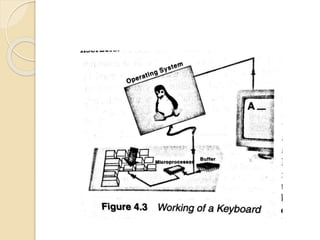
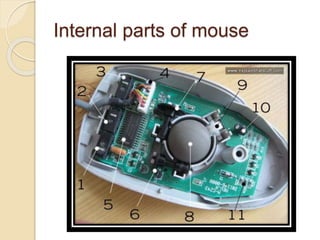
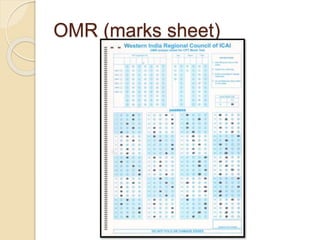
The document discusses the significance, types, and functionalities of input devices in computer systems, such as keyboards, pointing devices, and speech recognition systems. It highlights the process of data input, processing, and output via these devices, emphasizing their roles in converting raw data into usable information. Various input methods and their respective technologies, such as digital cameras and scanners, are also examined.