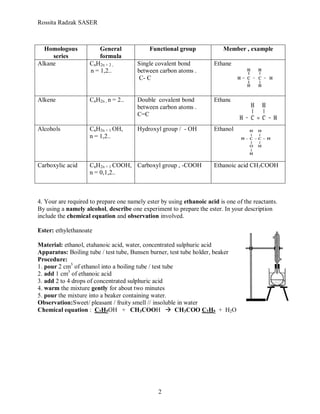
1. The document discusses various topics related to carbon compounds including hydrocarbons, alkenes, isomers, homologous series, functional groups, and reactions such as fermentation, oxidation, esterification, and dehydration of alcohols.
2. An experiment is described to prepare the ester ethyl ethanoate from ethanol and ethanoic acid using concentrated sulfuric acid. Upon mixing and warming the reactants, a sweet smell is observed and an insoluble product forms in water.
3. Differences between alkanes and alkenes are compared, including molecular structure, physical properties, reactivity, and chemical tests. Alkenes contain carbon-carbon double bonds and
![Rossita Radzak SASER
CARBON COMPOUND
1. Hydrocarbon – chemical compound containing carbon and hydrogen atom only.
2. Alkene – chemical compound containing carbon and hydrogen atom and at least
one carbon-carbon double bond.
3. Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula, but with different structural
formula.
C6H12O6
Fermention
KMnO4/ H+, CH3COOH
C2H5OH K2Cr2O7/ H+
Br2 Carboxyl
C2H4Br2 Hydroxyl
-COOH
-OH
H2 Oxidation
C2H6
C2H4
KMnO4/ H+, Double bond between
C2H4(OH)2 K2Cr2O7/ H+ C atoms, C=C Esterification
H2SO4
A
H2O d
C2H5OH CH3COO C2H5
d
i Ethyl ethanoate
HX
C2H5Br t
i CnH 2n+ 2 , n = 1,2 alkane
o CnH2n , n = 2, 3 alkene
- CH2- CH2- n CnH 2n+ 1 OH, n = 1, 2 alcohol
CnH 2n+1 COOH , n=0,1.. carboxylic acid
1. C2H4 + [O] + H2O C2H4(OH)2
2. C2H5OH + CH3COOH CH3COO C2H5 + H2O
3. C2H4 + H2O C2H5OH
4. C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11carboncompound-101008002133-phpapp02/75/Chapter-11-carbon-compound-1-2048.jpg)
![Rossita Radzak SASER
4. Dehydration of alcohol
Diagram of set up of apparatus
1. Complete and functional
2. Labels of set up of apparatus correct
Procedure:
1. Place some glass wool in a boiling tube
2. Use a dropper to add propan-1-ol to wet the glass wool.
3. Clamp the boiling tube horizontally and placed unglazed porcelain chips in the mid
section of the boiling tube.
Unglazed porcelain
Test tube
Glass wool
soaked in
Heat
propanol
water
4. Heat the unglazed porcelain chips strongly.
5. Then heat the glass wool gently to vaporize the propanol.
6. [Description of the chemical test to the gas collected in the test tube.]
Add 1 cm3 of bromine water and shake well.
Or,
Add 1 cm3 of acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution and shake well.
7. [Observation]:
Reddish brown colour of bromine decolourised Or,
Purple colour of potassium manganate(VII) solution decolourised
8. Chemical equation: C3H7OH C3H6 + H2O
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11carboncompound-101008002133-phpapp02/85/Chapter-11-carbon-compound-3-320.jpg)
![Rossita Radzak SASER
1. Compare and differentiate between namely alkene and alkane
Alkane ( hexane ) C6H14 Alkene ( hexene ) C6H12
1 Hydrocarbon ( contain C and H atom)
2 Low melting and boiling point
3 Insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvent
4 Cannot conduct electricity
5 Density less than water
6 Completely combustion produce CO2 + H2O
7 Saturated , single covalent bond, C-C Unsaturated , contain at least one double bond
C=C
8 Unreactive – undergo substitution with Reactive – undergo addition reaction
halogen in the presence of sunlight / UV ( hydrogenation, halogenations, oxidation,
ray polymerization, with halide, steam(hydration)
9 General formula , CnH2n+2 , n = 1,2 … , CnH2n , n= 2 …
10 Identify test
1. Combustion, burn less soot flame (% 1. More soot flame ( % of carbon per molecule is
of carbon per molecule is lower) higher).
Chemical tests
2. add bromine water , brown colour 2. decolorized brown colour
remains
3. add acidified KMnO4 , purple colour 3. purple colour is decolourized
remains
5. Table shows results of latex coagulation
Procedure Observation
Propanoic acid is added to latex Latex coagulates immediately
Latex is left under natural conditions Latex coagulates slowly
-
Protein - Rubber particles
membranes - -
- Rubber molecules
Explain why there is a difference in these observations
Answer:
1. acid ionizes in water to produce high concentration of / a lot of hydrogen ions
2. hydrogen ions , H+ neutralize the negative charges on the protein membranes
3. the rubber particles collide and the protein membranes break
4. rubber molecules are released and combine with one another and entangle.
5. the existence of bacteria in natural conditions
6. the growth of bacteria produce / lactic acid /weak acid / low concentration of H+ ions.
7. due to the slow bacterial action, the coagulation of latex take a longer time to occur.
[ monomer of natural rubber : 2 – methylbuta-1,3- diene , C5H8 / isoprene ]
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11carboncompound-101008002133-phpapp02/85/Chapter-11-carbon-compound-4-320.jpg)
![Rossita Radzak SASER
Explain how to prevent coagulation of latex
1. add ammonia solution
2. ammonia solution contains / ionized to produce hydroxide ions , OH-
3. hydroxide ions , OH- neutralized the hydrogen ions , H+ / acid produced by the
bacteria
4. the rubber particles remain negatively charged and coagulation is prevented.
6. [Paper 3]
Aim : To compare the elasticity of vulcanised and unvulcanised rubber
Problem statement: Does vulcanised rubber more elastic than unvulcanised rubber
Hypothesis: Vulcanised rubber is more elastic than unvulcanised rubber
Manipulated variable : vulcanised rubber and unvulcanised rubber
Responding variable : length of rubber strip / elasticity
Fixed variable : mass of weight , size of rubber
Material and apparatus : retort stand, bulldog clip, meter ruler, weight, vulcanised and
unvulcanised rubber
Procedure:
2. hang both rubber strips to the retort stand with bulldog clip.
3. measure the initial length of both rubber strips and record.
4. hang 50 g weight to the end of each rubber using bulldog clip.
5. remove the weight and measure the length of both rubber strips and record.//
6. record all the data obtained.
Result / Data
Type of rubber Initial length , cm Length after removal of
weight , cm
vulcanised
unvulcanised
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11carboncompound-101008002133-phpapp02/85/Chapter-11-carbon-compound-5-320.jpg)
![Rossita Radzak SASER
[Paper 2]
Conclusion:
1. Vulcanised rubber is more elastic than unvulcanised rubber due to the presence of cross-
linkage of sulfur atoms between the rubber molecules. Vulcanised rubber could return
to its original length after removal of the weight.
Note: 1. Rubber can be vulcanized by dipping natural rubber sheets into disulphur dichloride
solution
in methylbenzene or heated with sulphur.
2. Vulcanised rubber is more heat resistance due to the presence of cross-linkage of
sulfur atoms increases the size of rubber molecules. Force of attraction between
molecules will increase.
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11carboncompound-101008002133-phpapp02/85/Chapter-11-carbon-compound-6-320.jpg)