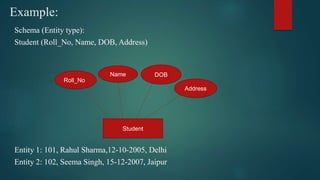
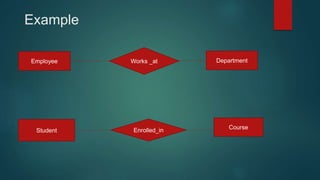
The document discusses the Entity Relationship (ER) model, which was introduced in 1976 to define the conceptual view of a database. The ER model represents real-world entities and relationships between entities using entity sets, attributes, and relationship types. These constructs allow the ER model to map to a relational database schema and serve as a design tool for database developers and a communication tool for users. Key ER modeling concepts covered include entities, attributes, relationships, cardinalities, and participation constraints.