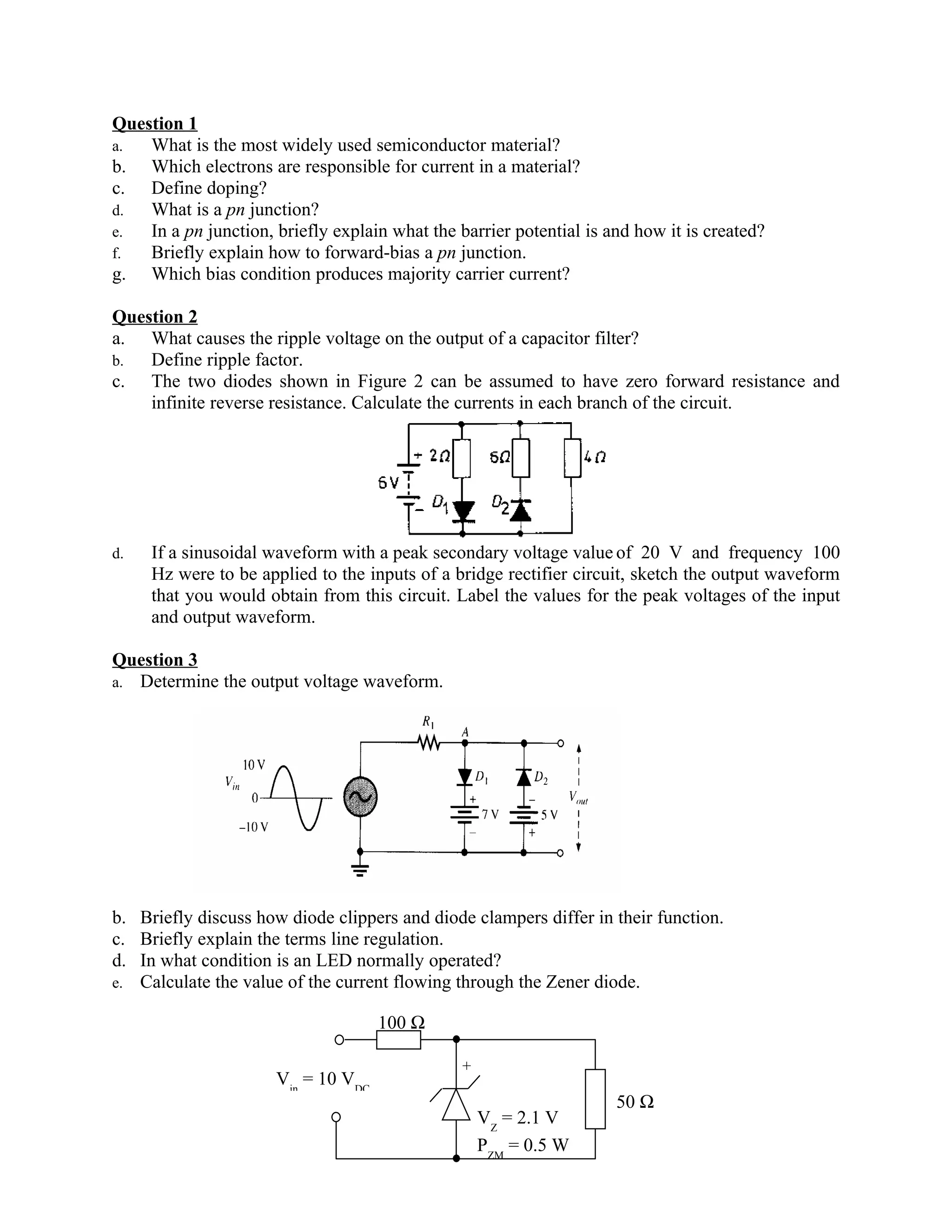
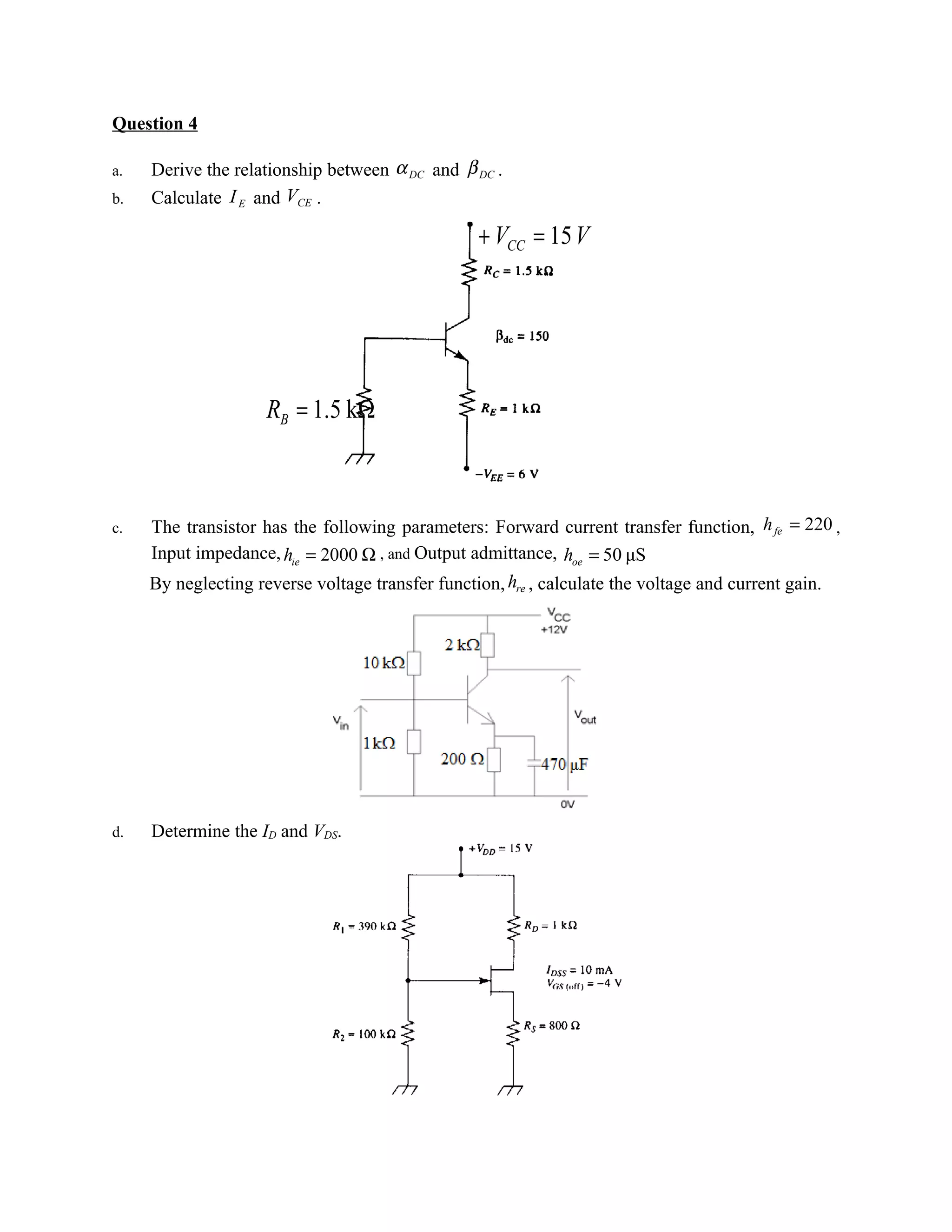
This document contains 4 questions related to electronics concepts. Question 1 covers semiconductor materials, current carriers, doping, pn junctions, and biasing. Question 2 covers ripple voltage, ripple factor, and calculating branch currents in a diode circuit. Question 3 covers diode clippers, clampers, line regulation, and LED operation conditions. Question 4 covers relationships between DC current gain parameters, transistor biasing, calculating voltage and current gain based on transistor parameters, and determining current and voltage in a transistor circuit.