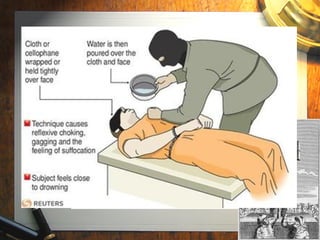
This document discusses the Bill of Rights and examines the challenge of balancing individual rights with the needs of government. It outlines the key protections guaranteed by the first ten amendments to the US Constitution, including freedom of speech, religion, press, assembly, protections against unwarranted search and seizure, self-incrimination, and the right to bear arms. It also notes some limitations and exceptions to rights like free speech. Students are tasked with exploring these issues through analyzing scenarios, debates, and news articles related to the amendments.