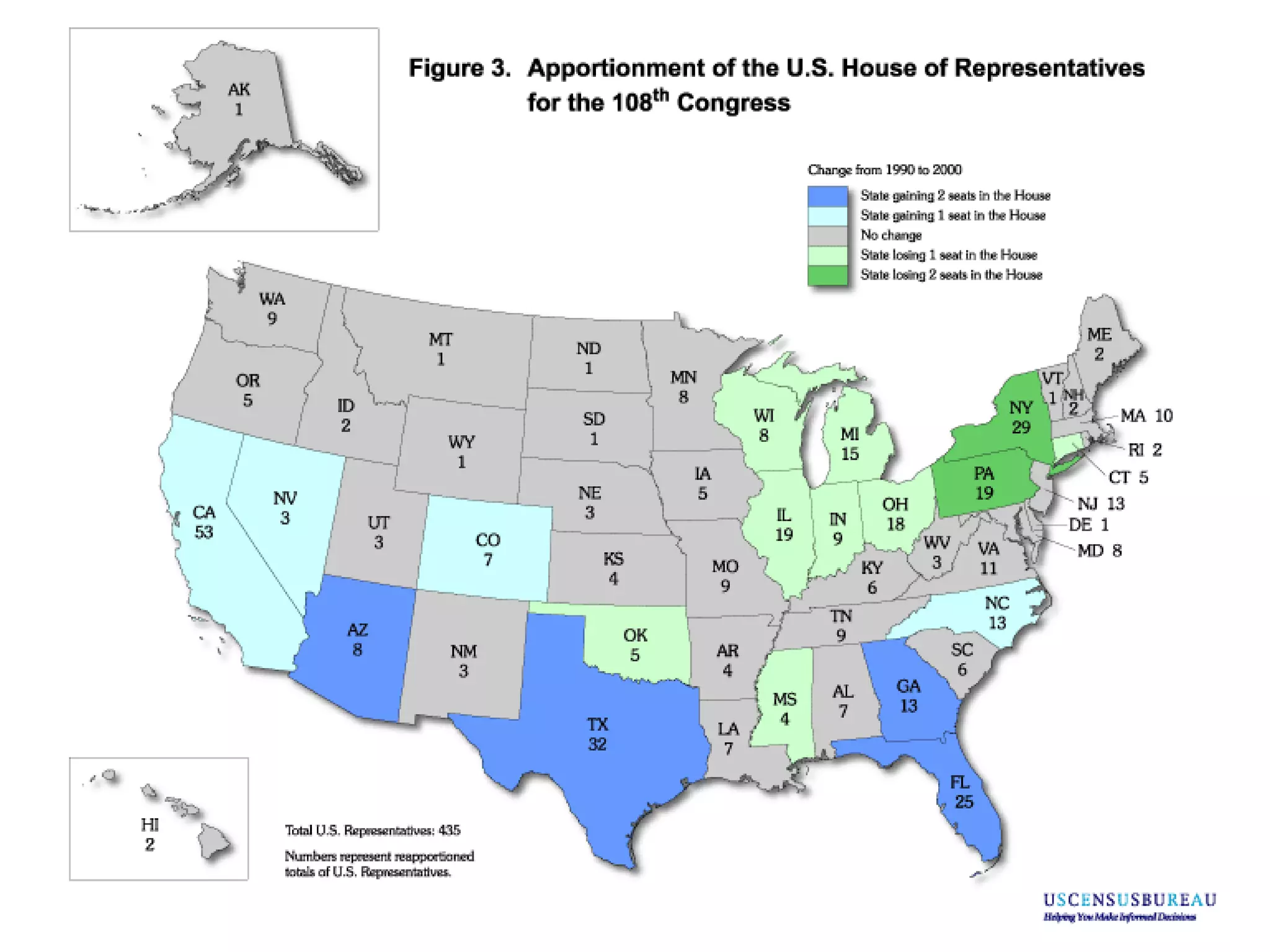
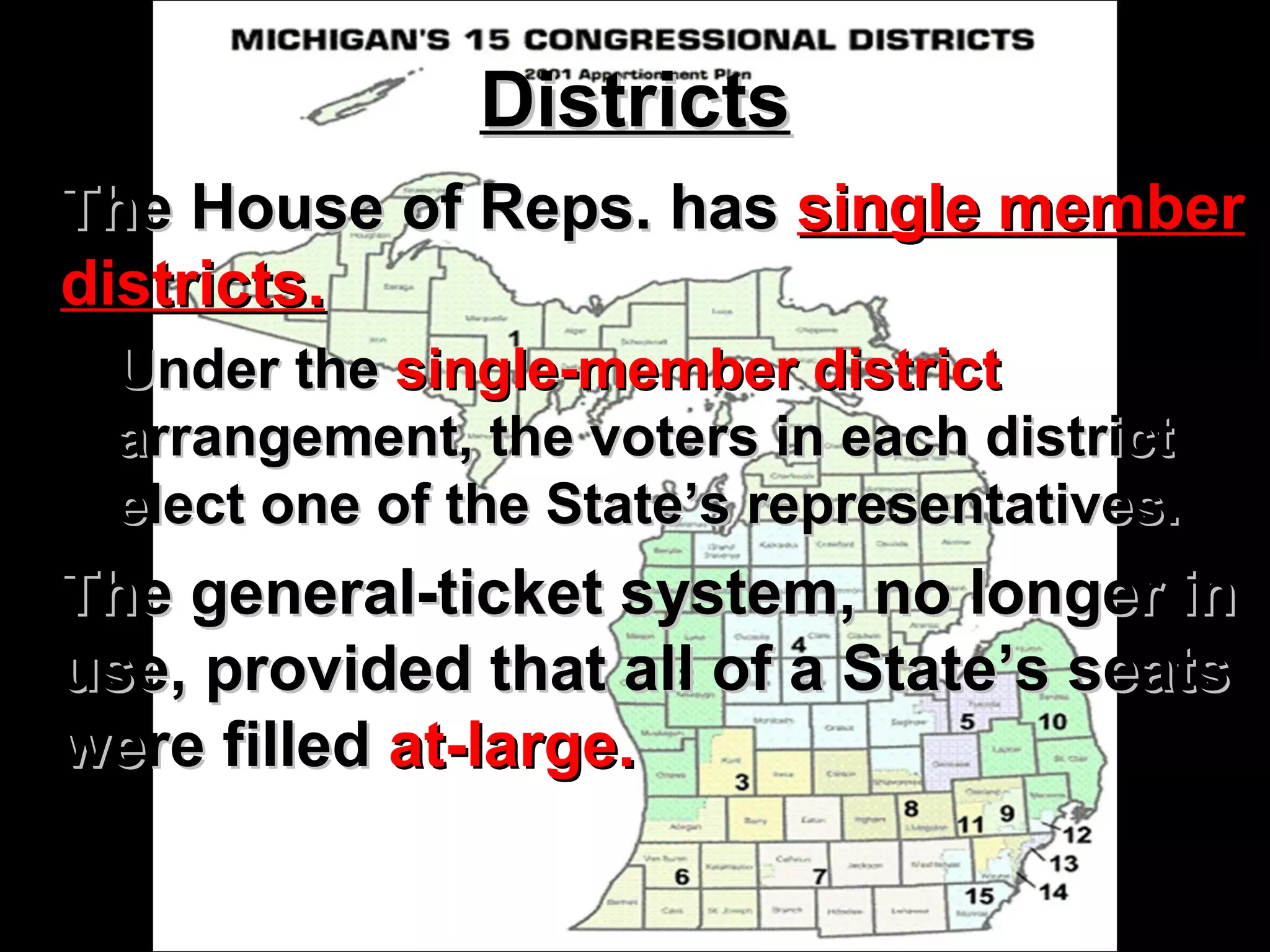
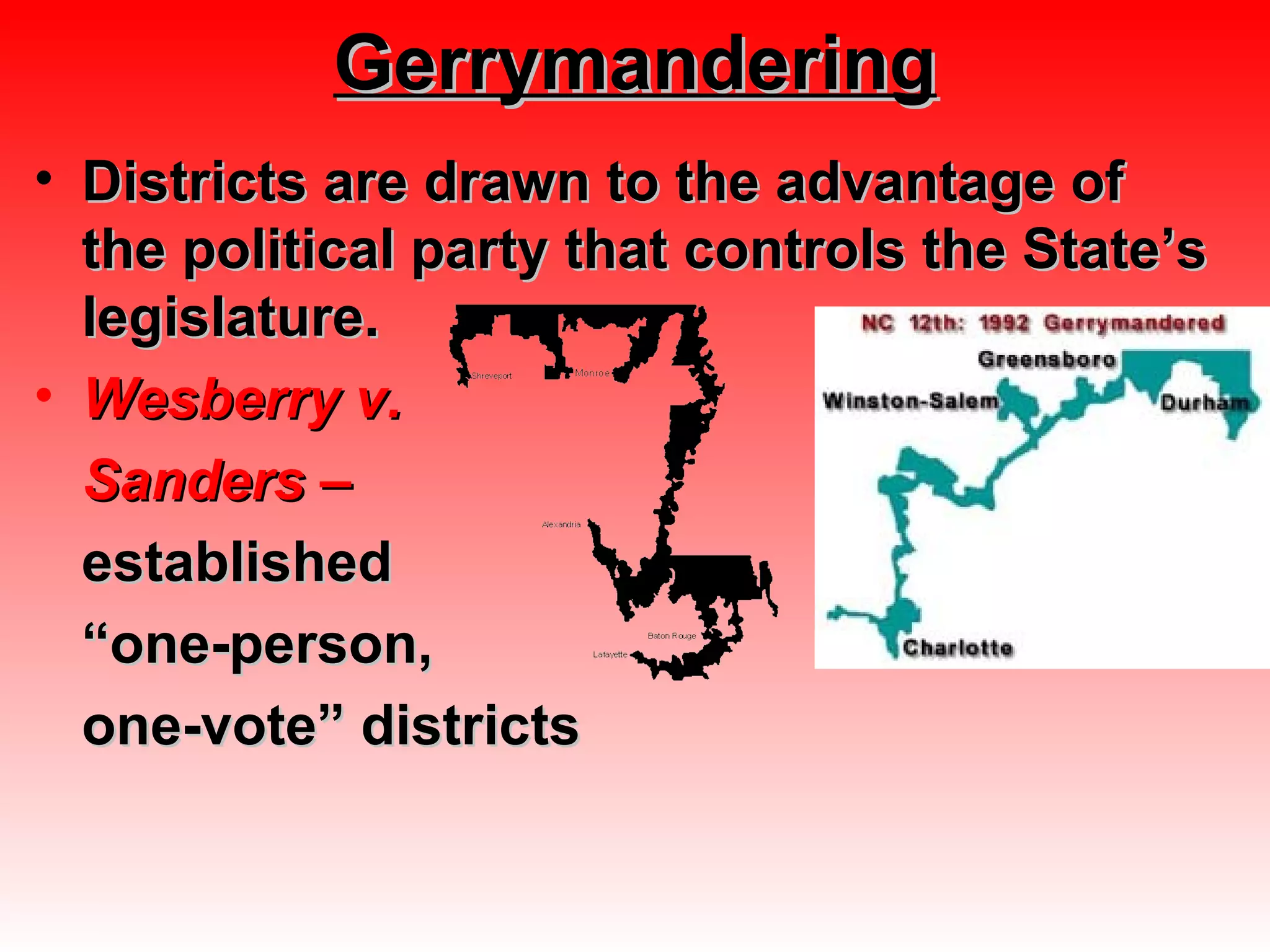
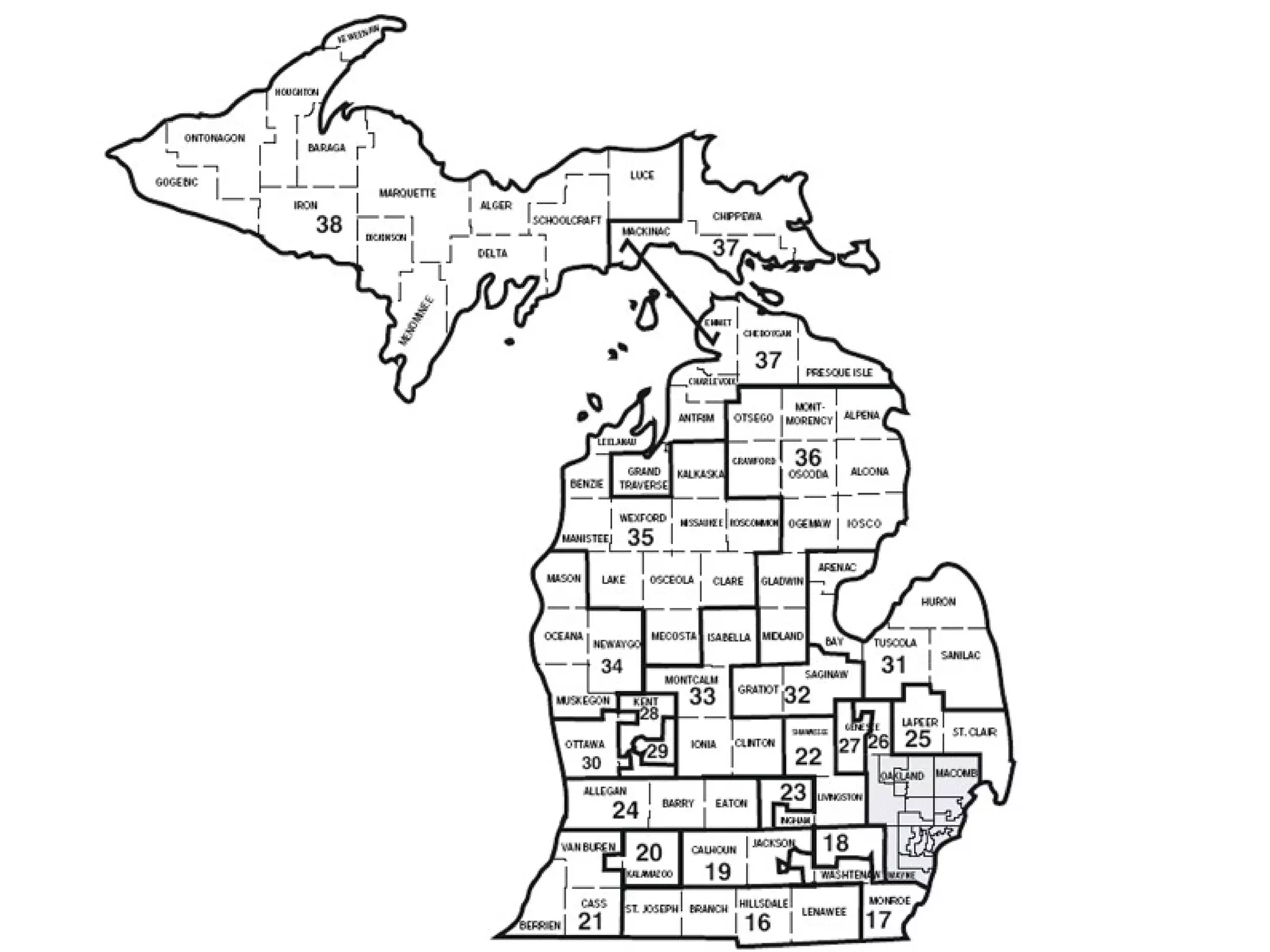
The document summarizes key aspects of the U.S. House of Representatives and Senate. It outlines that the House has 435 members who serve 2-year terms representing districts, while the Senate has 100 members with 6-year terms, with 2 senators per state. It discusses member qualifications, roles in lawmaking and oversight, representation of constituents, and compensation.