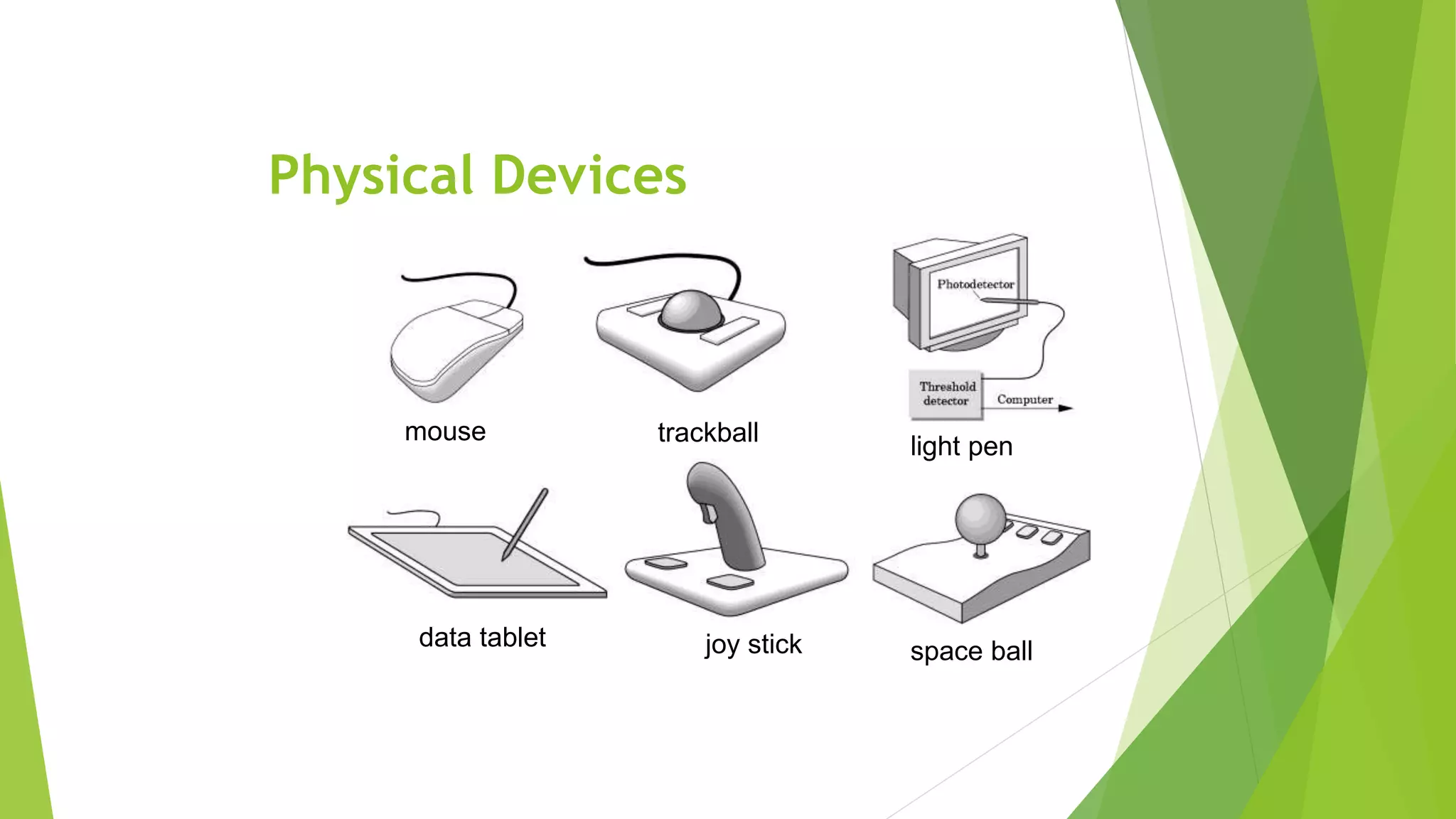
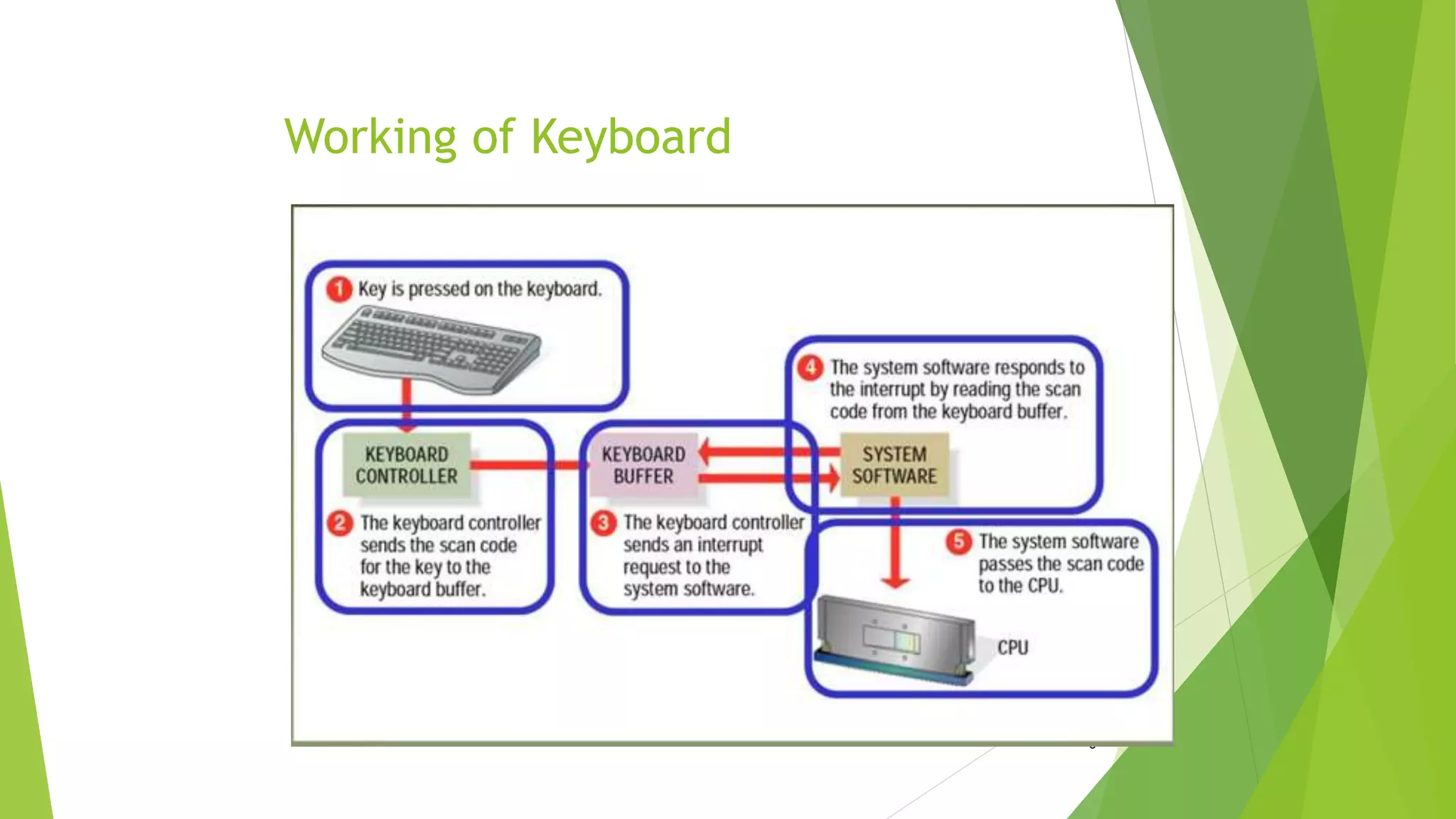
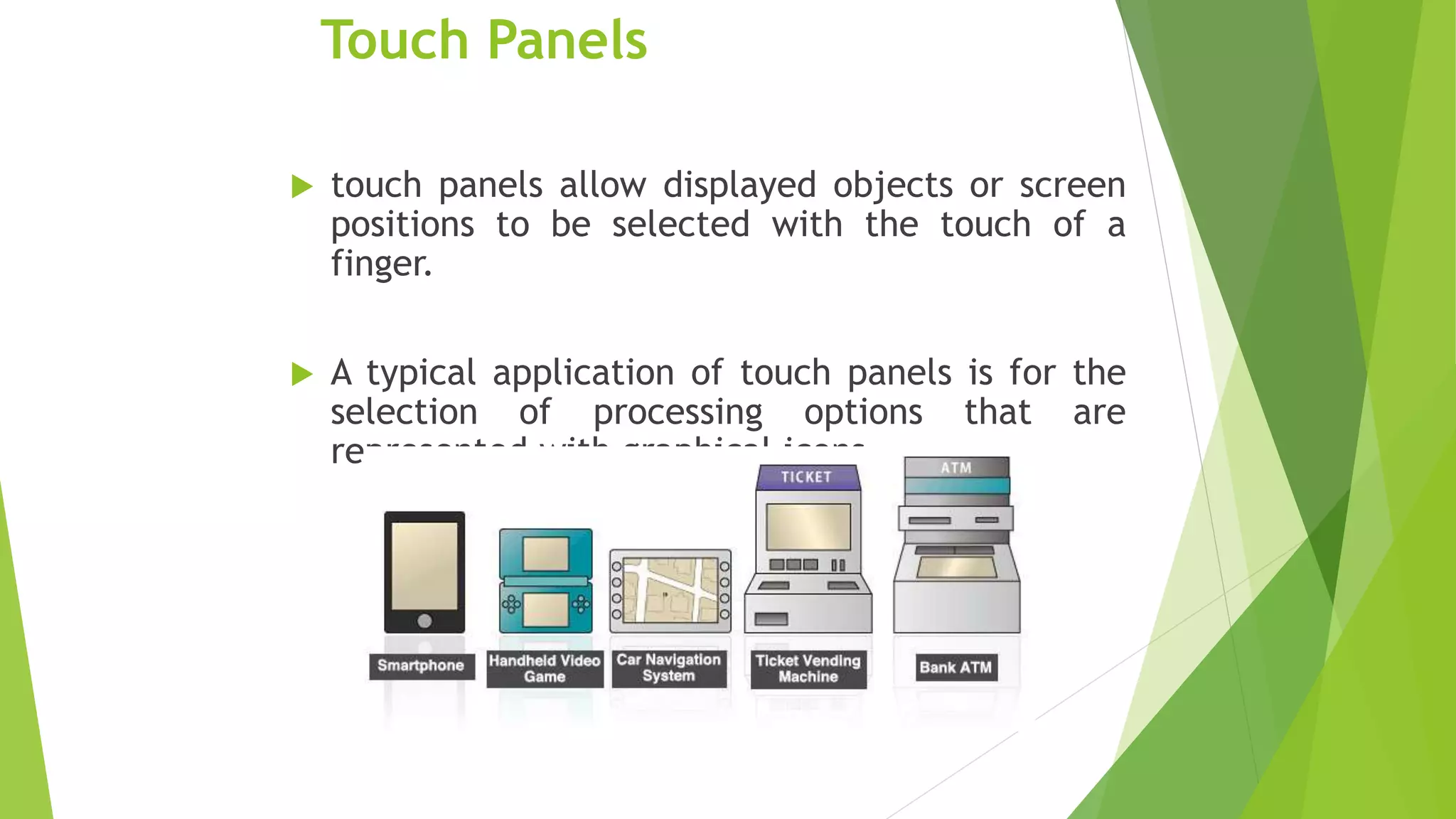
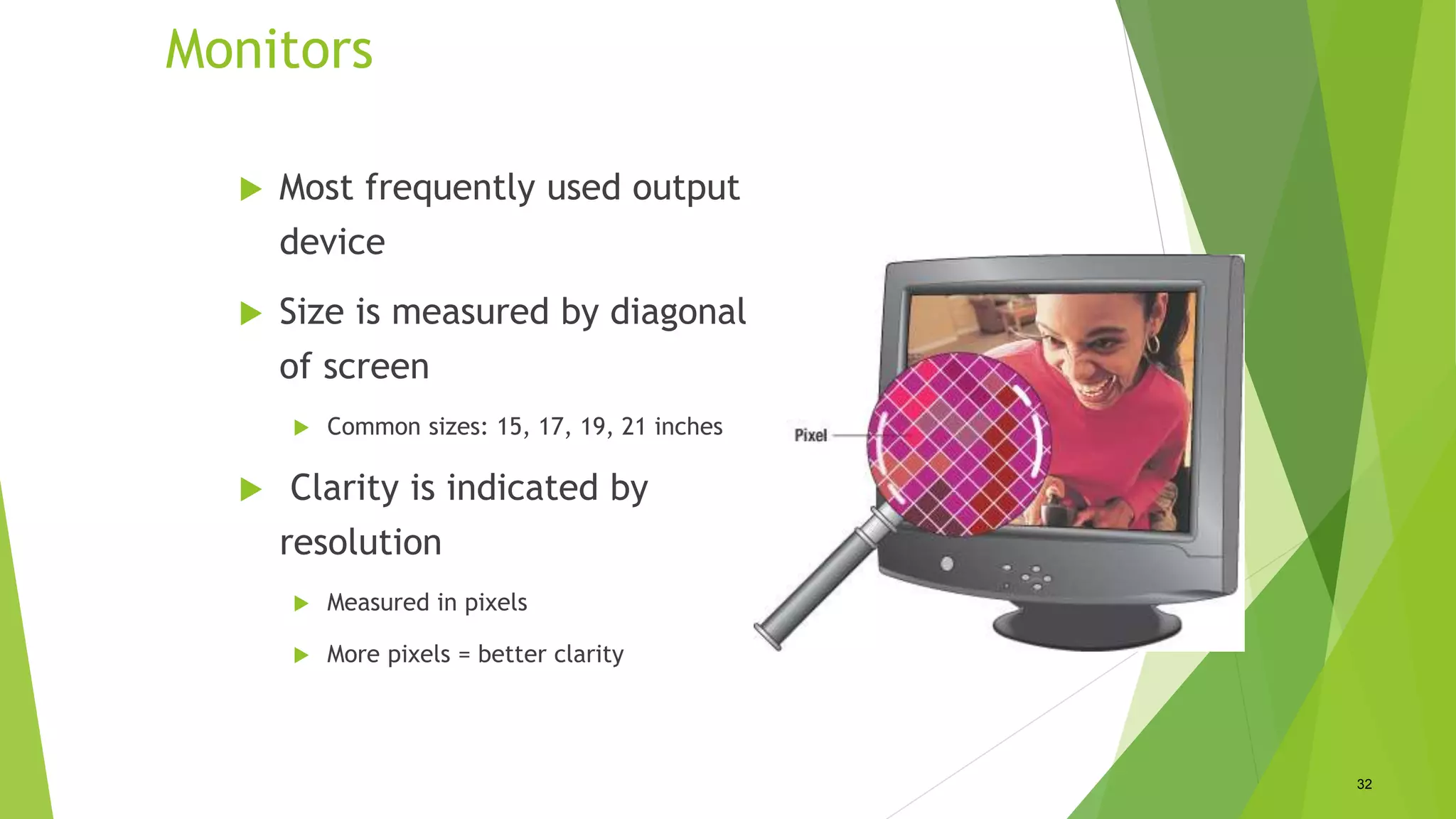
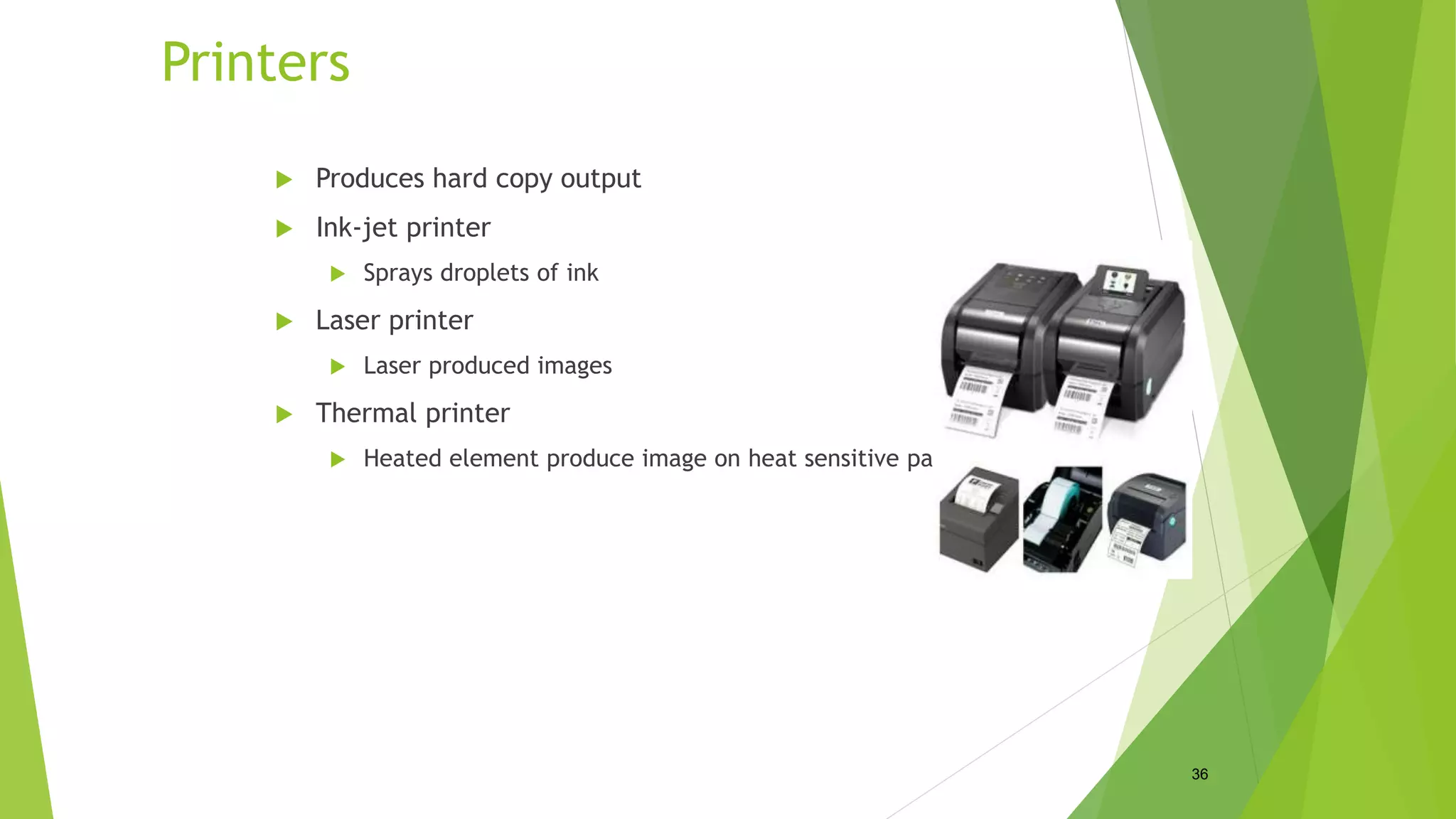
This document discusses various types of computer input and output hardware devices. It describes common input devices like keyboards, mice, touchscreens, microphones, and scanners. It also covers output devices such as monitors, printers, speakers, and multifunction devices. The document provides details on how different devices work and standards for items like monitor resolution.