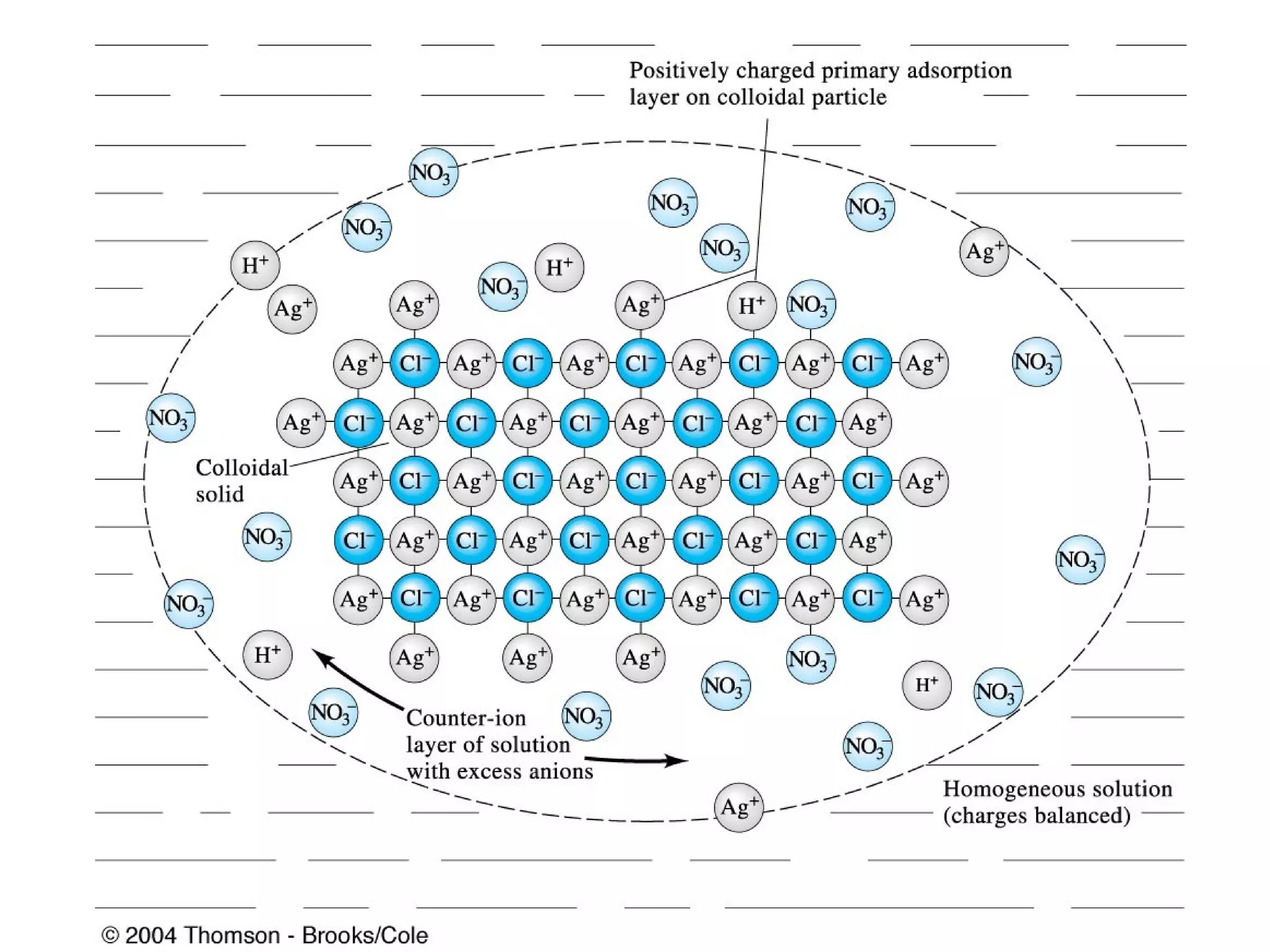
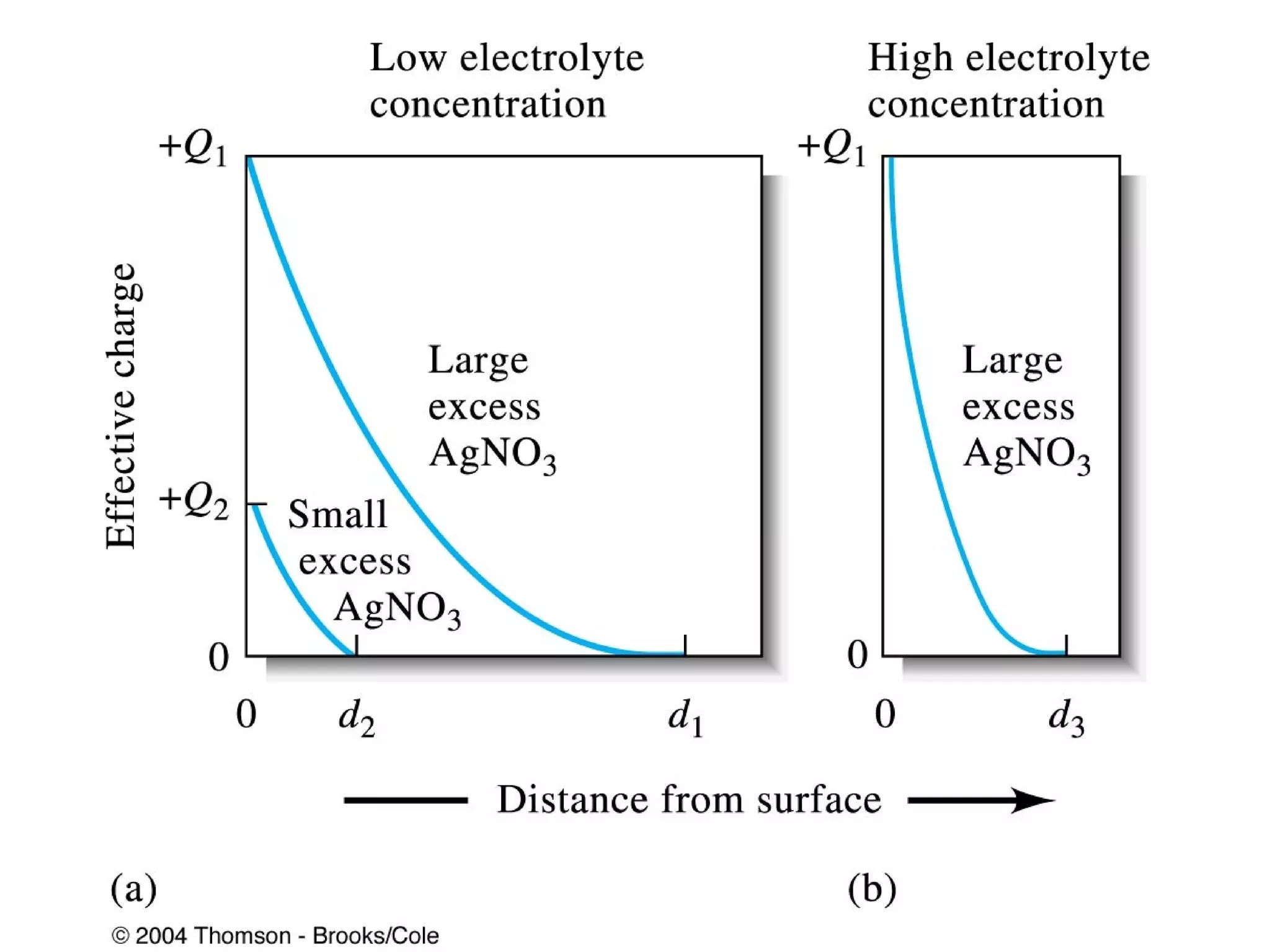
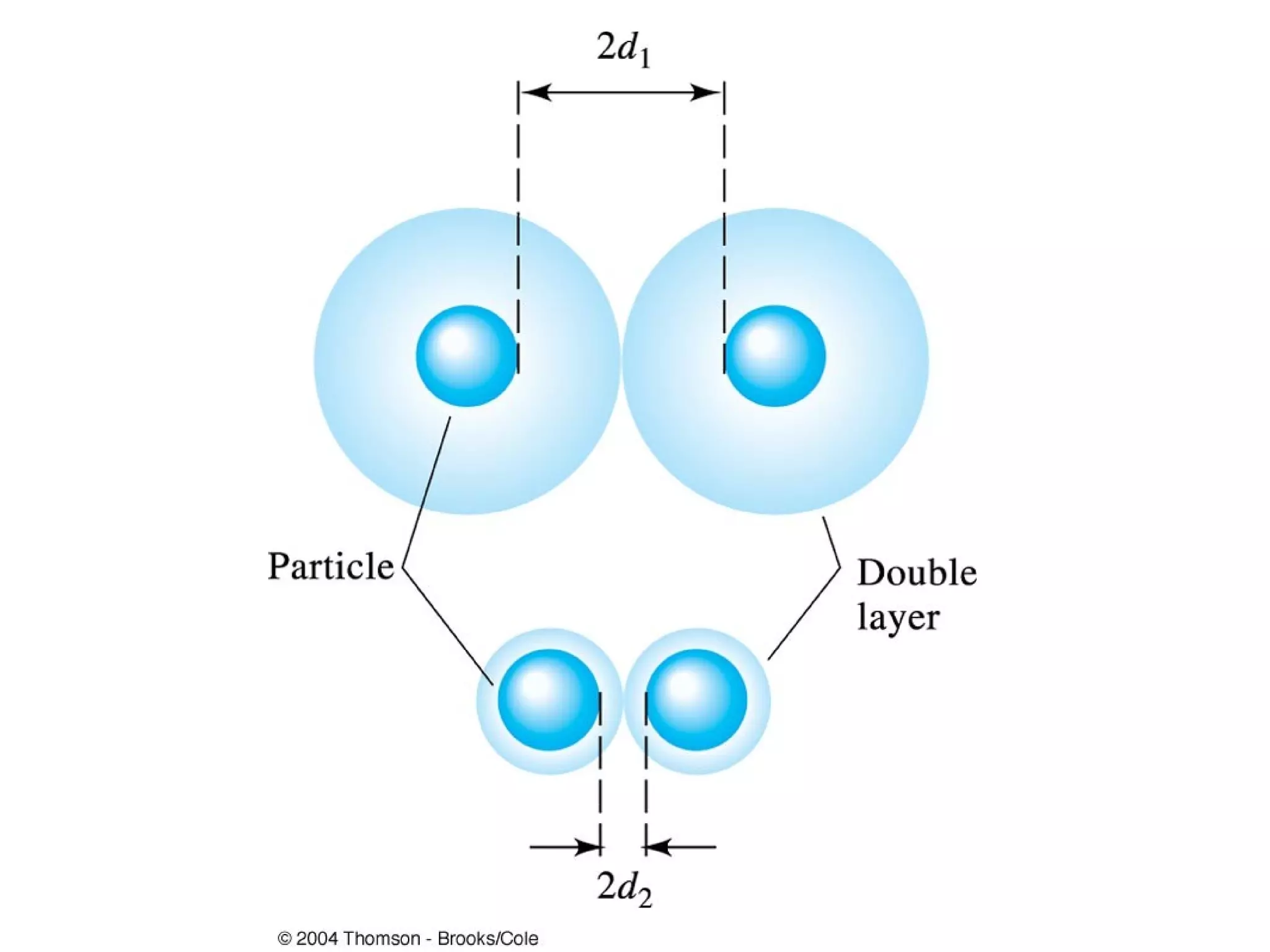
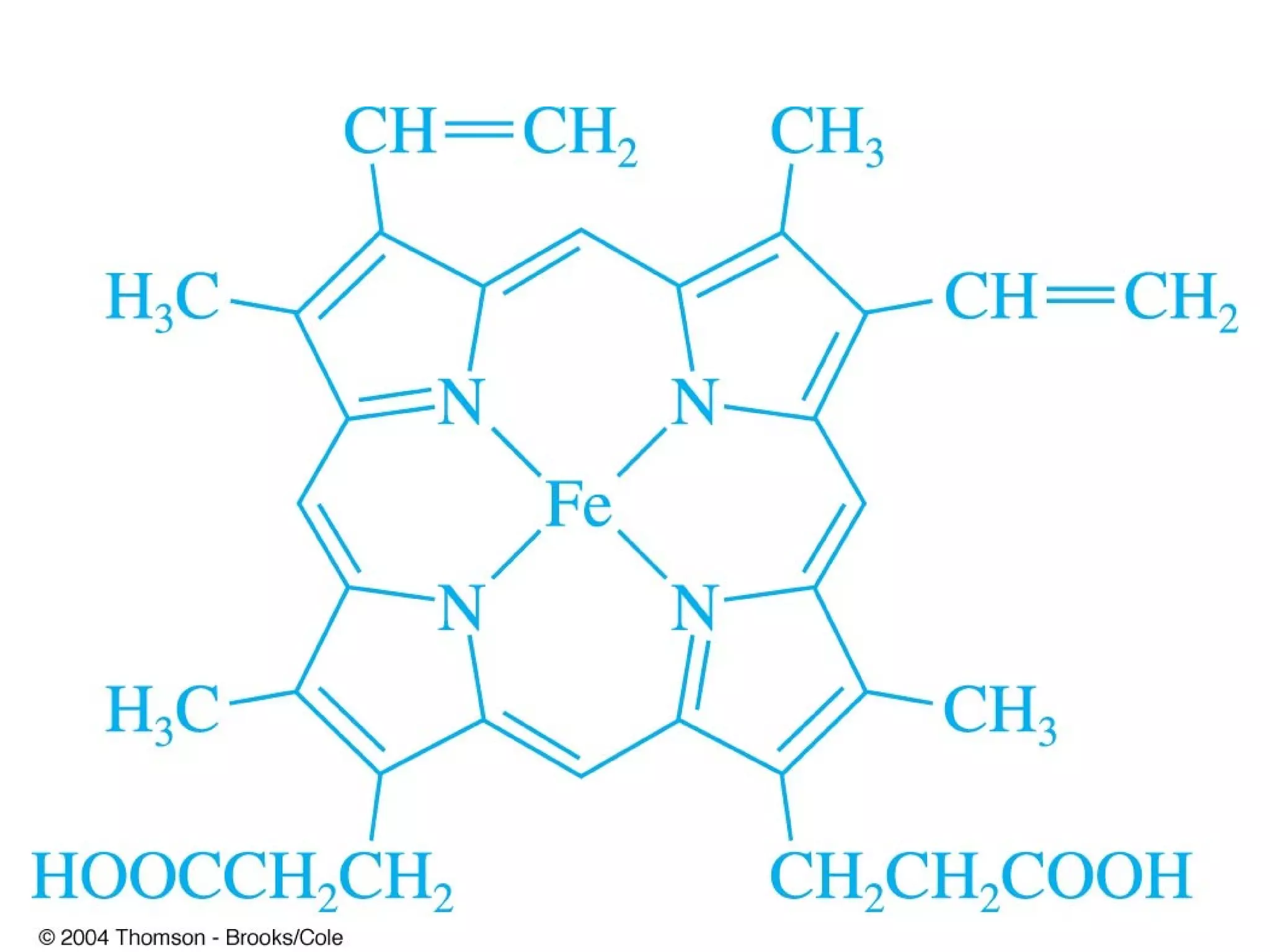
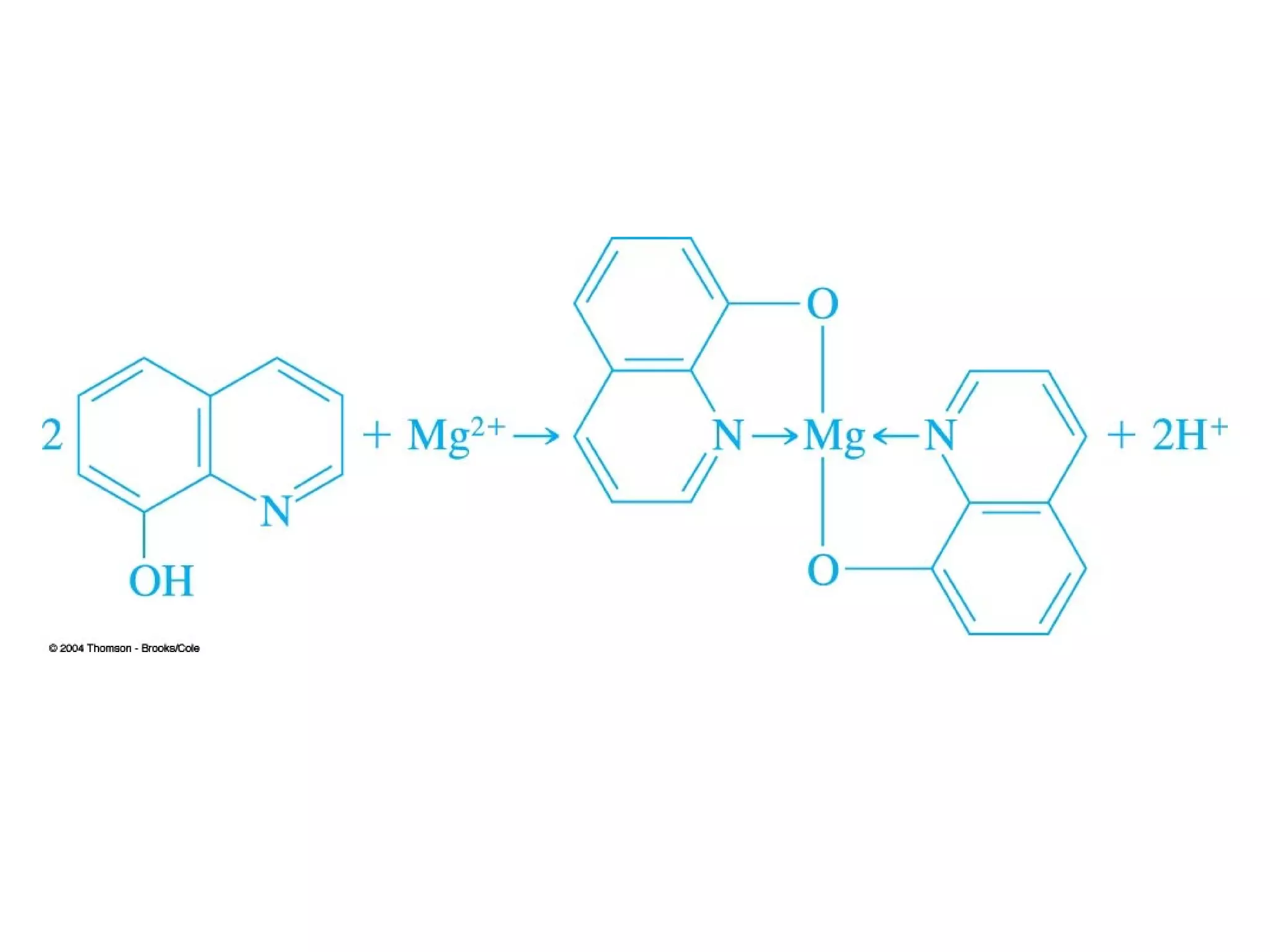
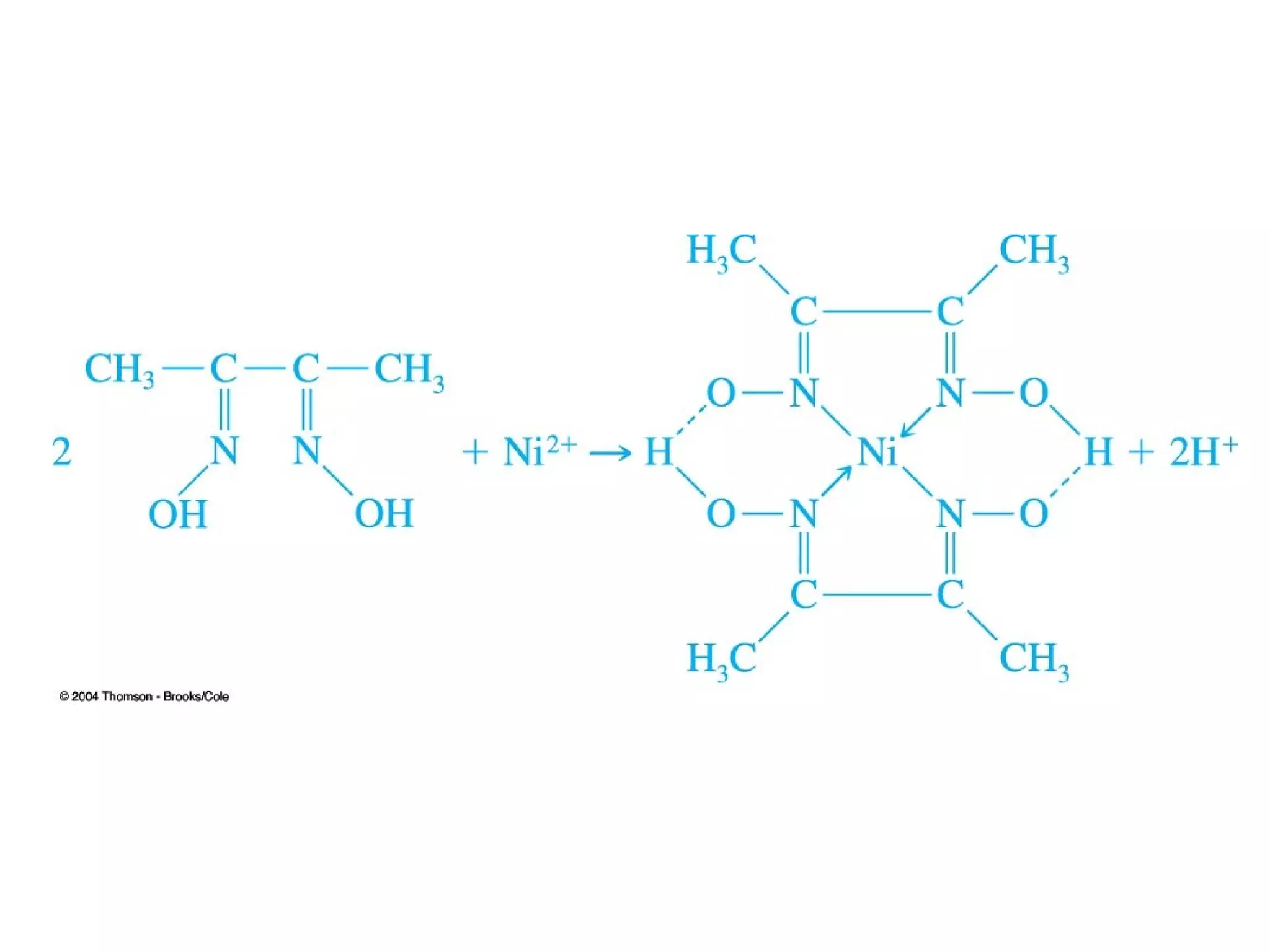
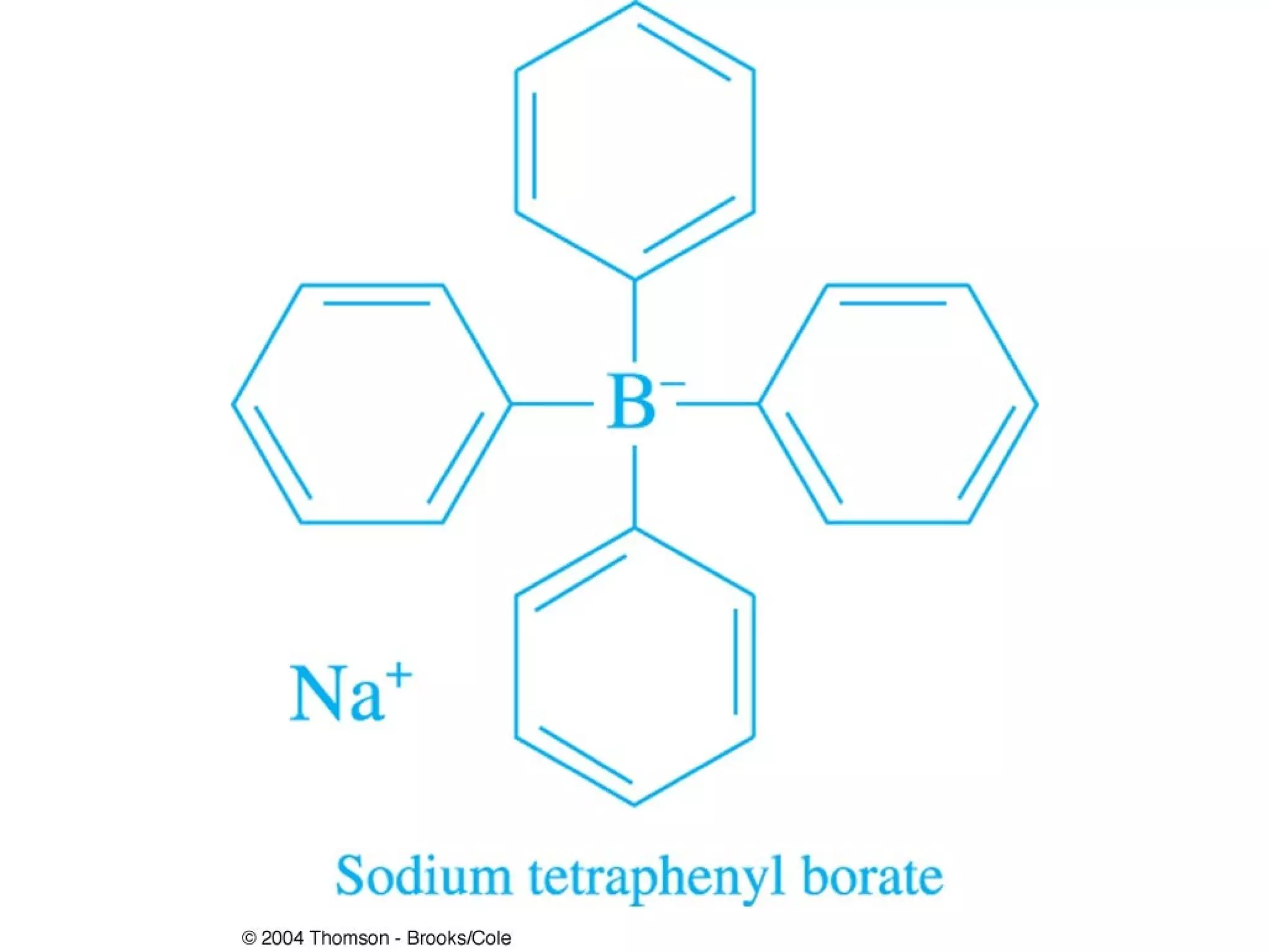
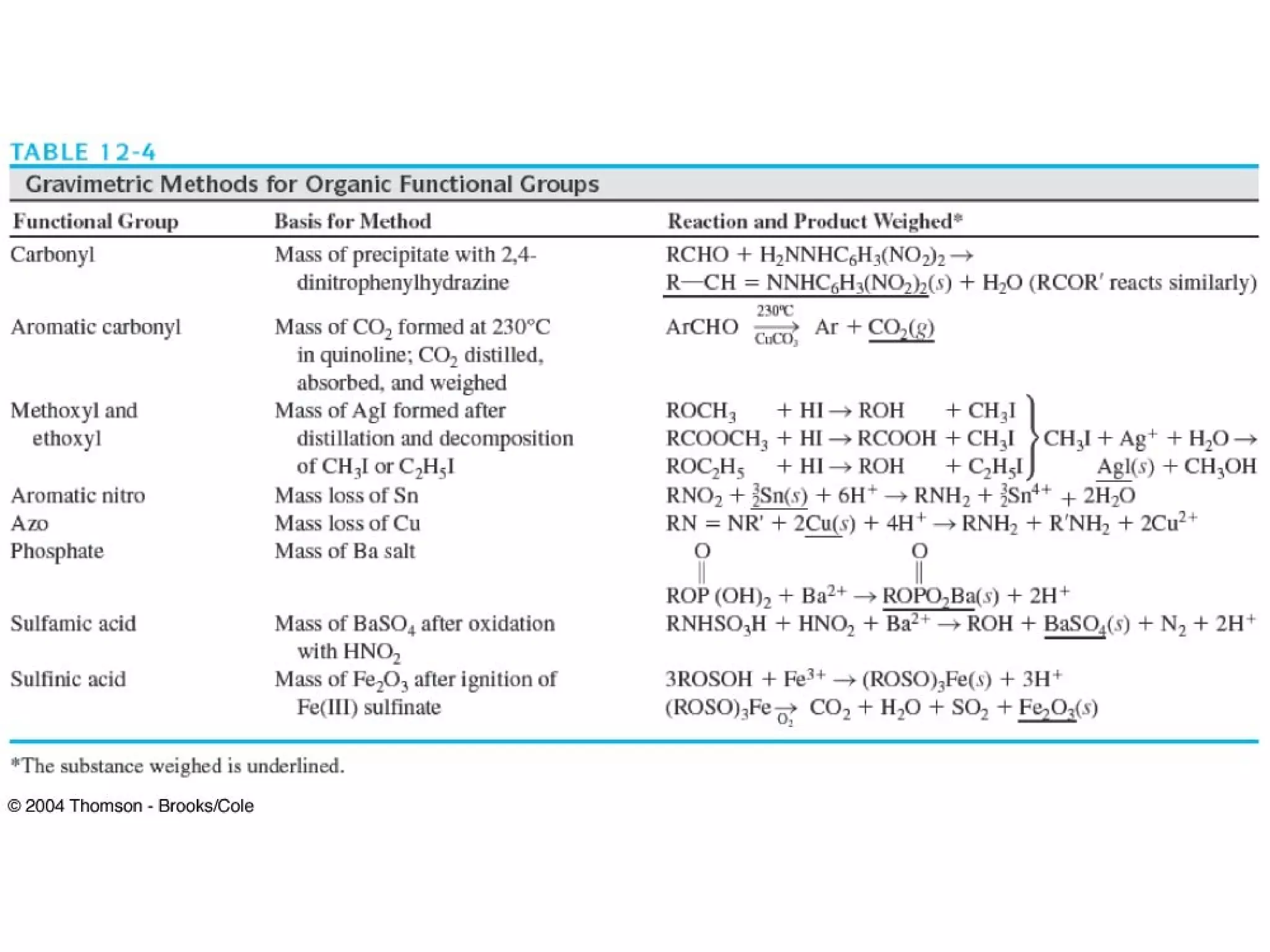
This document discusses gravimetric analysis methods which involve weighing precipitates or volatile decomposition products. It describes two major types - precipitation methods where the analyte is converted to a precipitate, and volatilization methods where the analyte or its products are vaporized. Ideal precipitates are readily filtered, insoluble, stable, and of known composition. Larger particle sizes are easier to filter but particle size depends on factors like solubility, temperature and concentration. Precipitates can form by nucleation or growth, and experimental controls aim to produce crystalline rather than colloidal precipitates. Coprecipitation of impurities is also discussed.