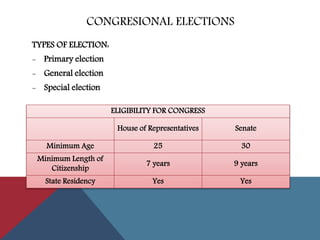
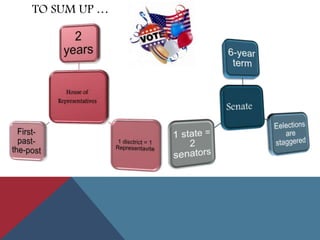
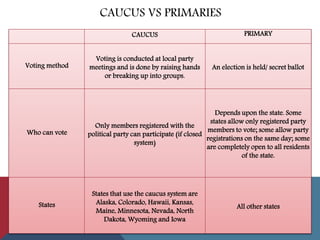
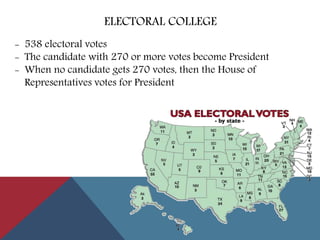
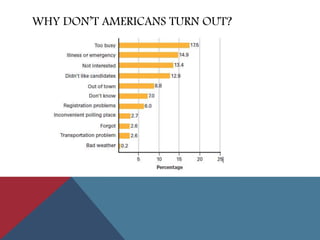
This document provides information about political parties and elections in the United States. It discusses the roles and functions of political parties, the two-party system, and third parties. It also describes the different types of elections in the US including primaries, general elections, and initiatives and referendums. Presidential elections are summarized, outlining the nomination process, conventions, electoral college and terms limits. Congressional and other public office elections are also briefly covered.