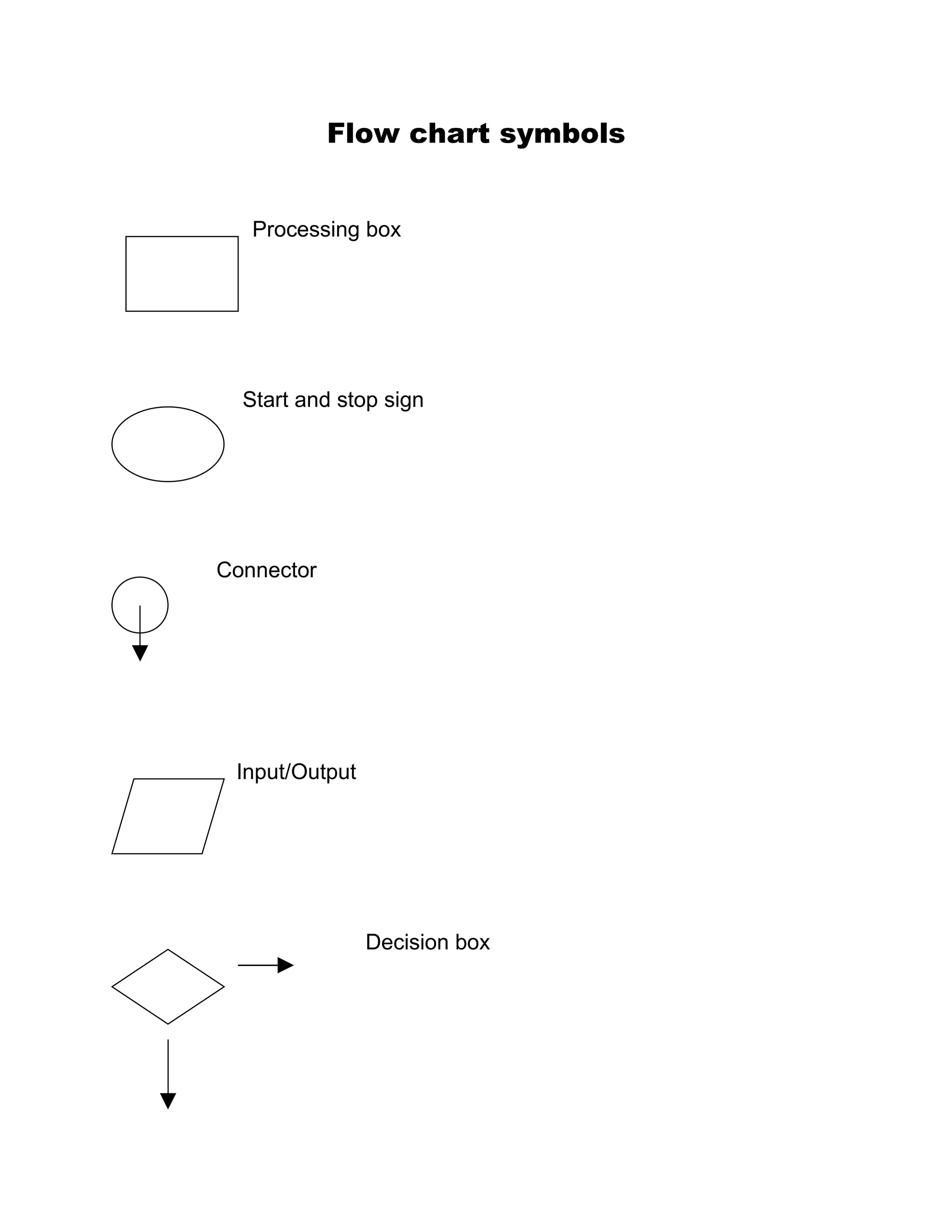
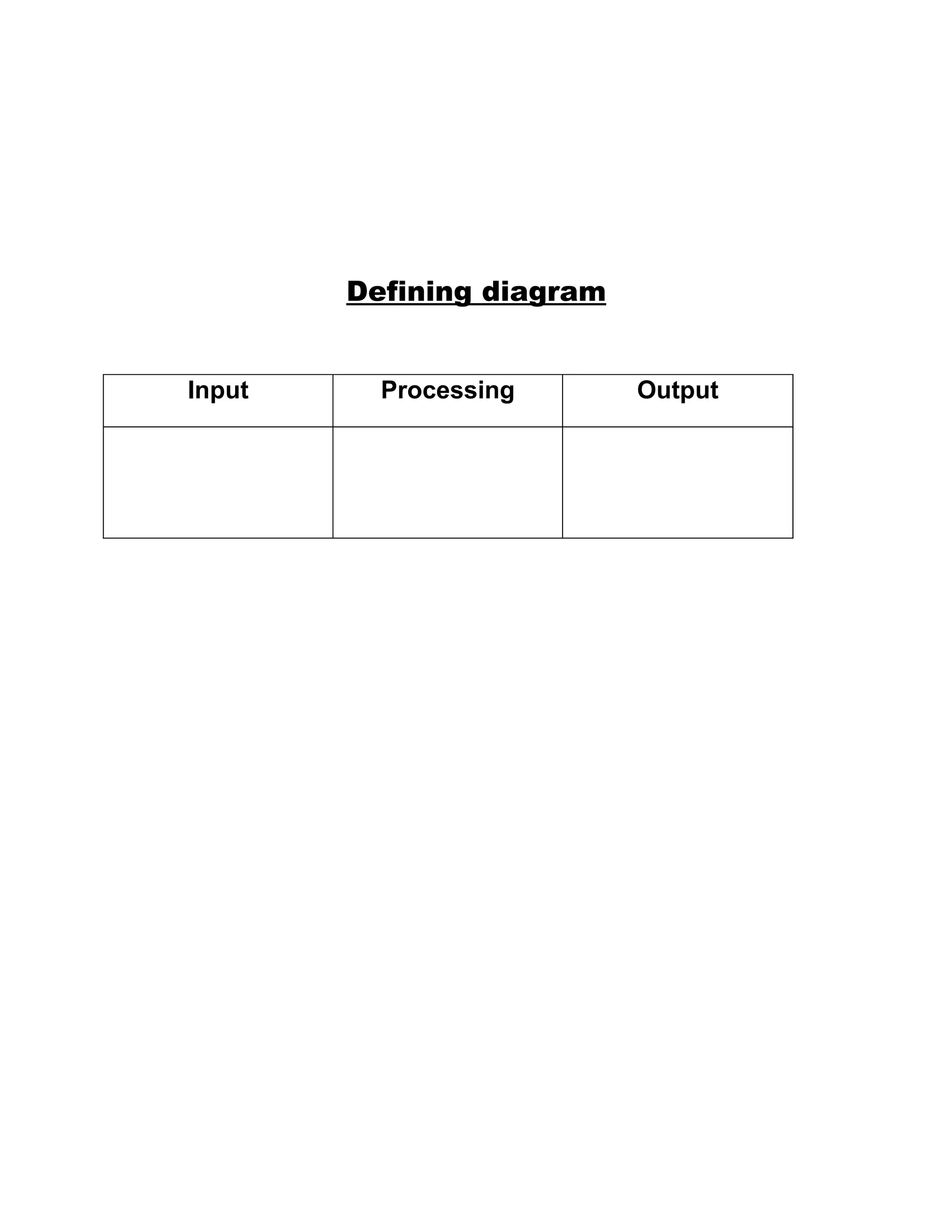
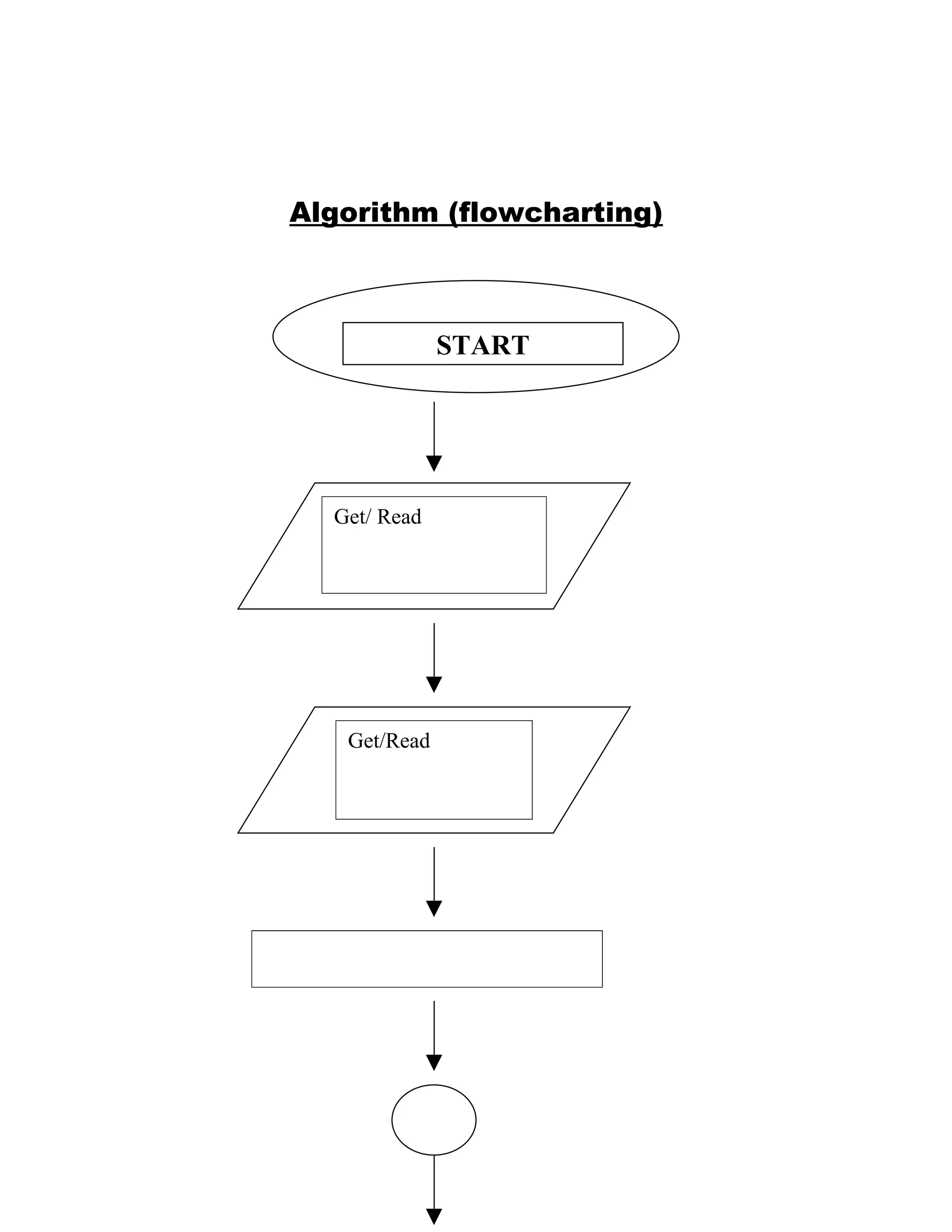
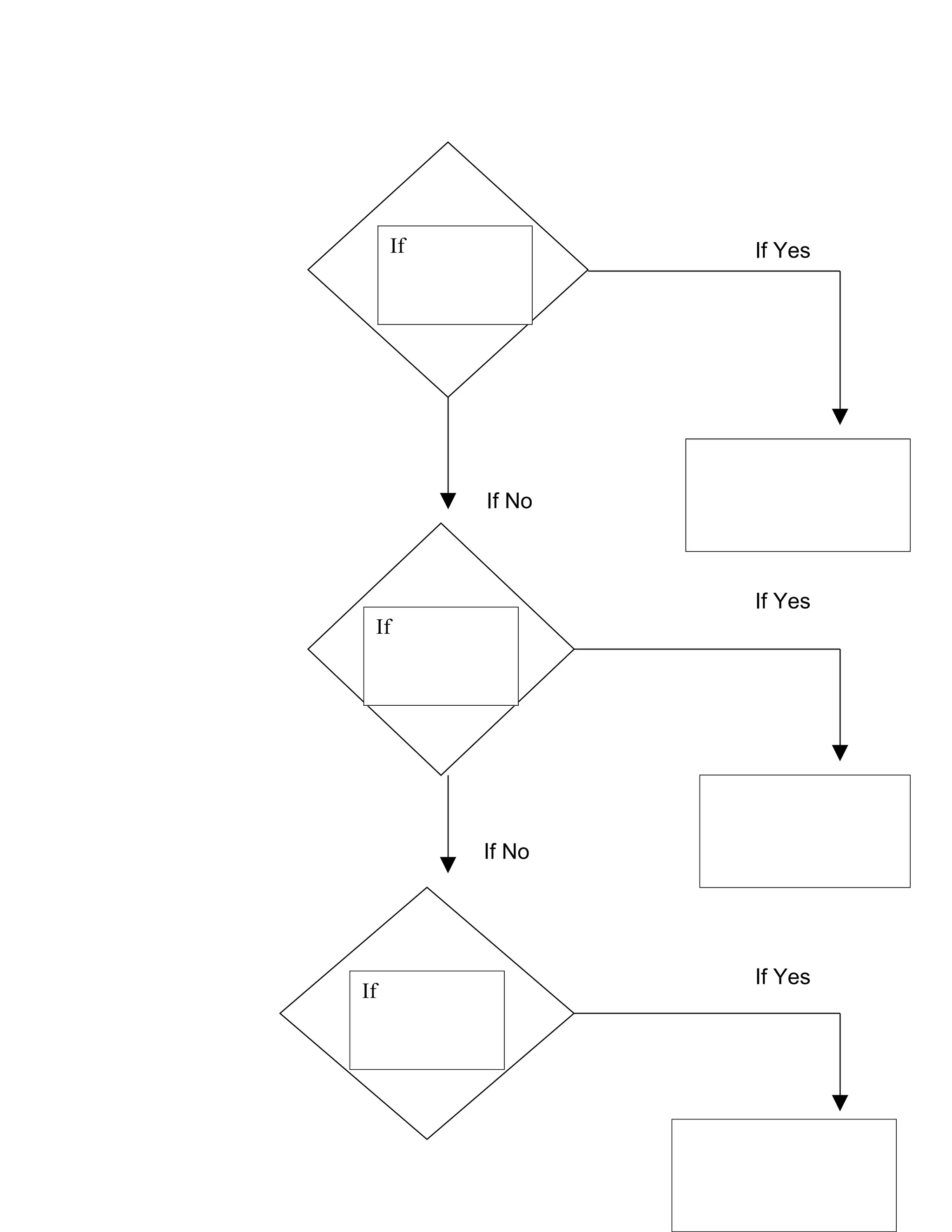
The document outlines the problem solving and implementation phases of the problem solving method. It consists of 5 steps: 1) define the problem, 2) find solutions, 3) evaluate alternatives, 4) represent the most efficient solution as an algorithm, and 5) test the algorithm. The implementation phase has 3 steps: 1) translate the algorithm into a programming language, 2) execute the program, and 3) maintain the program. It also includes flow chart symbols and an example problem definition, diagram, and pseudo code for tracking masqueraders who paid for costumes.