Let's go through this step-by-step:
1) The log-likelihood function for a Poisson with parameter λ is:
l(λ; y) = ylog(λ) - λ - log(y!)
2) Take the derivative of the log-likelihood with respect to λ:
∂l/∂λ = y/λ - 1
3) Set the derivative equal to 0 and solve for λ:
y/λ - 1 = 0
y/λ = 1
λ = y
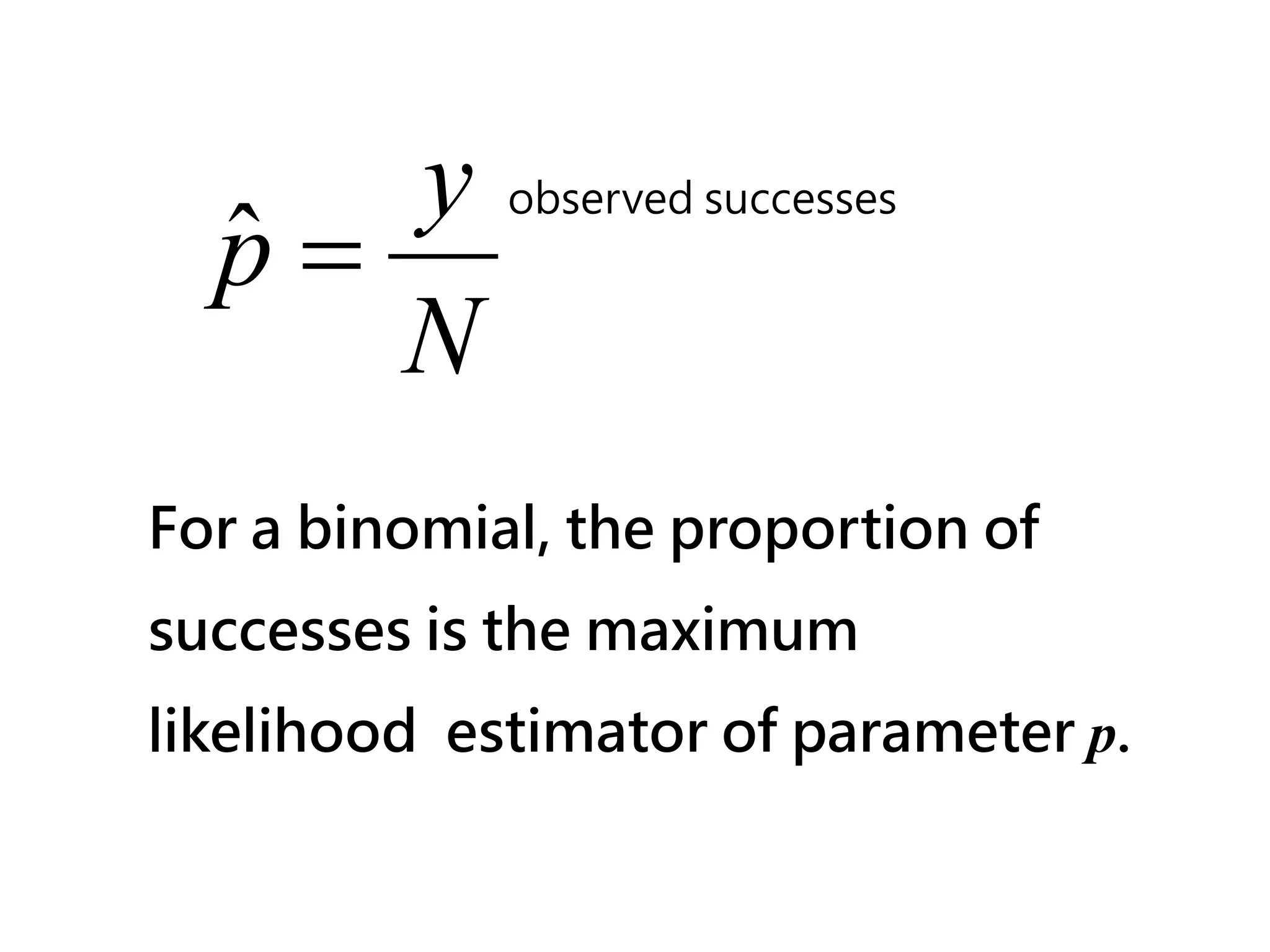
Therefore, the MLE for the Poisson parameter λ is simply the observed value y.





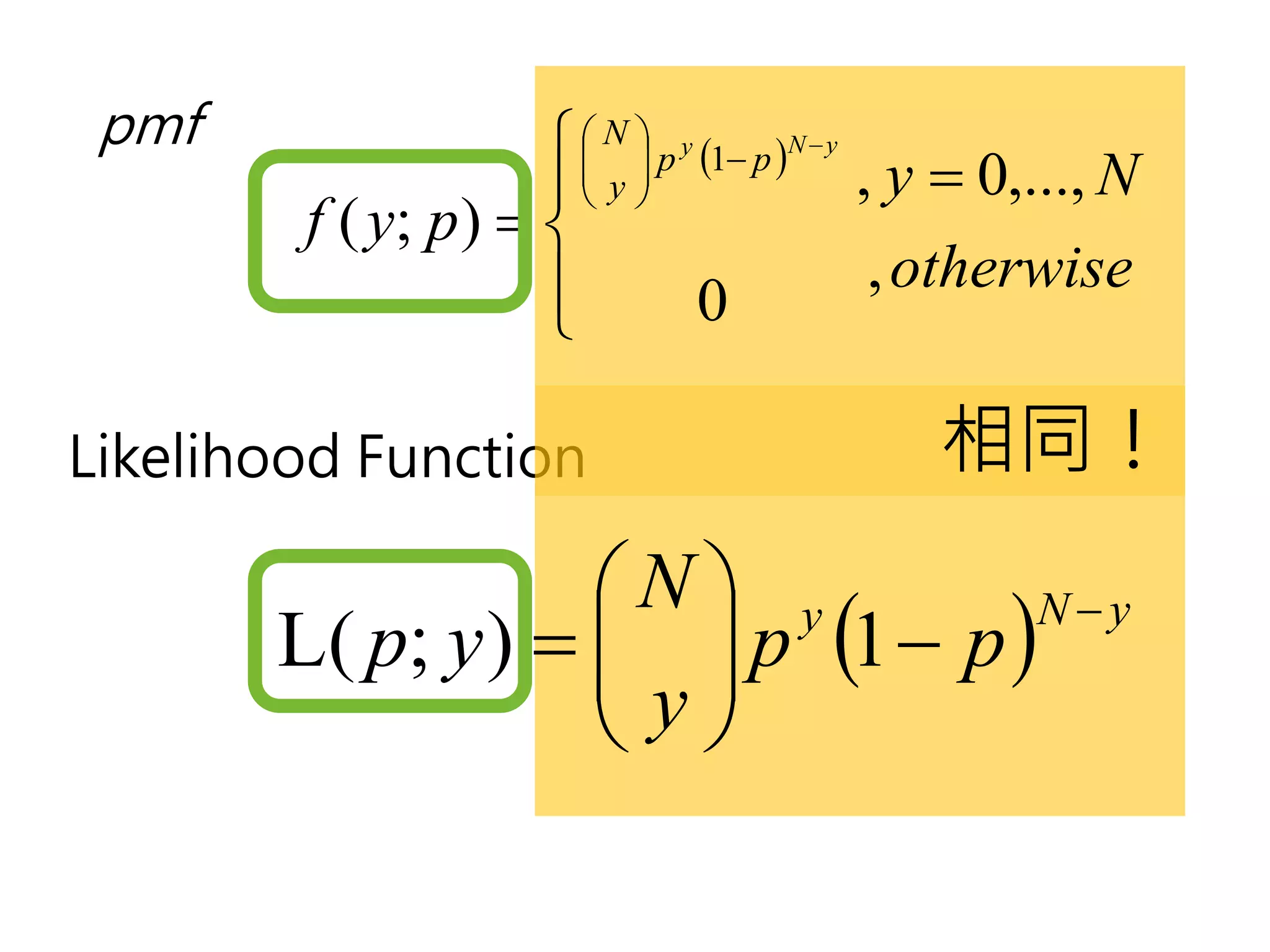
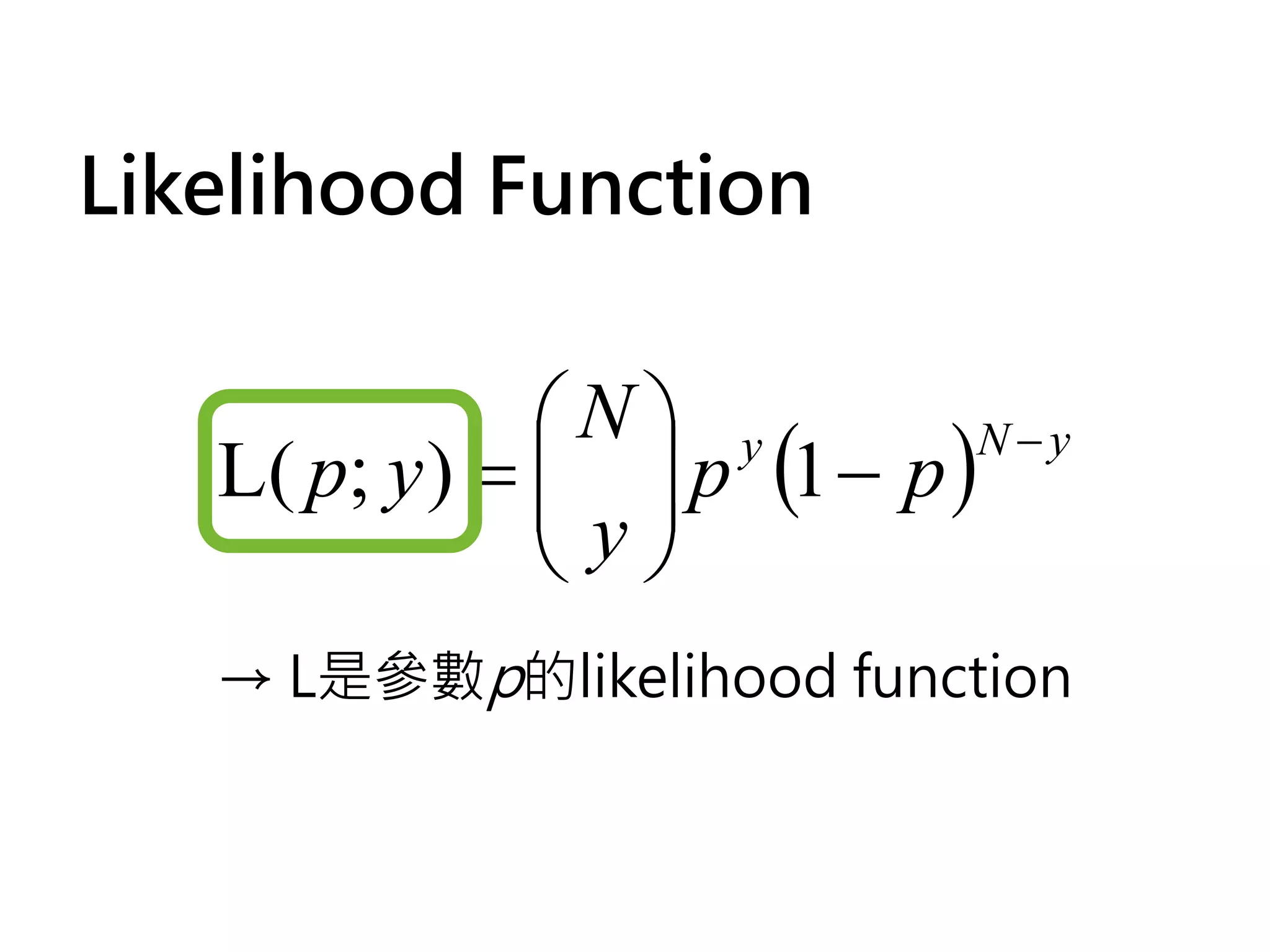









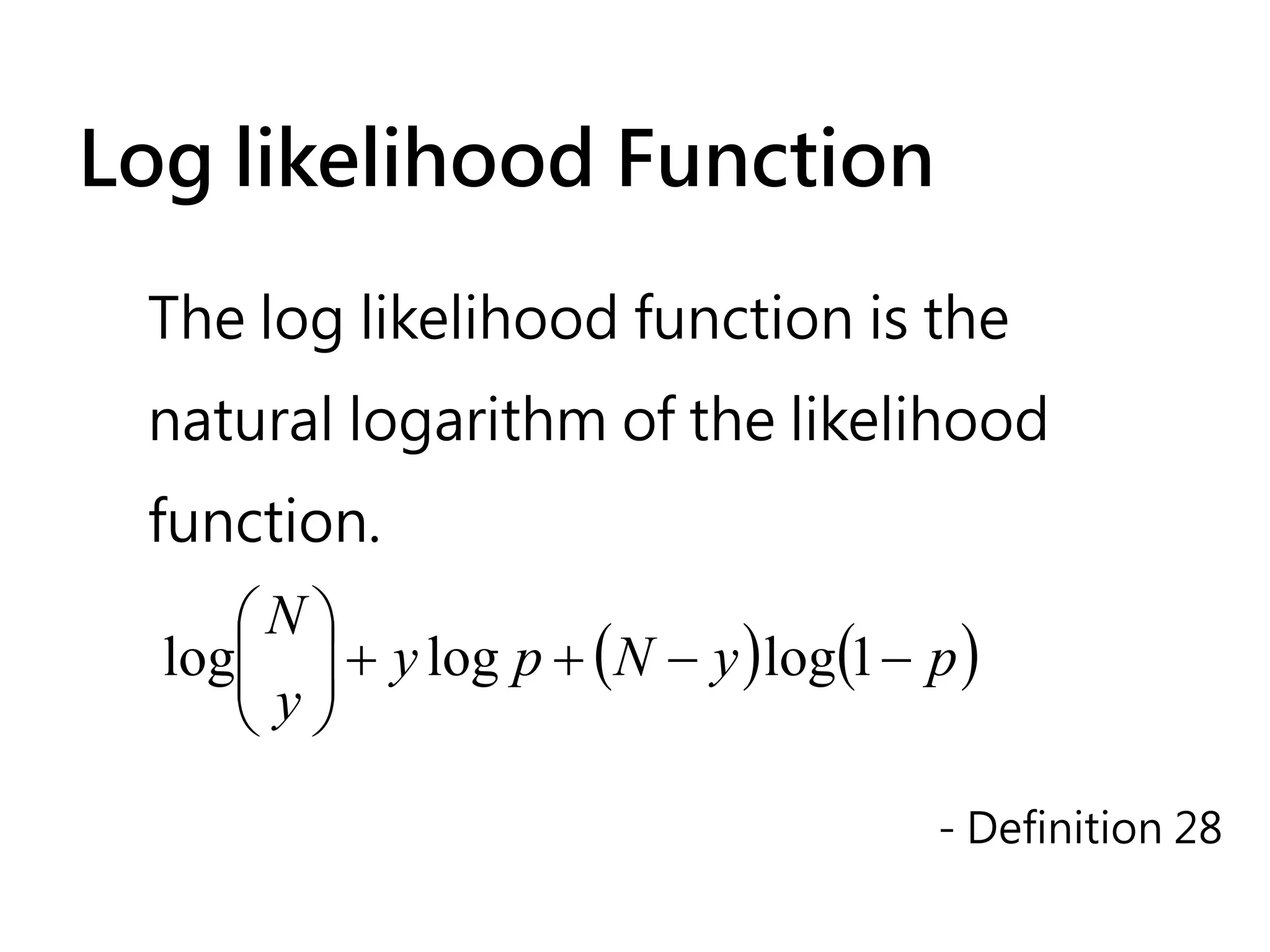
![如何取binomial的log
l ( p;y ) = log[L( p; y )] N y
L( p; y ) = p (1 − p )
N−y
y
N y N−y
= log p (1 − p )
y
N
( ) (
= log + log p + log (1 − p )
y
y N−y
)
N
= log + y log p + ( N − y ) log(1 − p )
y
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-2-1-4-111121012518-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-2-1-4-21-2048.jpg)




![Step 1. 對p進行微分
∂l ( p; y ) ∂ N
= log + y log p + (N − y ) log(1 − p )
∂p ∂p y
∂ N ∂ ∂
= log + [ y log p ] + [( N − y ) log(1 − p )]
∂p y ∂p
∂p
y N−y
= 0+ −
p 1− p
y N−y
= -
p 1− p](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-2-1-4-111121012518-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-2-1-4-28-2048.jpg)