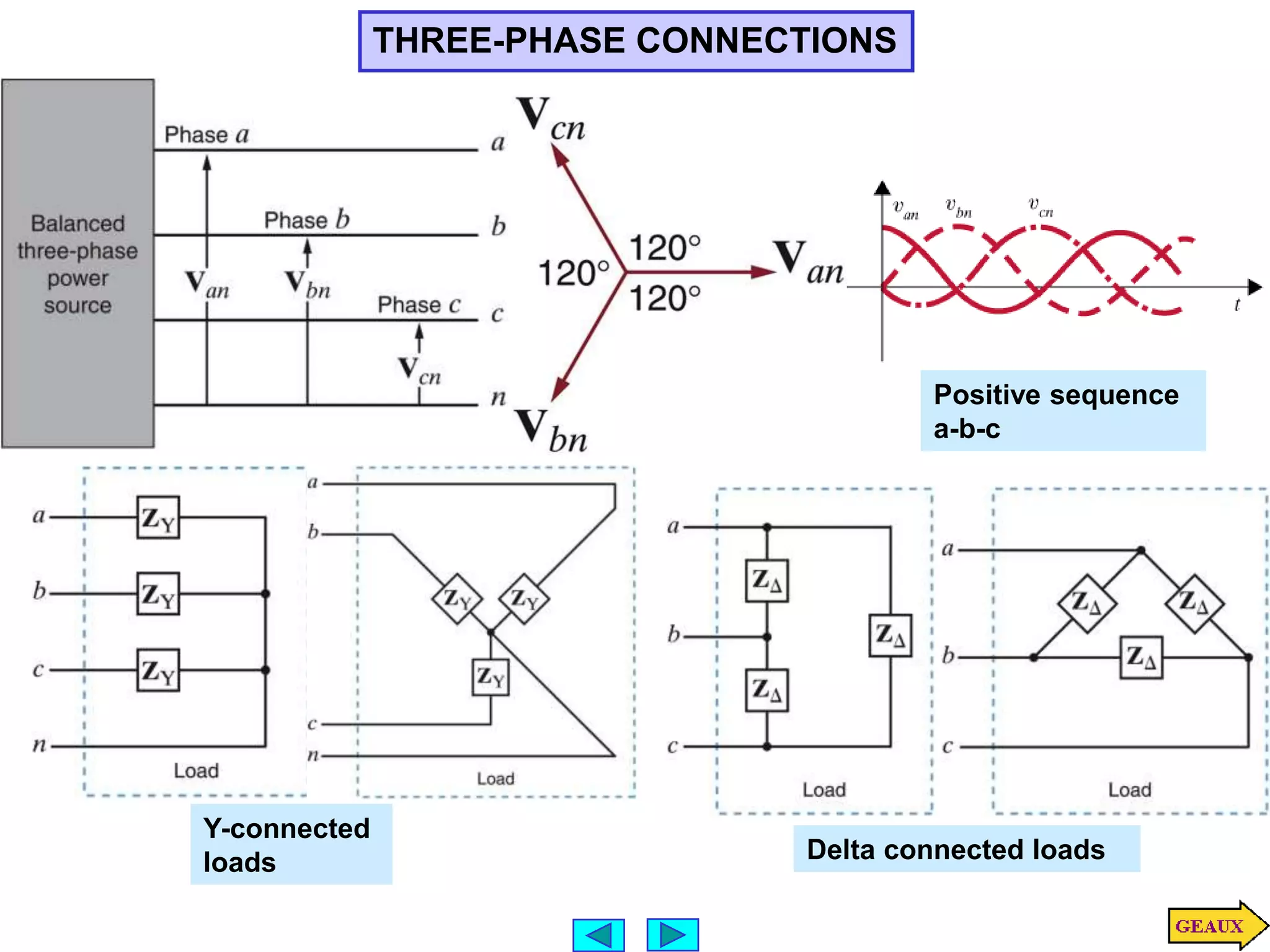
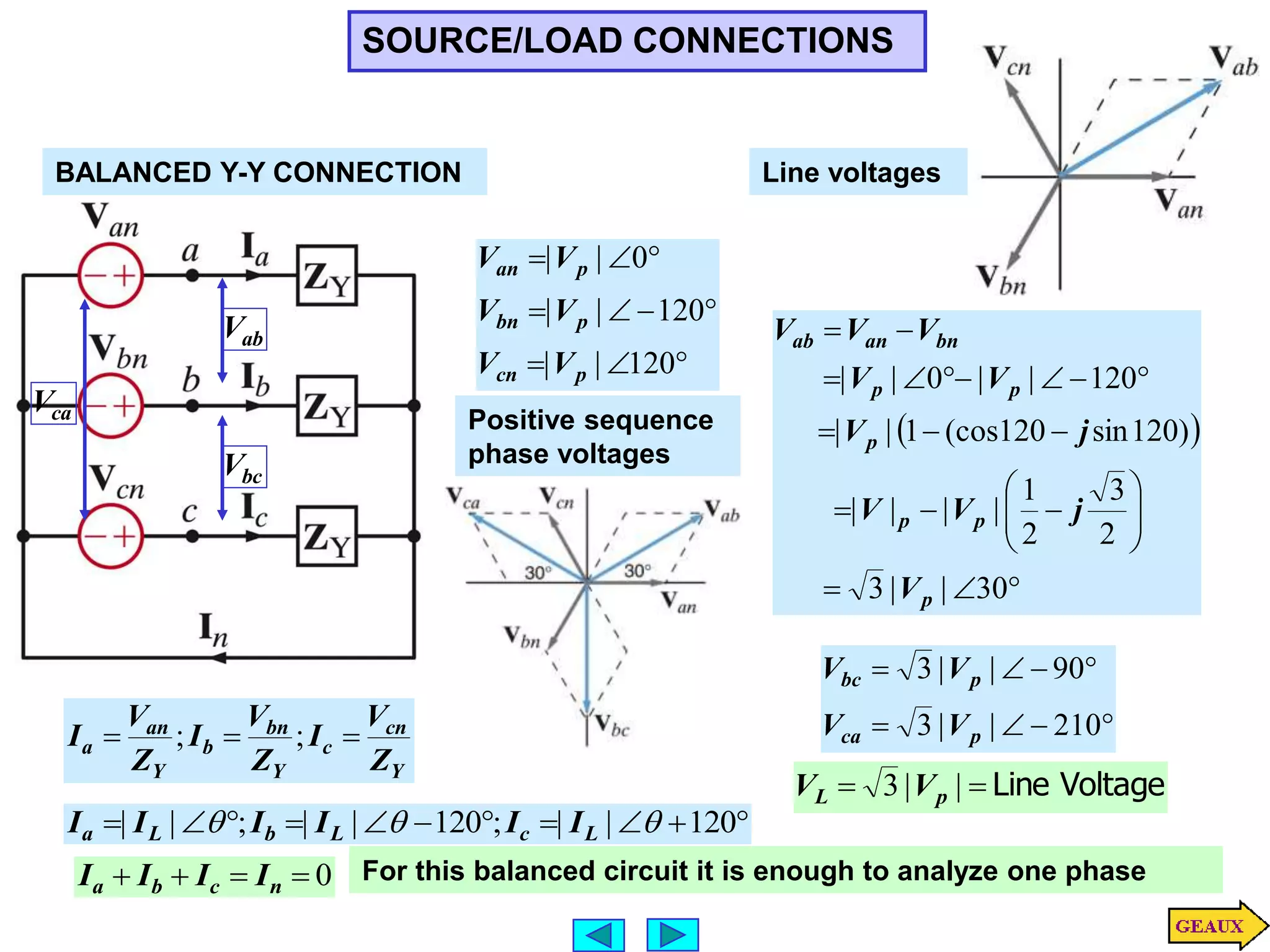
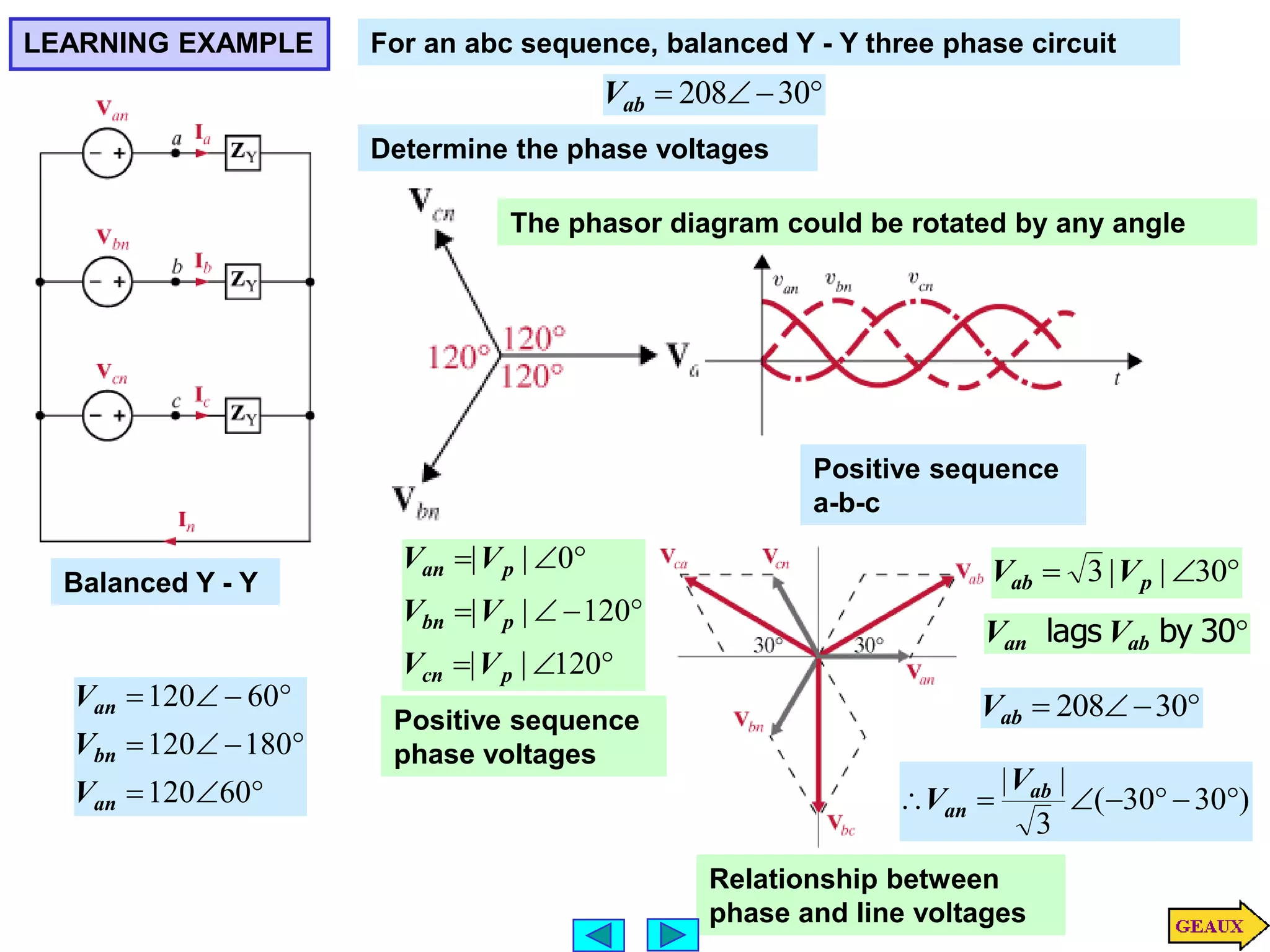
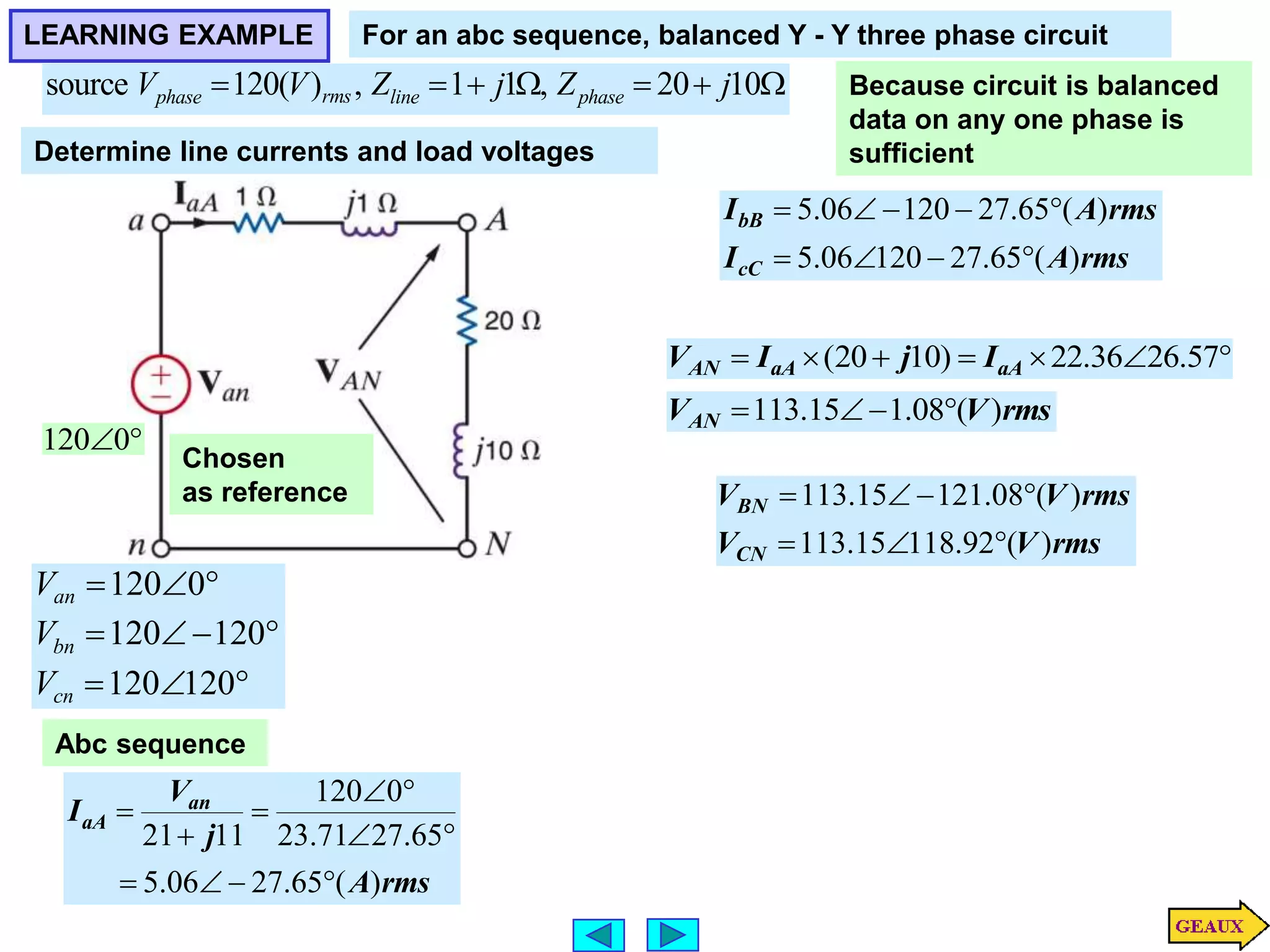
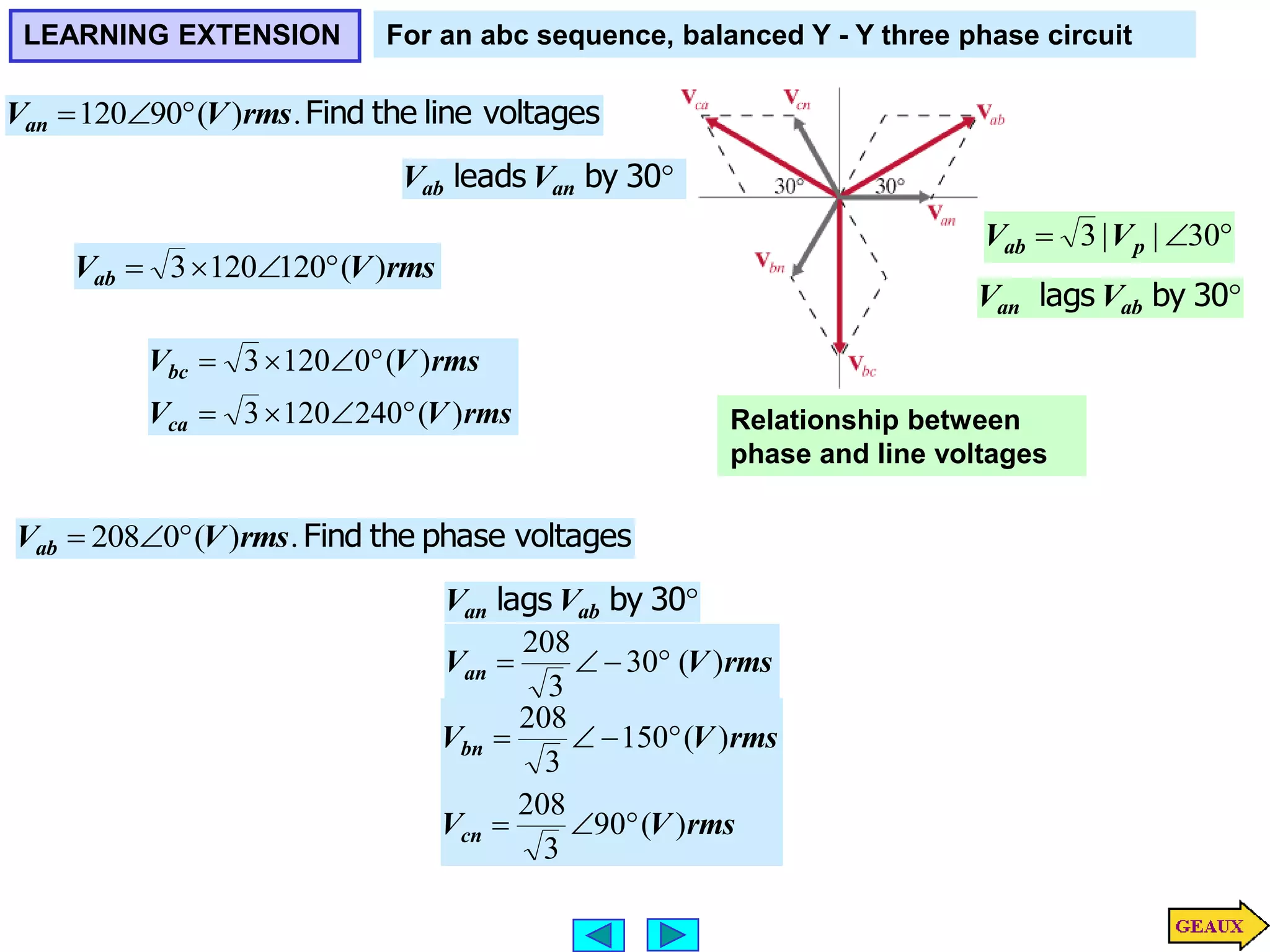
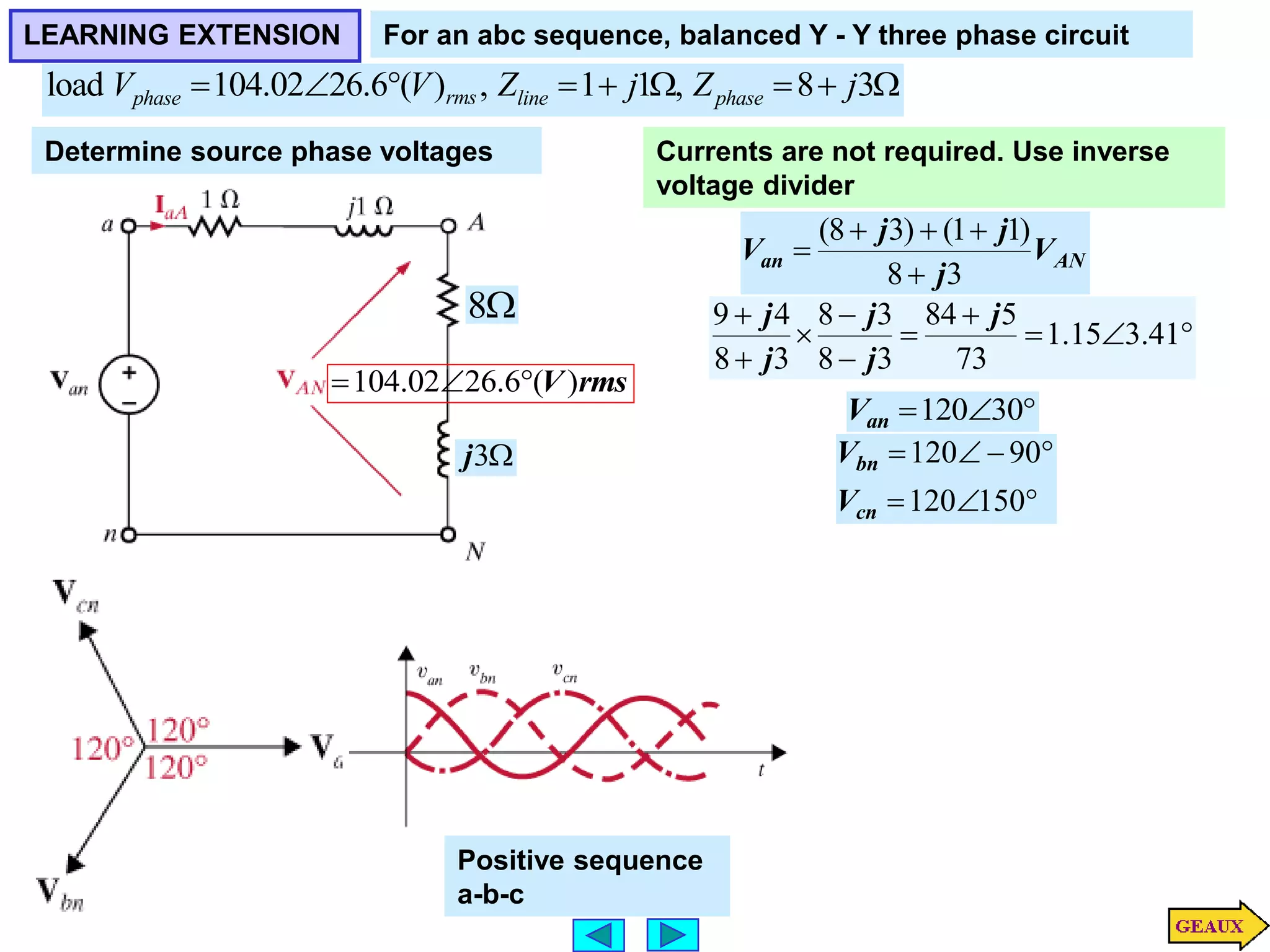
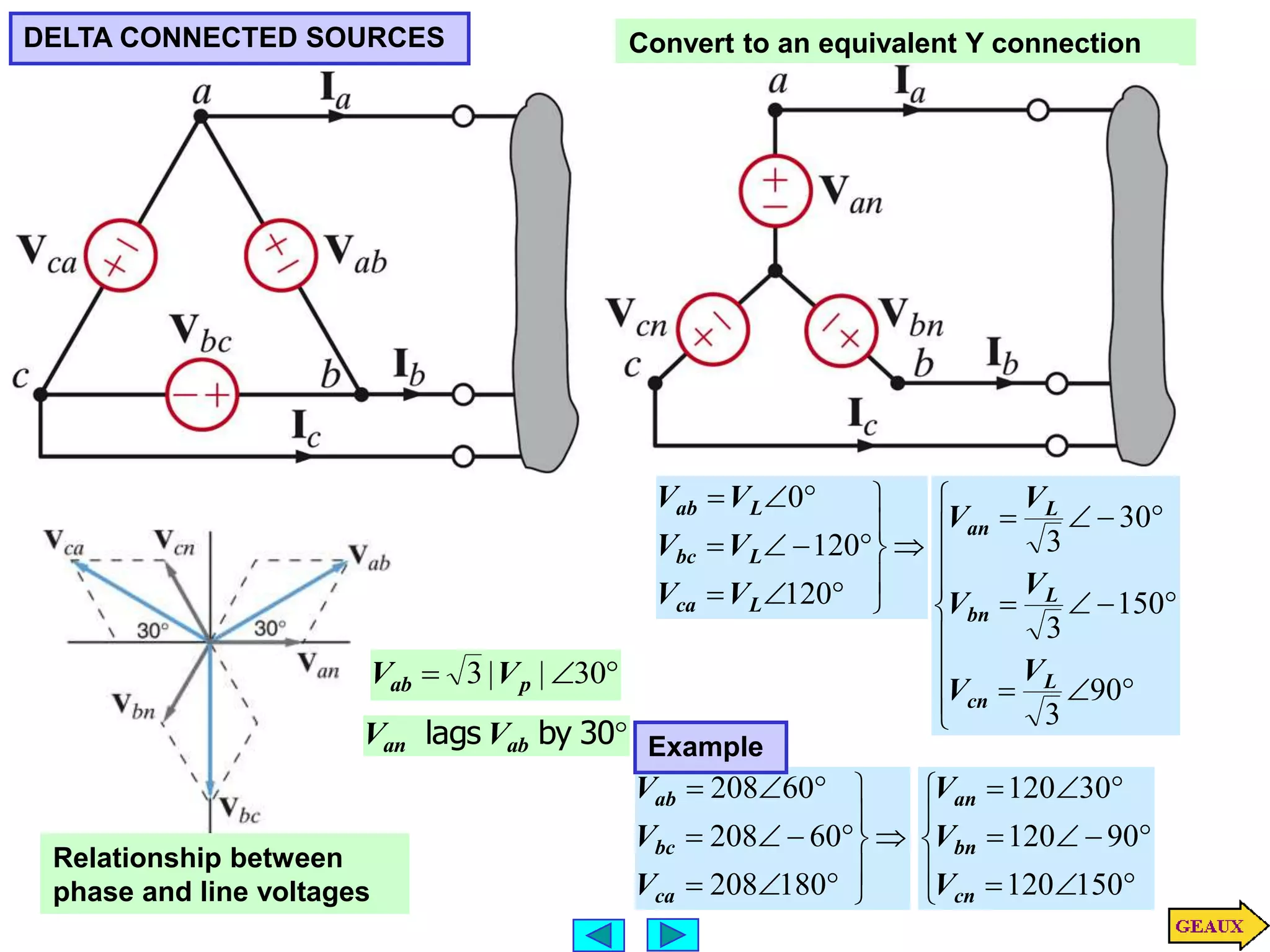
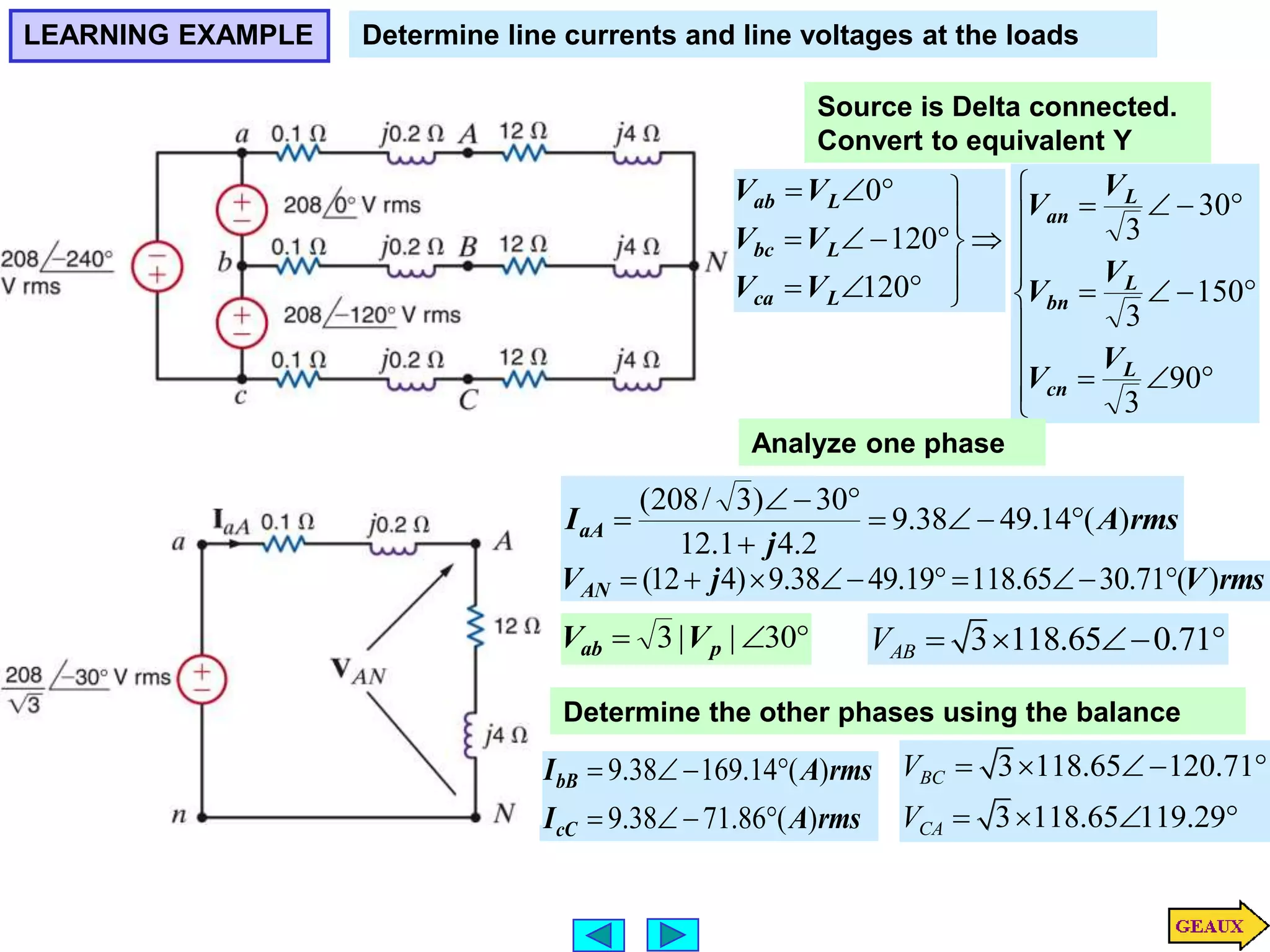
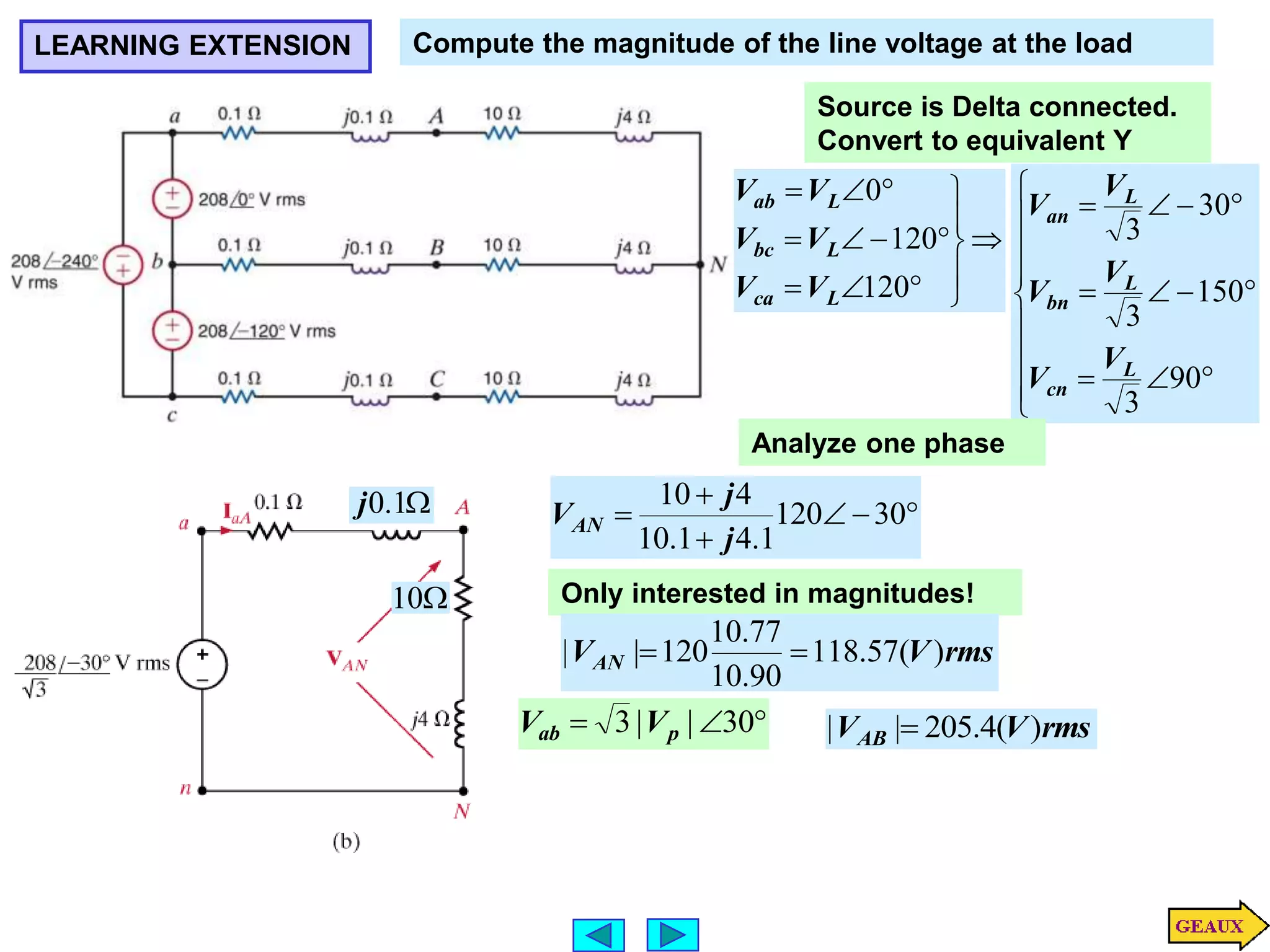
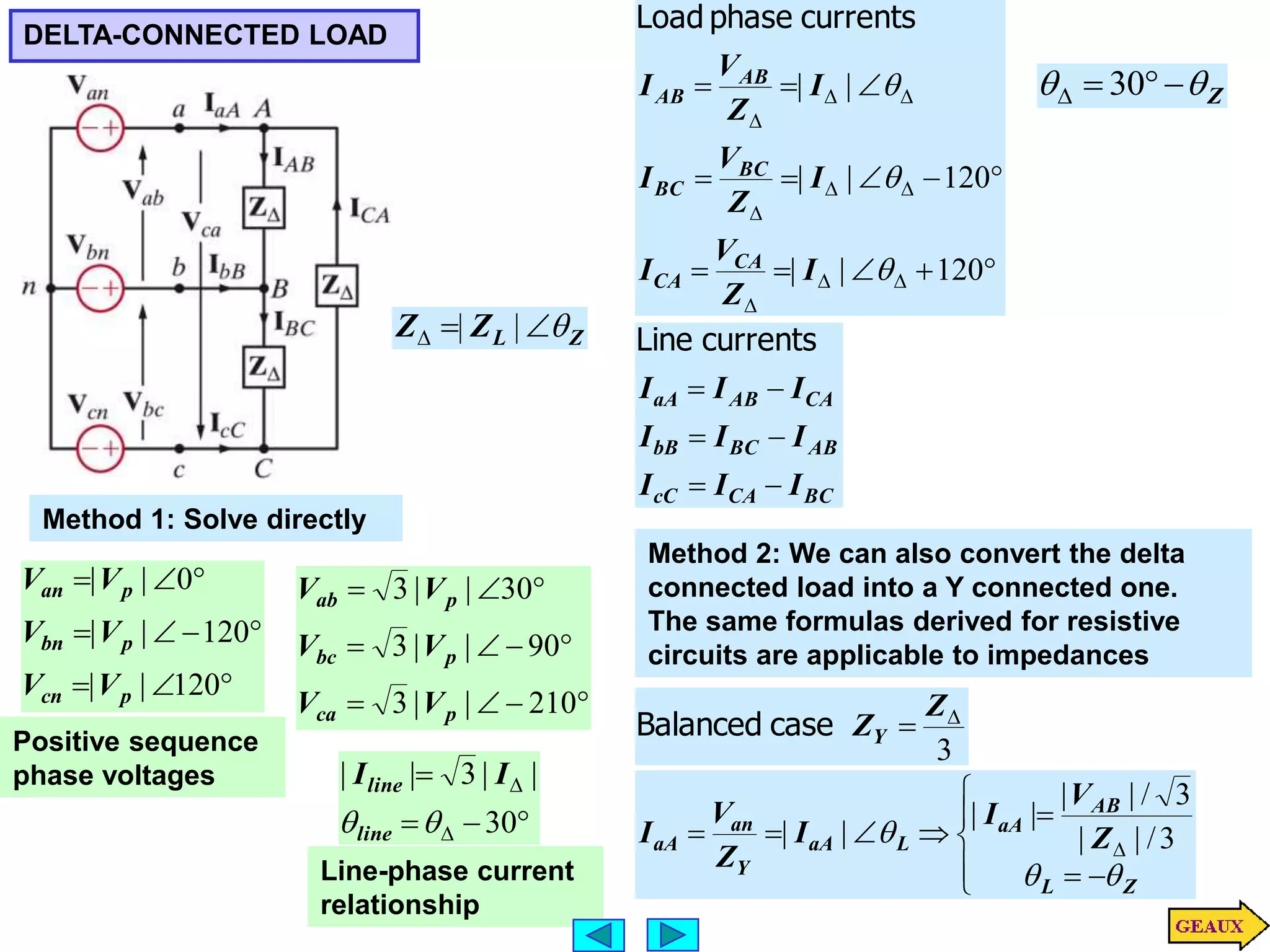
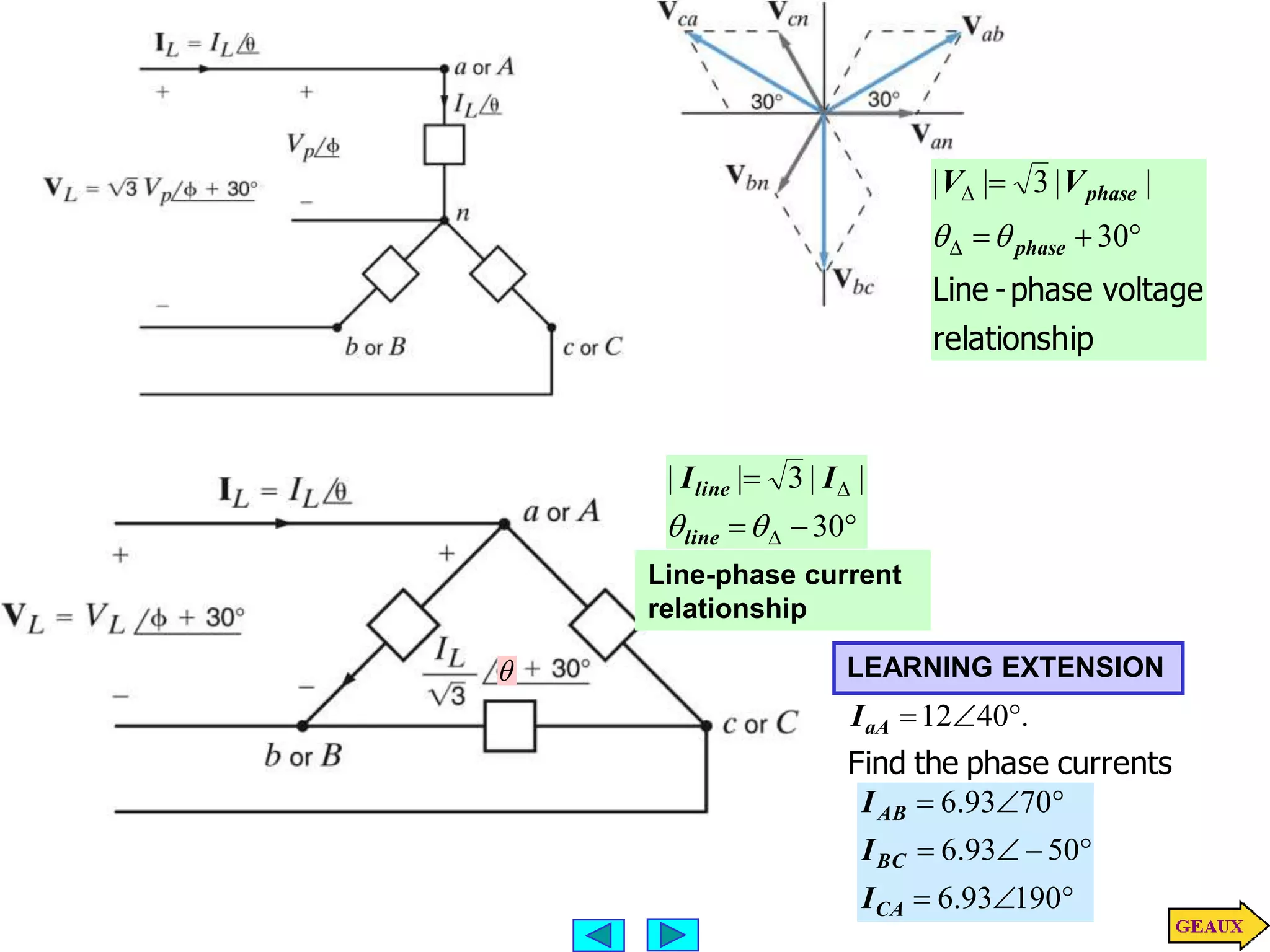
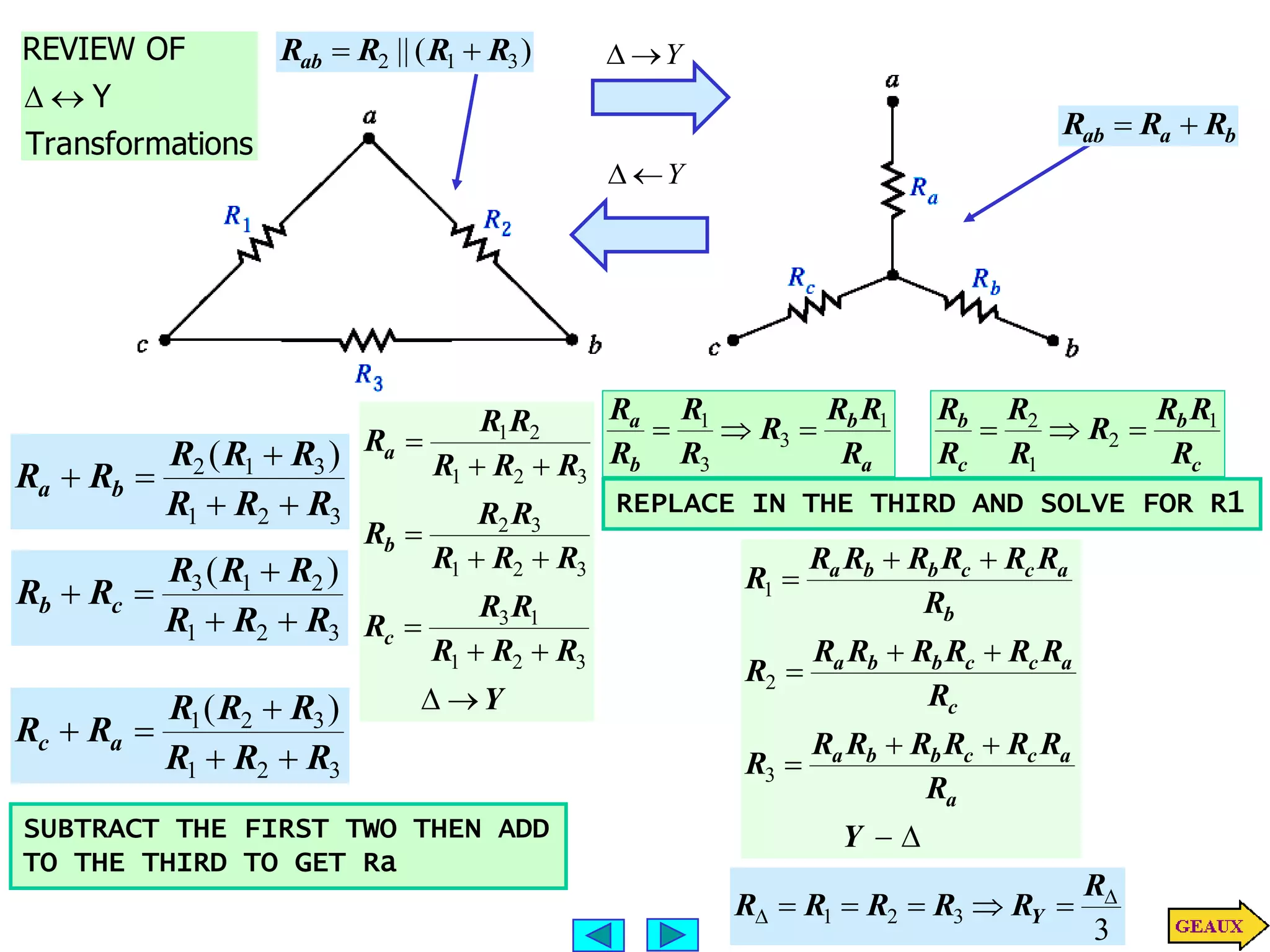
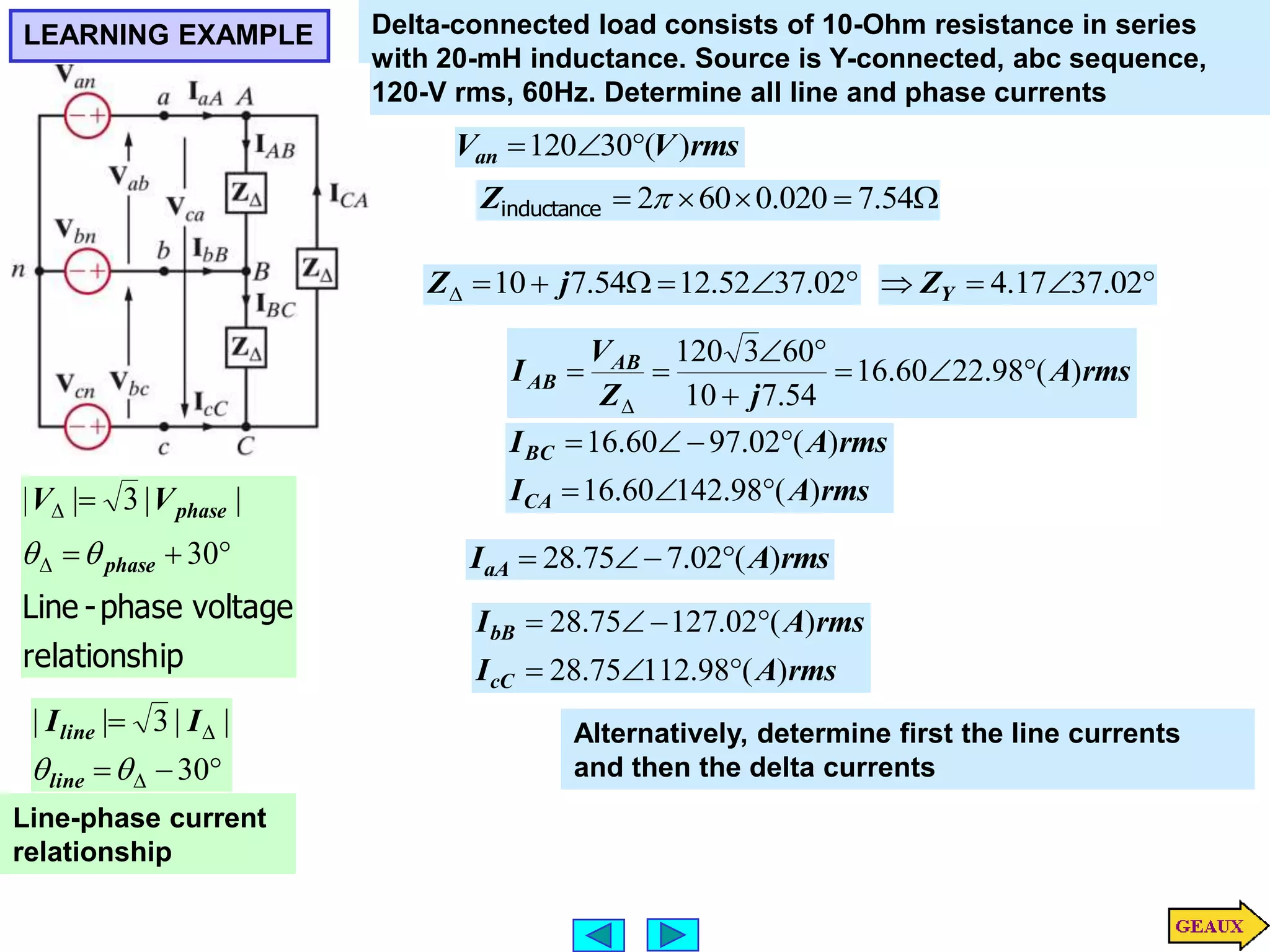
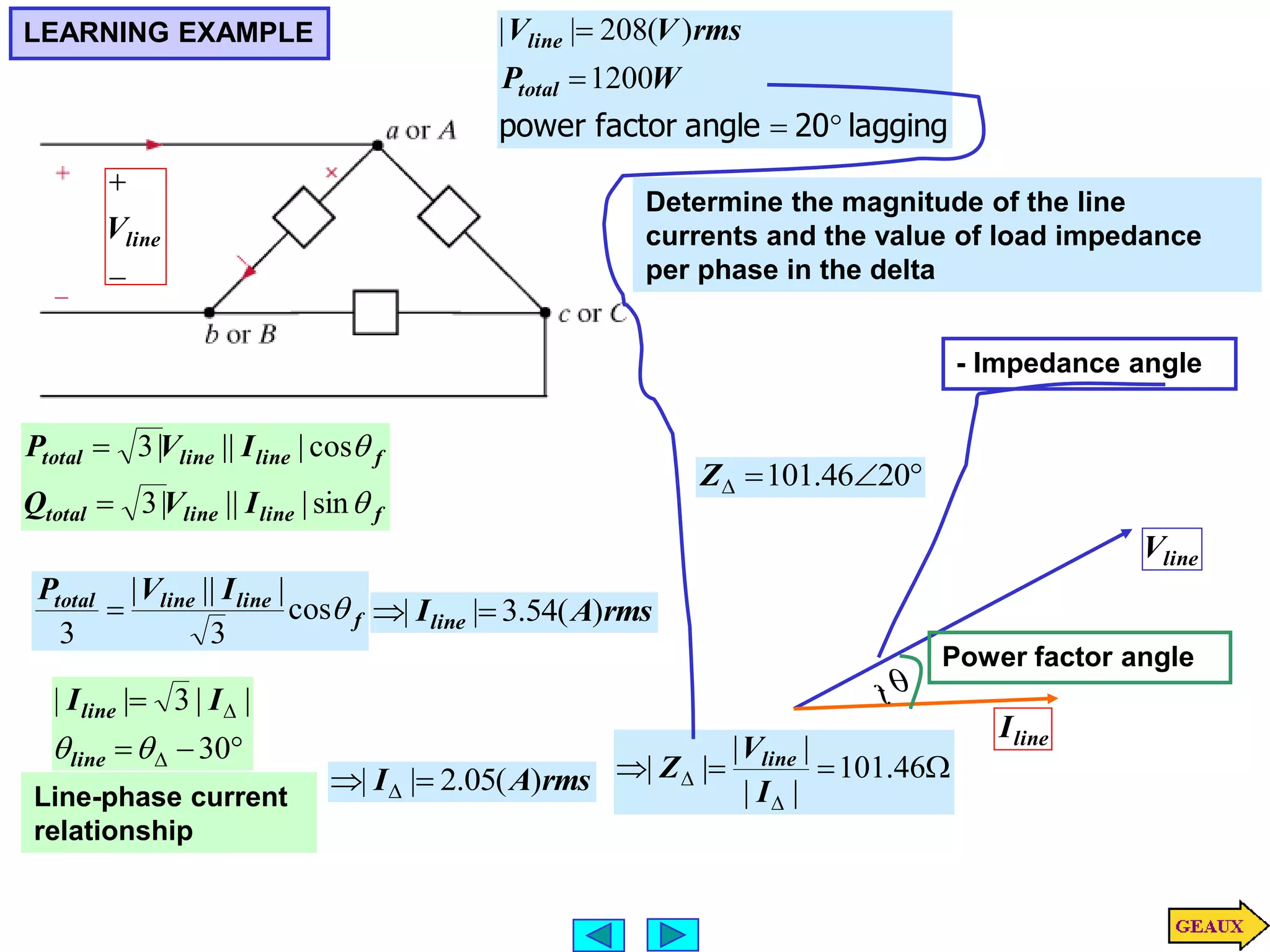
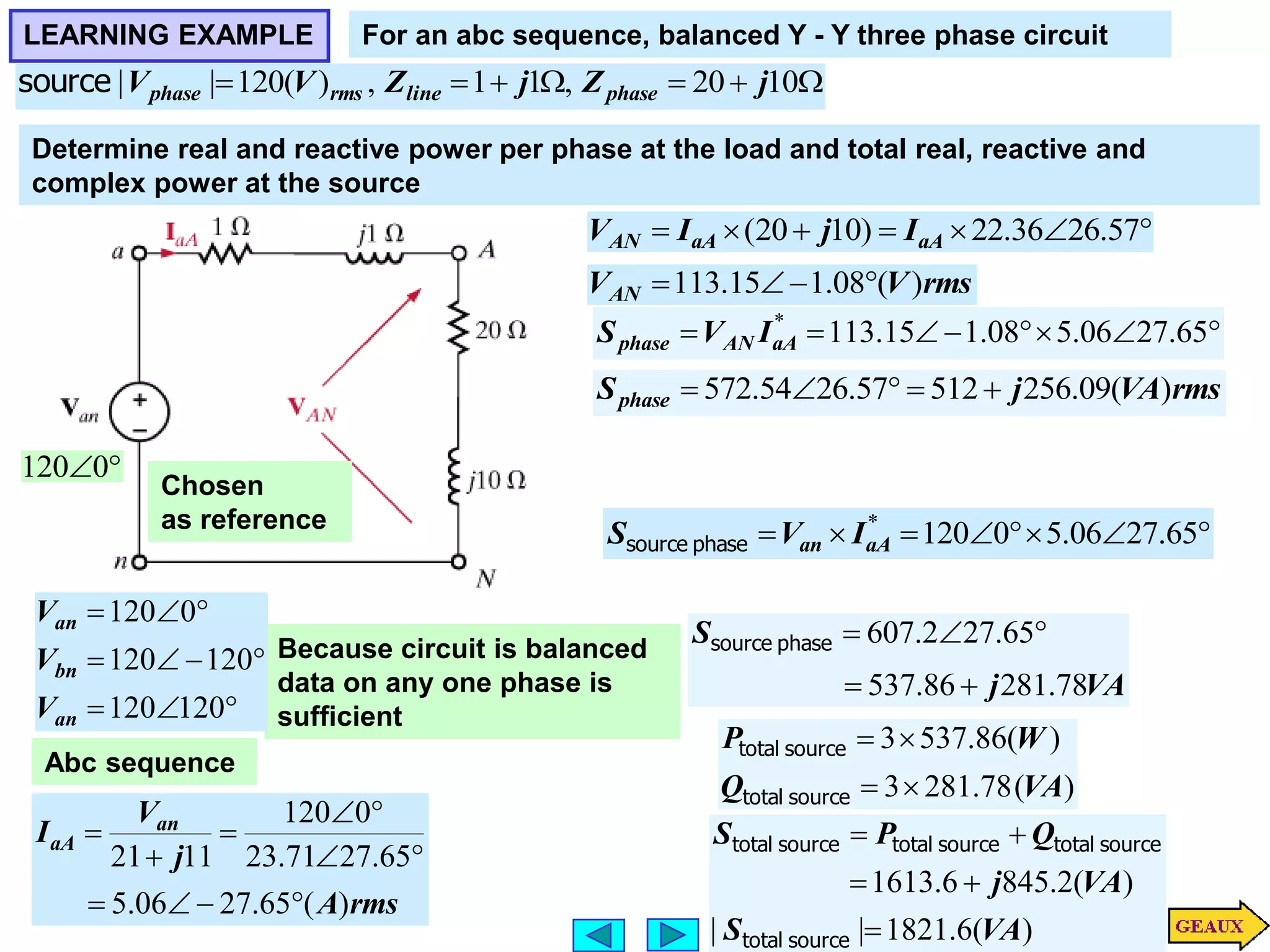
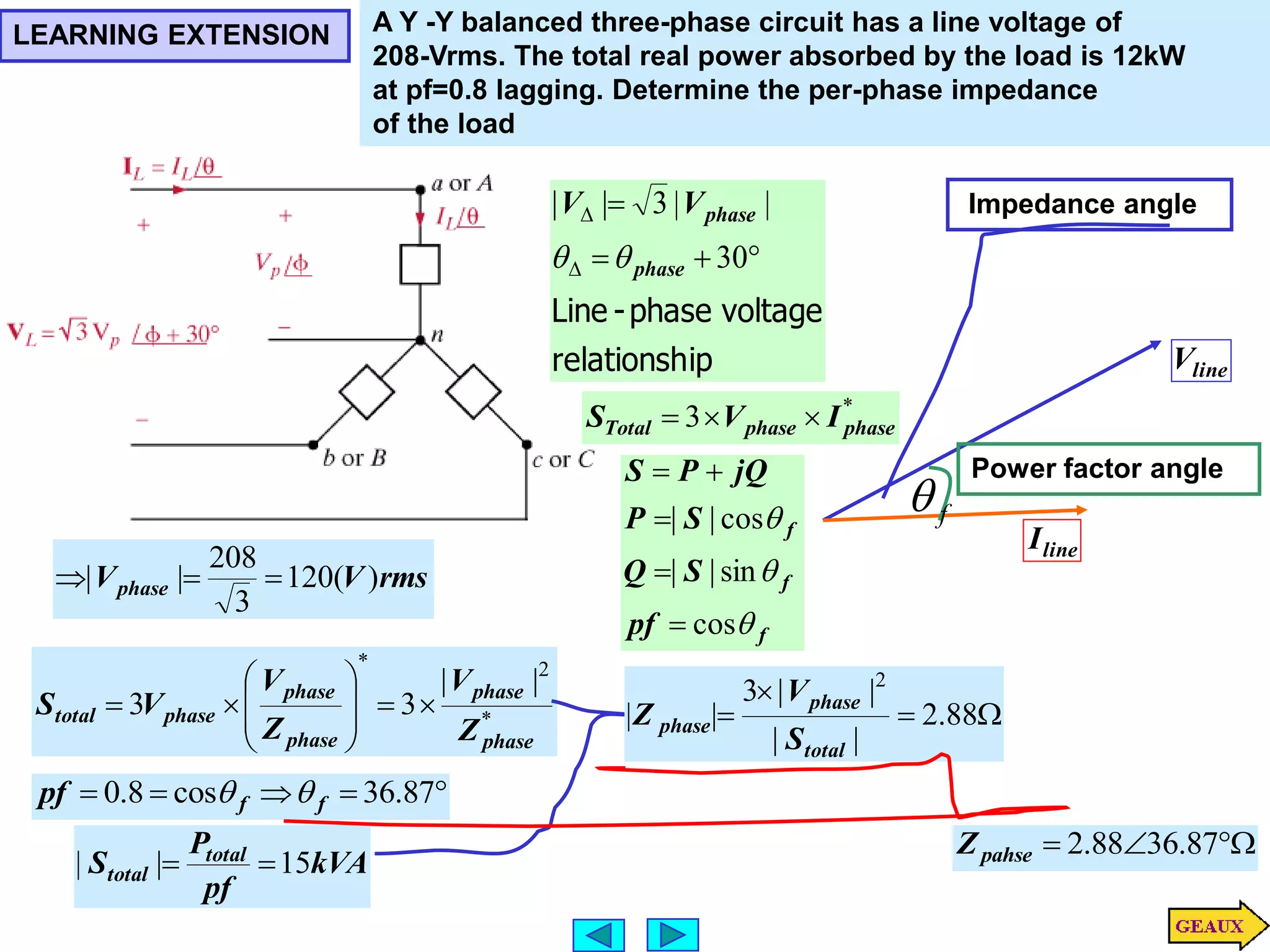
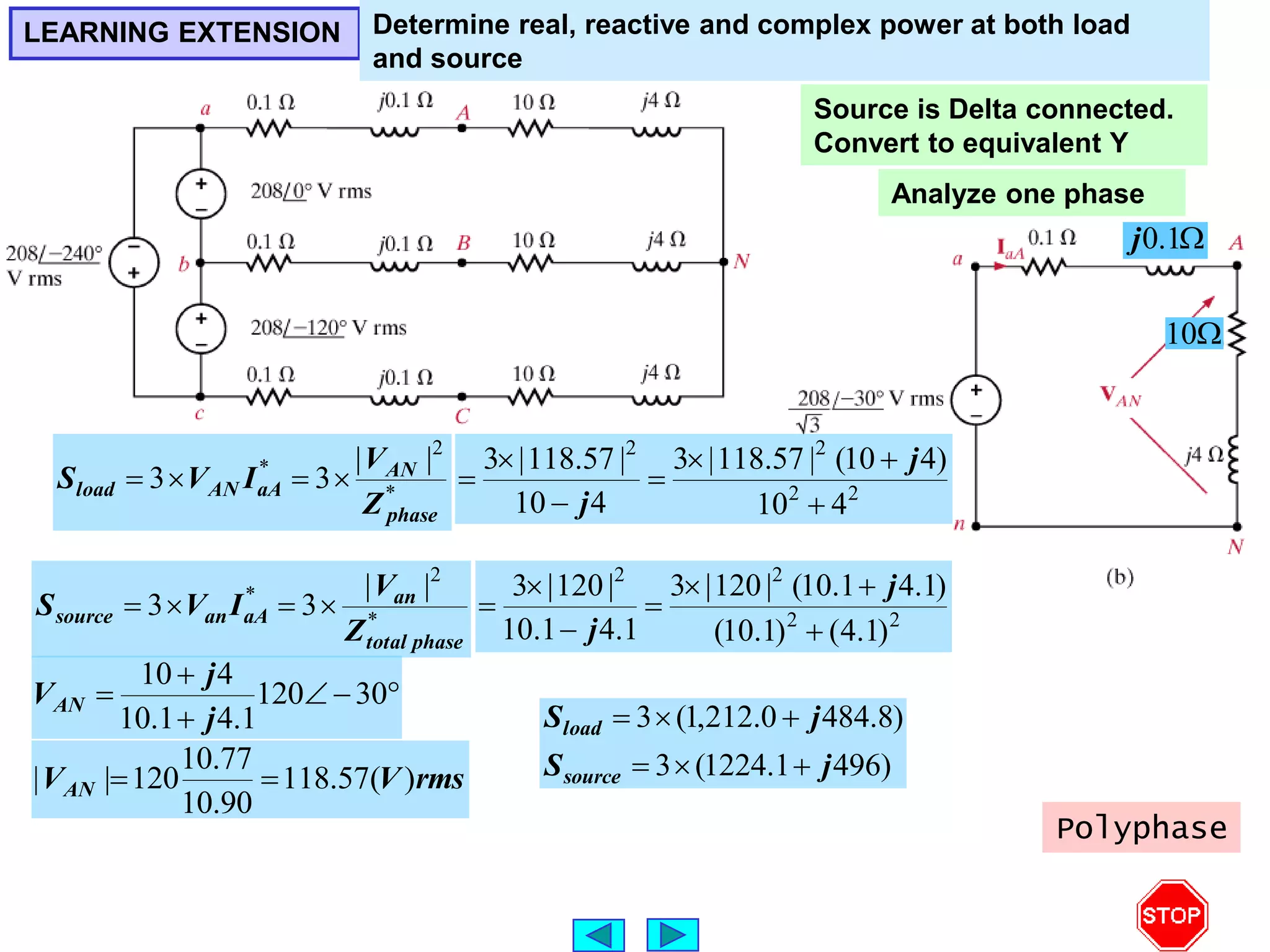
This document discusses three phase circuits. It covers the advantages of polyphase circuits, basic configurations including delta-wye connections, and power relationships in three phase circuits. Key concepts covered include instantaneous power in balanced three phase circuits remaining constant, voltage and current relationships in wye-wye and delta connections, and how to determine line currents and voltages from given phase information. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating values for various three phase circuit connections.